Abstract
Powassan virus, a North American tickborne group B arbovirus, multiplied after simultaneous inoculation into bottles or tubes of virus and trypsinized suspension of continuous-line cultures of rhesus monkey kidney cells, strain LLC-MK2. Cytopathic effects comprising cell rounding and cytoplasmic vacuolation were first observed five days after inoculation. Mixture of Powassan antiserum with virus before inoculation into tissue cultures inhibited the appearance of cytopathic effects. Hemagglutinins for rooster erythrocytes, optimally at pH 6.4 and 22° C., first appeared in tissue culture supernatant fluids four days after inoculation.
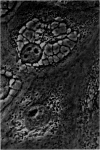
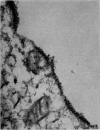
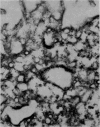
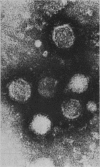
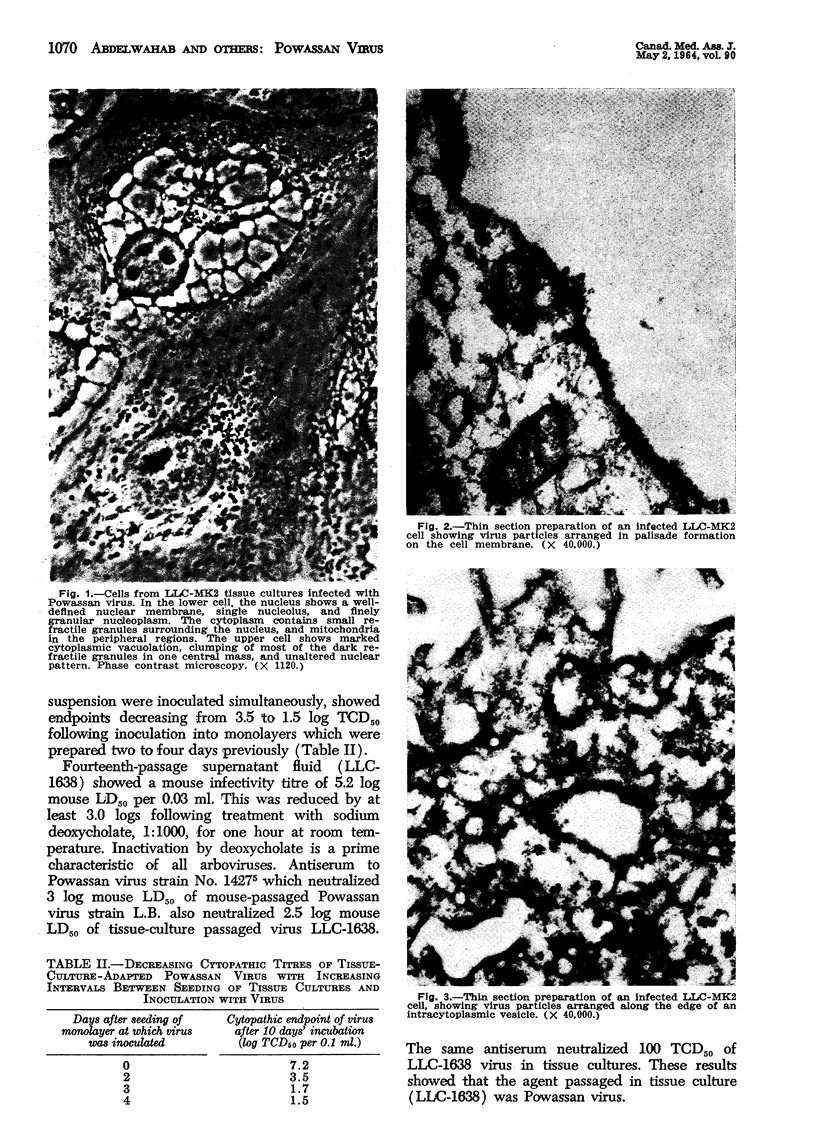
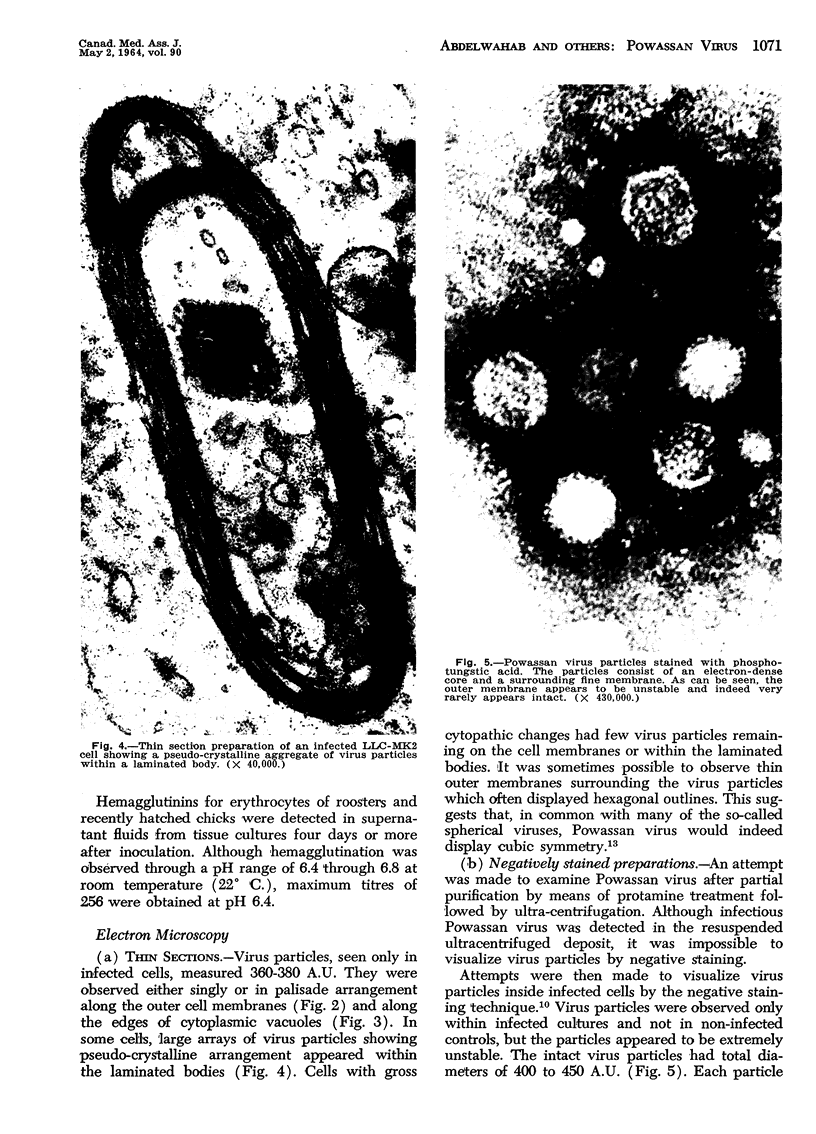
Electron microscopic observation of thin sections of infected tissue culture cells showed virus particles 360-380 A.U. along outer cell membranes and edges of cytoplasmic vacuoles. In phosphotungstic acid negatively stained preparations, intact virus particles, 400-450 A.U. total diameter, were observed inside infected cells. In particles in which the peripheral layer became discontinuous, geometrically arranged subunits compatible with cubic symmetry were observed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALMEIDA J. D. A CLASSIFICATION OF VIRUS PARTICLES BASED ON MORPHOLOGY. Can Med Assoc J. 1963 Oct 19;89:787–798. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALMEIDA J. D., HOWATSON A. F. A negative staining method for cell-associated virus. J Cell Biol. 1963 Mar;16:616–620. doi: 10.1083/jcb.16.3.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BANTA J. E. Cultivation of dengue, western equine encephalomyelitis, Japanese encephalitis and West Nile viruses in selected mammalian cell cultures. Am J Hyg. 1958 May;67(3):286–299. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUCKLEY S. M. Propagation, cytopathogenicity, and hemagglutination-hemadsorption of some arthropod-borne viruses in tissue culture. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Jul 21;81:172–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb49305.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASALS J. Antigenic relationship between Powassan and Russian spring-summer encephalitis viruses. Can Med Assoc J. 1960 Feb 13;82:355–358. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE D. H., CASALS J. Techniques for hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition with arthropod-borne viruses. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1958 Sep;7(5):561–573. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1958.7.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIERCKS F. H., HAMMON W. M. Hamster kidney cell tissue cultures for propagation of Japanese B encephalitis virus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Mar;97(3):627–632. doi: 10.3181/00379727-97-23827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORNE R. W., WILDY P. Symmetry in virus architecture. Virology. 