Abstract
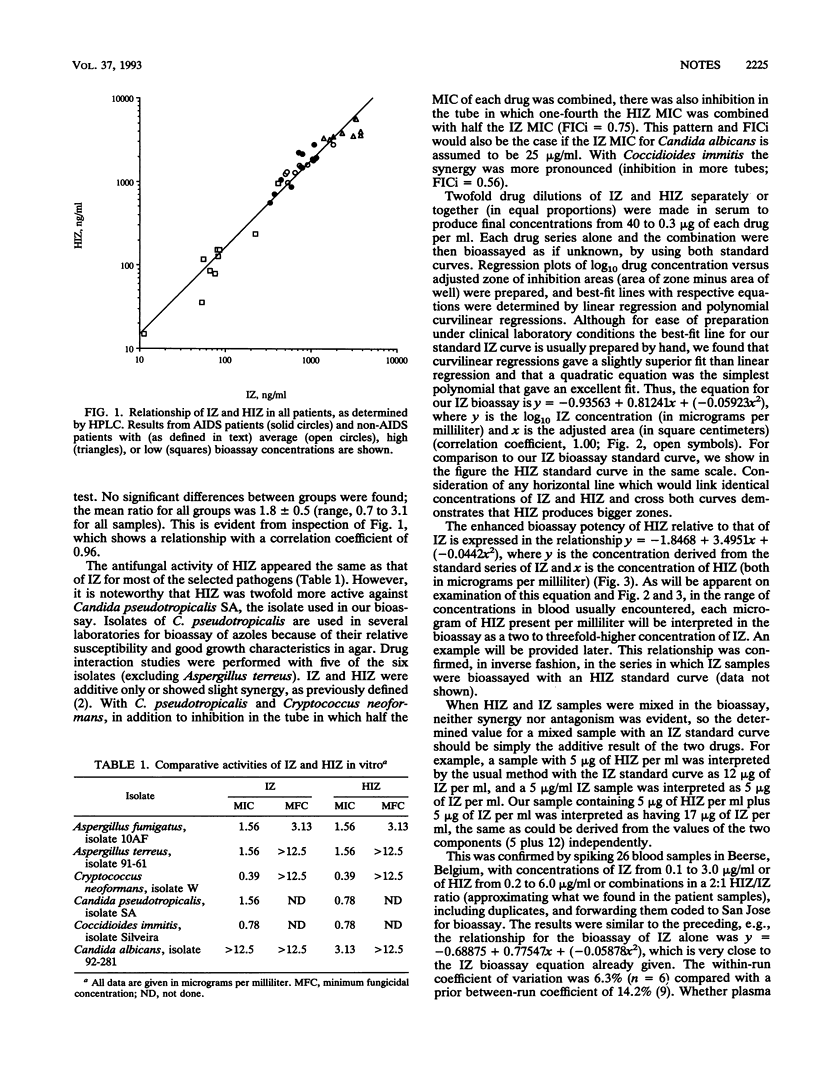
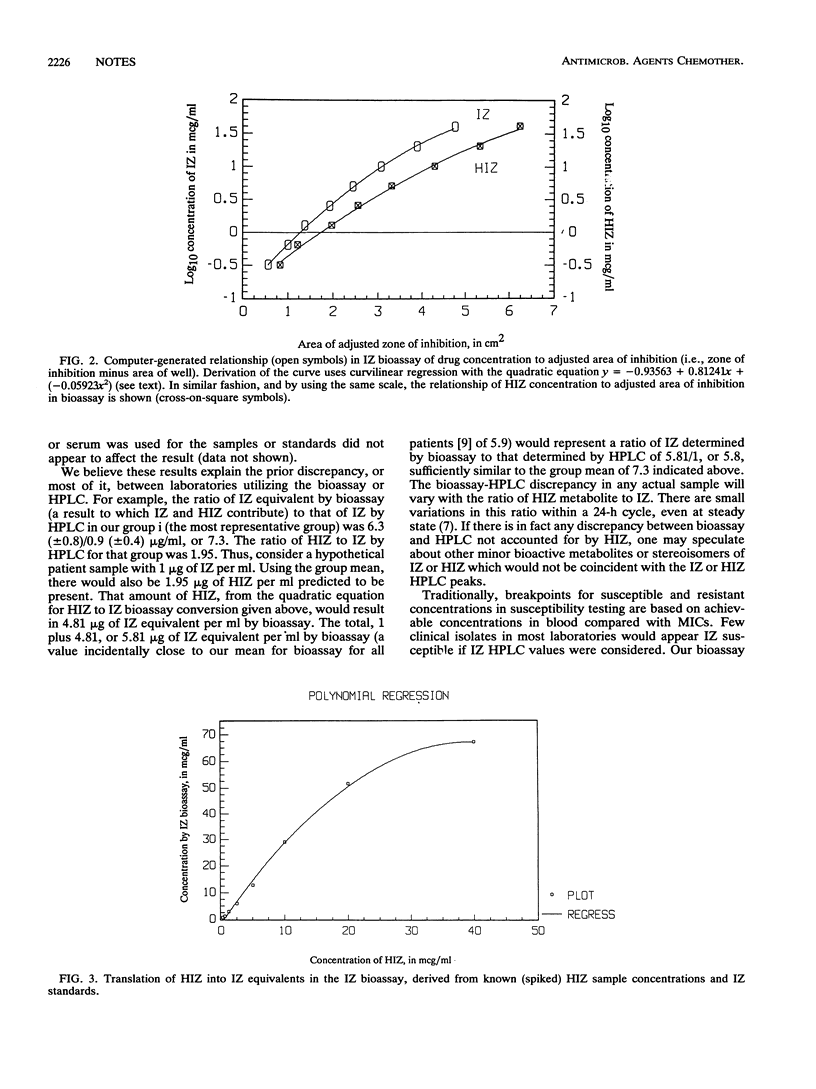
Pharmacologic studies of itraconazole (IZ), a triazole antifungal, indicated unexplained differences between bioassay and chromatographic determinations and large variations in steady-state blood concentrations. We show that concentrations of a hydroxylated metabolite, hydroxyitraconazole (HIZ), are approximately twofold higher than IZ over a range of concentrations. Though HIZ and IZ appear equipotent against selected pathogens, HIZ is two to three times more active against a commonly used bioassay fungus but minimally affects IZ activity. Hence, HIZ probably contributes importantly to the therapeutic activity attributed to IZ and contributes approximately four to six times the activity of IZ in bioassays, explaining discrepancies observed between assay methods.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Denning D. W., Hanson L. H., Perlman A. M., Stevens D. A. In vitro susceptibility and synergy studies of Aspergillus species to conventional and new agents. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;15(1):21–34. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(92)90053-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson L. H., Stevens D. A. Comparison of antifungal activity of amphotericin B deoxycholate suspension with that of amphotericin B cholesteryl sulfate colloidal dispersion. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Feb;36(2):486–488. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.2.486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardin T. C., Graybill J. R., Fetchick R., Woestenborghs R., Rinaldi M. G., Kuhn J. G. Pharmacokinetics of itraconazole following oral administration to normal volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Sep;32(9):1310–1313. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.9.1310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heykants J., Van Peer A., Van de Velde V., Van Rooy P., Meuldermans W., Lavrijsen K., Woestenborghs R., Van Cutsem J., Cauwenbergh G. The clinical pharmacokinetics of itraconazole: an overview. Mycoses. 1989;32 (Suppl 1):67–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.1989.tb02296.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker R. M., Denning D. W., Hanson L. H., Rinaldi M. G., Graybill J. R., Sharkey P. K., Pappagianis D., Stevens D. A. Interaction of azoles with rifampin, phenytoin, and carbamazepine: in vitro and clinical observations. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;14(1):165–174. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.1.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker R. M., Williams P. L., Arathoon E. G., Stevens D. A. Treatment of mycoses with itraconazole. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;544:451–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb40443.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnock D. W., Turner A., Burke J. Comparison of high performance liquid chromatographic and microbiological methods for determination of itraconazole. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Jan;21(1):93–100. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woestenborghs R., Lorreyne W., Heykants J. Determination of itraconazole in plasma and animal tissues by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1987 Jan 23;413:332–337. doi: 10.1016/0378-4347(87)80249-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



