Abstract
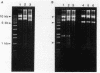
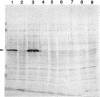
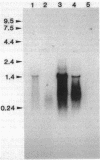
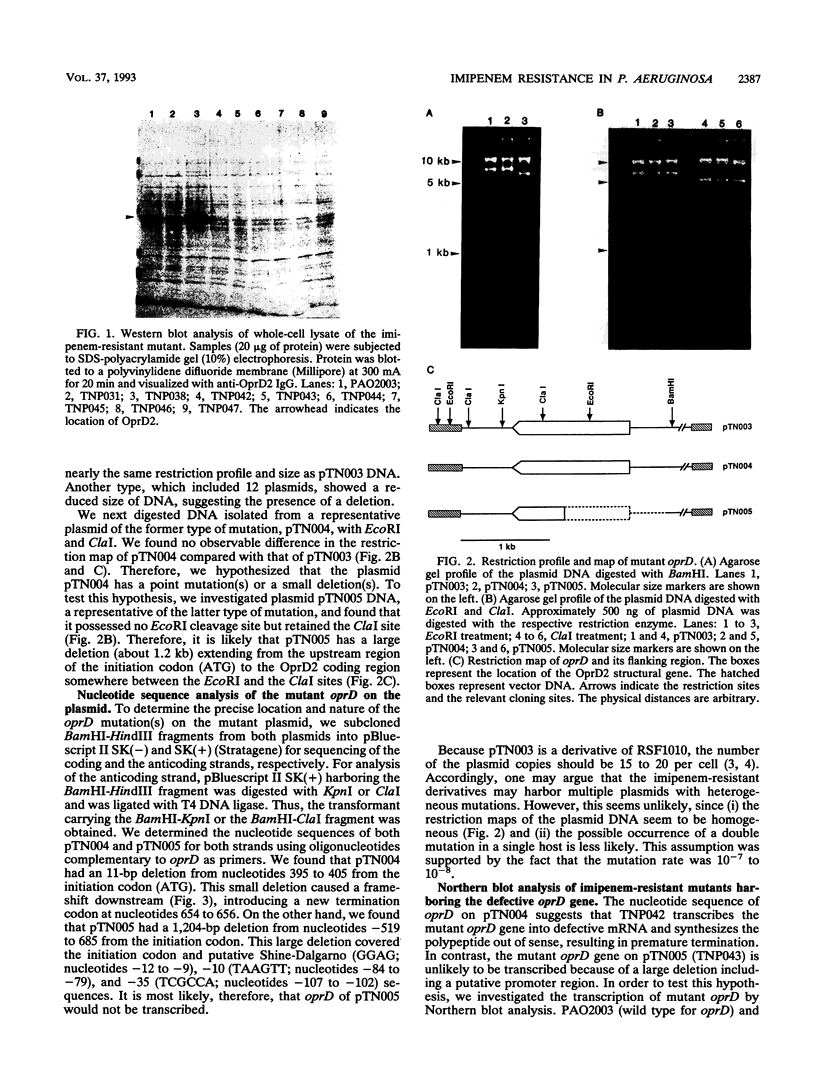
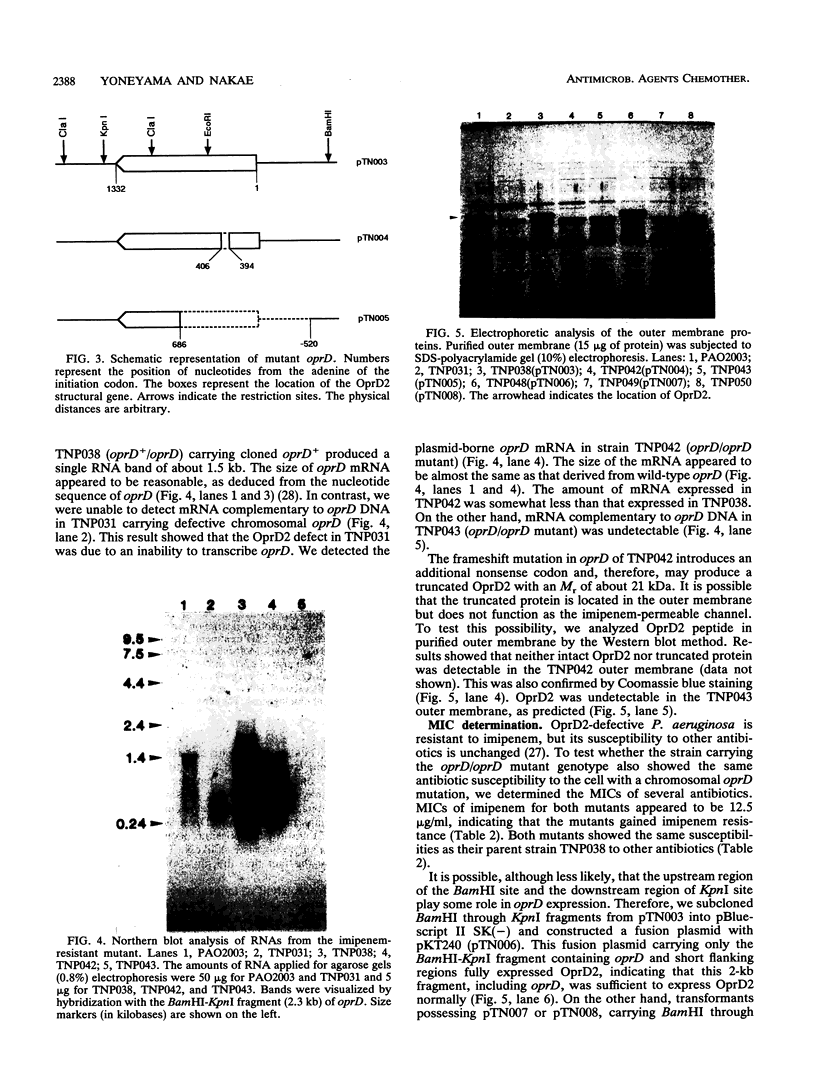
Most imipenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates produce an immunologically undetectable level of protein D2 (OprD2). To study the efficient elimination of the protein, we selected 23 independent imipenem-resistant mutants from a strain harboring the plasmid carrying cloned oprD and having a mutation in chromosomal oprD. All these oprD/oprD (plasmid/chromosomal) mutants expressed undetectable levels of OprD2, as shown from an assay by the immunoblotting method. Restriction maps of the DNAs from all 23 mutant plasmids could be divided into two groups. Restriction mapping and sequencing analysis of DNA from one representative plasmid from each group showed that both mutant oprD genes had a deletion. One had an 11-bp deletion in the coding region generating a frameshift mutation and a premature termination codon. Another had a large deletion encompassing the upstream site of its putative promoter region through the coding region. Northern blotting analysis showed that the gene with the 11-bp deletion was transcribed to about 1.5 kb of mRNA, but the gene with the large deletion produced undetectable RNA complementary to the oprD DNA probe. Since we analyzed only plasmid-borne oprD, we cannot exclude the possibility that the imipenem resistance caused by the chromosomal mutation is by a different mechanism(s). It is suggested, yet, that clear elimination of OprD2 from most imipenem-resistant P. aeruginosa isolates is due to efficient selection of the oprD deletion mutants.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiba H., Adhya S., de Crombrugghe B. Evidence for two functional gal promoters in intact Escherichia coli cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11905–11910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angus B. L., Carey A. M., Caron D. A., Kropinski A. M., Hancock R. E. Outer membrane permeability in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: comparison of a wild-type with an antibiotic-supersusceptible mutant. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Feb;21(2):299–309. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagdasarian M. M., Amann E., Lurz R., Rückert B., Bagdasarian M. Activity of the hybrid trp-lac (tac) promoter of Escherichia coli in Pseudomonas putida. Construction of broad-host-range, controlled-expression vectors. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90197-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagdasarian M., Timmis K. N. Host: vector systems for gene cloning in Pseudomonas. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;96:47–67. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68315-2_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellido F., Martin N. L., Siehnel R. J., Hancock R. E. Reevaluation, using intact cells, of the exclusion limit and role of porin OprF in Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane permeability. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(16):5196–5203. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.16.5196-5203.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Hancock R. E. Properties of the large ion-permeable pores formed from protein F of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in lipid bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Aug 20;646(2):298–308. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90336-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büscher K. H., Cullmann W., Dick W., Wendt S., Opferkuch W. Imipenem resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa is due to diminished expression of outer membrane proteins. J Infect Dis. 1987 Oct;156(4):681–684. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.4.681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuoka T., Masuda N., Takenouchi T., Sekine N., Iijima M., Ohya S. Increase in susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to carbapenem antibiotics in low-amino-acid media. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Mar;35(3):529–532. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.3.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L., St John A. C. Intracellular protein degradation in mammalian and bacterial cells: Part 2. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:747–803. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Kageyama M. Separation and characterization of the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biochem. 1978 Jul;84(1):179–191. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakae T. Identification of the outer membrane protein of E. coli that produces transmembrane channels in reconstituted vesicle membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Aug 9;71(3):877–884. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90913-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakae T. Outer-membrane permeability of bacteria. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1986;13(1):1–62. doi: 10.3109/10408418609108734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Vaara M. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):1–32. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.1-32.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn J. P., Dudek E. J., DiVincenzo C. A., Lucks D. A., Lerner S. A. Emergence of resistance to imipenem during therapy for Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. J Infect Dis. 1986 Aug;154(2):289–294. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.2.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo J. M., Zusman D. R. Determinants of an unusually stable mRNA in the bacterium Myxococcus xanthus. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Oct;6(20):2975–2988. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01756.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satake S., Yoneyama H., Nakae T. Role of OmpD2 and chromosomal beta-lactamase in carbapenem resistance in clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Aug;28(2):199–207. doi: 10.1093/jac/28.2.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trias J., Dufresne J., Levesque R. C., Nikaido H. Decreased outer membrane permeability in imipenem-resistant mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Aug;33(8):1202–1206. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.8.1202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trias J., Nikaido H. Outer membrane protein D2 catalyzes facilitated diffusion of carbapenems and penems through the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jan;34(1):52–57. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trias J., Nikaido H. Protein D2 channel of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane has a binding site for basic amino acids and peptides. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15680–15684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneyama H., Nakae T. Cloning of the protein D2 gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its functional expression in the imipenem-resistant host. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jun 3;283(2):177–179. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80582-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneyama H., Yoshihara E., Nakae T. Nucleotide sequence of the protein D2 gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Aug;36(8):1791–1793. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.8.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshihara E., Nakae T. Identification of porins in the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa that form small diffusion pores. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6297–6301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshihara E., Yoneyama H., Nakae T. In vitro assembly of the functional porin trimer from dissociated monomers in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):952–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F., Nikaido H. Permeability of Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane to hydrophilic solutes. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):636–642. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.636-642.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]