1961 Nov;15:348–373. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90366-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HULL R. N., CHERRY W. R., TRITCH O. J. Growth characteristics of monkey kidney cell strains LLC-MK1, LLC-MK2, and LLC-MK2(NCTC-3196) and their utility in virus research. J Exp Med. 1962 May 1;115:903–918. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.5.903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KISSLING R. E. Growth of several arthropod-borne viruses in tissue culture. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Nov;96(2):290–294. doi: 10.3181/00379727-96-23458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOVAC W., KUNZ C., STOCKINGER L. [Electron microscopic demonstration of the virus of early summer meningoencephalitis in HeLa cells]. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1962;11:544–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVITT J., NAUDE W. D., POLSON A. PURIFICATION AND ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF PANTROPIC RIFT VALLEY FEVER VIRUS. Virology. 1963 Jul;20:530–533. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90103-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCLEAN D. M., LARKE R. P. Powassan and Silverwater viruses: ecology of two Ontario arboviruses. Can Med Assoc J. 1963 Jan 26;88:182–185. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORGAN C., HOWE C., ROSE H. M. Structure and development of viruses as observed in the electron microscope. V. Western equine encephalomyelitis virus. J Exp Med. 1961 Jan 1;113:219–234. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.1.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUSSGAY M., WEIBEL J. Electron microscopic and biological studies on the growth of Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus in KB cells. Virology. 1962 Jan;16:52–62. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90201-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLEAN D. M., DONOHUE W. L. Powassan virus: isolation of virus from a fatal case of encephalitis. Can Med Assoc J. 1959 May 1;80(9):708–711. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALMINEN A. A method for the production of arborvirus hemagglutinins in tissue culture. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand Suppl. 1962;Suppl 154:343–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS L. A., KENNEDY R. C., EKLUND C. M. Isolation of a virus closely related to Powassan virus from Dermacentor andersoni collected along North Cache la Poudre River, Colo. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Jun;104:355–359. doi: 10.3181/00379727-104-25836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITNEY E. SEROLOGIC EVIDENCE OF GROUP A AND B ARTHROPOD-BORNE VIRUS ACTIVITY IN NEW YORK STATE. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1963 May;12:417–424. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1963.12.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]