Abstract
Two examples of hematological toxicity following phenylbutazone therapy are described, one of agranulocytosis and one of aplastic anemia. In the first case, prednisolone in a dosage of 20 mg. daily restored neutrophil percentage and the total leukocyte count to normal, but the patient with aplastic anemia, having shown no response to corticosteroid therapy, became dependent on repeated blood transfusion.
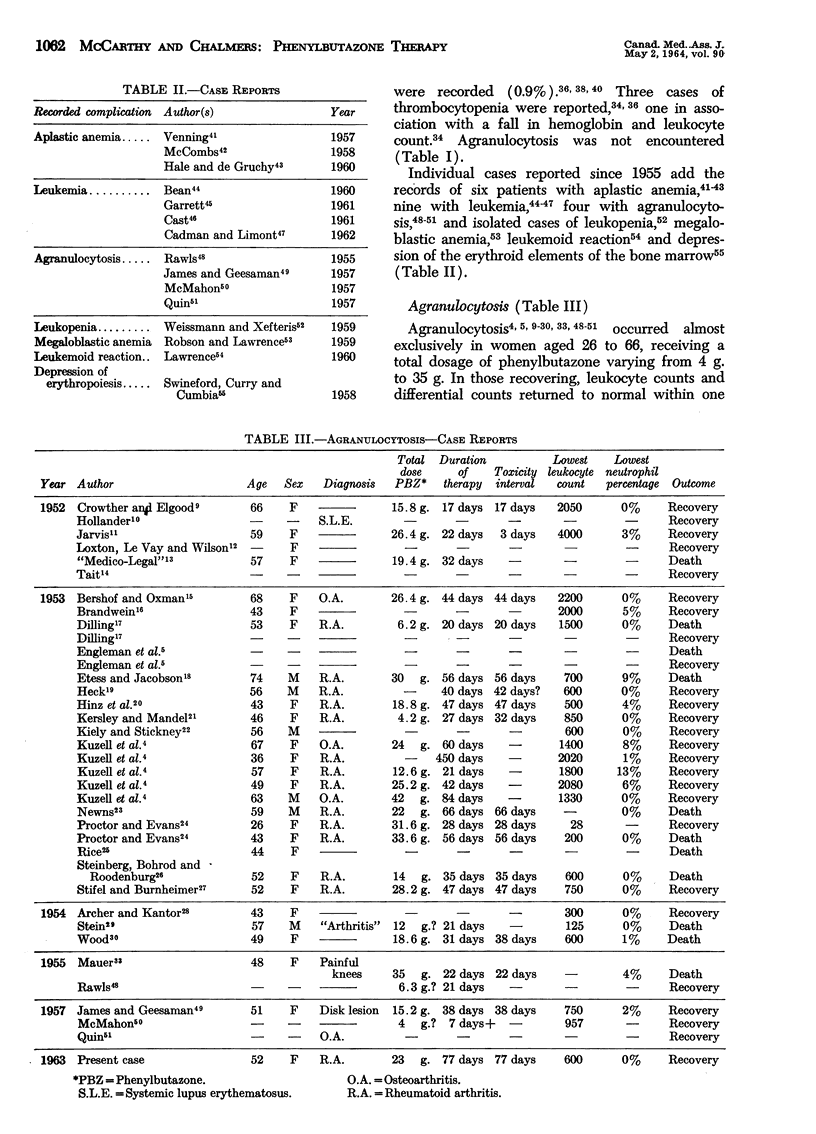
The English literature on the hematological toxicity of phenylbutazone is reviewed. Ten fatal cases of agranulocytosis have been recorded, as have eight cases of aplastic anemia, of which five proved fatal. Other toxic effects noted have included leukopenia, depression of erythropoiesis, megaloblastic anemia, thrombocytopenia and leukemia.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARCHER B. H., KANTOR M. G. Agranulocytosis with recovery following the use of phenylbutazone (Butazolidin). N Y State J Med. 1954 Feb;54(3):394–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENSTEAD J. G. Deaths of two patients treated by phenylbutazone. Br Med J. 1953 Mar 28;1(4812):711–712. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4812.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERSHOF E., OXMAN A. C. Agranulocytosis following use of phenylbutazone (butazolidin). J Am Med Assoc. 1953 Feb 14;151(7):557–558. doi: 10.1001/jama.1953.02940070023007b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DILLING N. V. Fatal agranulocytosis and gastric ulceration due to phenylbutazone. Lancet. 1953 Jun 20;1(6773):1230–1231. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(53)92260-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ETESS A. D., JACOBSON A. S. Fatality due to agranulocytosis following use of phenylbutazone (butazolidin). J Am Med Assoc. 1953 Feb 21;151(8):639–640. doi: 10.1001/jama.1953.02940080039009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEESAMAN R. E., JAMES F. L. Agranulocytosis due to phenylbutazone. Ann Intern Med. 1957 Jan;46(1):152–155. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-46-1-152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HECK F. J. The influence of drugs on blood and bone marrow. Postgrad Med. 1953 Mar;13(3):185–193. doi: 10.1080/00325481.1953.11711307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIELY J. M., STICKNEY J. M. Agranulocytosis caused by phenylbutazone and 4-amino-antipyrine. Proc Staff Meet Mayo Clin. 1953 Jun 17;28(12):341–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUZELL W. C., SCHAFFARZICK R. W., NAUGLER W. E., GAUDIN G., MANKLE E. A. Phenylbutazone; further clinical evaluation. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1953 Nov;92(5):646–661. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1953.00240230046005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASON R. M., STEINBERG V. L. Long-term use of phenylbutazone in rheumatoid arthritis. Br Med J. 1960 Sep 17;2(5202):828–830. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5202.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCMAHON M. F. Clinical effects of Butazolidin. Rheumatism. 1957 Jan;13(1):17–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOHLER D. N., LEAVELL B. S. Aplastic anemia: an analysis of 50 cases. Ann Intern Med. 1958 Aug;49(2):326–362. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-49-2-326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCOMBS A. P. Case histories of two patients with toxic symptoms of drug reaction. J Am Med Womens Assoc. 1958 Jul;13(7):263–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NASSIM J. R., PILKINGTON T. Toxic effects of phenylbutazone. Br Med J. 1953 Jun 13;1(4823):1310–1311. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4823.1310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBSON H. N., LAWRENCE J. R. Megaloblastic anaemia induced by phenylbutazone. Br Med J. 1959 Sep 19;2(5150):475–477. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5150.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMYTH C. J., CLARK G. M. Phenylbutazone in rheumatoid arthritis. J Chronic Dis. 1957 Jun;5(6):734–750. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(57)90081-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STIFEL J. L., BURNHEIMER J. C. Agranulocytosis following administration of phenylbutazone (butazolidin). J Am Med Assoc. 1953 Feb 14;151(7):555–556. doi: 10.1001/jama.1953.02940070021007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWINEFORD O., Jr, CURRY J. C., CUMBIA J. W. Phenylbutazone toxicity: depression of erythropoiesis; a case report. Arthritis Rheum. 1958 Apr;1(2):174–177. doi: 10.1002/art.1780010210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VENNING G. R. Aplastic anaemia due to phenylbutazone. Br Med J. 1957 Jul 20;2(5037):146–146. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5037.146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSMANN G., XEFTERIS E. D. Phenylbutazone leukopenia. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1959 Jun;103(6):957–961. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1959.00270060109014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WERBLOW S. C., NEBER J. Agranulocytosis following phenylbutazone therapy. J Am Med Assoc. 1953 Apr 11;151(15):1286–1289. doi: 10.1001/jama.1953.02940150026006a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD I. H. Fatal case of agranulocytosis following phenylbutazone. Br Med J. 1954 Apr 3;1(4865):802–802. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4865.802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



