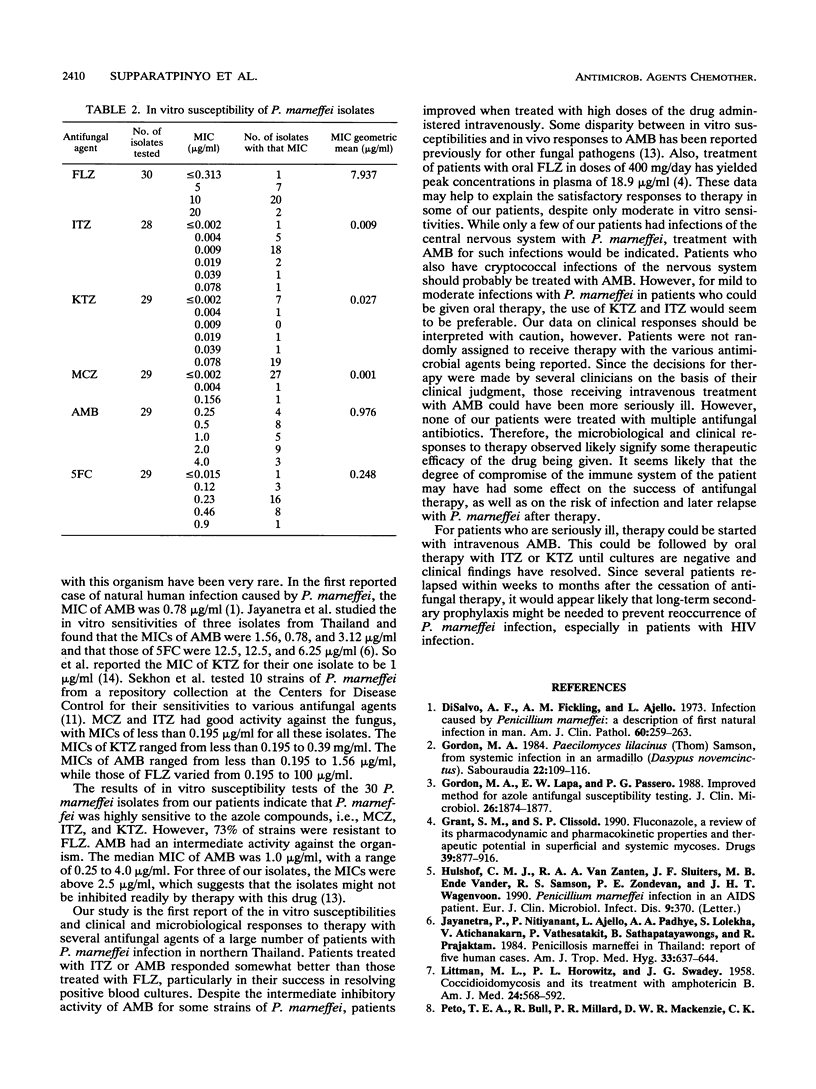
Abstract
Eighty-six patients with laboratory evidence of human immunodeficiency virus infection presented to Chiang Mai University Hospital in Chiang Mai, Thailand, between 1 June 1990 and 30 June 1992 with systemic infection caused by the dimorphic fungus Penicillium marneffei. Thirty isolates of P. marneffei from clinical specimens from these patients were tested for their in vitro susceptibilities to amphotericin B, 5-fluorocytosine, miconazole, ketoconazole, itraconazole, and fluconazole. P. marneffei was highly susceptible to miconazole, itraconazole, ketoconazole, and 5-fluorocytosine. Amphotericin B showed intermediate antifungal activity, while fluconazole was the least active; some strains of the fungus were resistant to fluconazole. The clinical and microbiological responses correlated with the overall patterns of in vitro susceptibility to the azoles, whereas results with amphotericin B were more difficult to assess. Antibiotic failures of initial therapy occurred in 8 of 35 (22.8%) patients treated with amphotericin B, 3 of 12 (25%) patients treated with itraconazole, and 7 of 11 (63.6%) patients treated with fluconazole. Itraconazole or ketoconazole should be considered to be the drug of first choice in the treatment of mild to moderately severe P. marneffei infection. Parenteral therapy with amphotericin B may be required for seriously ill patients. Since at least 12 patients who responded to initial therapy relapsed within 6 months regardless of initial antifungal therapy, maintenance oral therapy with itraconazole or ketoconazole may be necessary.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DiSalvo A. F., Fickling A. M., Ajello L. Infection caused by Penicillium marneffei: description of first natural infection in man. Am J Clin Pathol. 1973 Aug;60(2):259–263. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/60.2.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon M. A., Lapa E. W., Passero P. G. Improved method for azole antifungal susceptibility testing. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Sep;26(9):1874–1877. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.9.1874-1877.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon M. A. Paecilomyces lilacinus (Thom) Samson, from systemic infection in an armadillo (Dasypus novemcinctus). Sabouraudia. 1984;22(2):109–116. doi: 10.1080/00362178485380181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant S. M., Clissold S. P. Fluconazole. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic potential in superficial and systemic mycoses. Drugs. 1990 Jun;39(6):877–916. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199039060-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulshof C. M., van Zanten R. A., Sluiters J. F., van der Ende M. E., Samson R. S., Zondervan P. E., Wagenvoort J. H. Penicillium marneffei infection in an AIDS patient. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990 May;9(5):370–370. doi: 10.1007/BF01973751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayanetra P., Nitiyanant P., Ajello L., Padhye A. A., Lolekha S., Atichartakarn V., Vathesatogit P., Sathaphatayavongs B., Prajaktam R. Penicilliosis marneffei in Thailand: report of five human cases. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1984 Jul;33(4):637–644. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1984.33.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTMAN M. L., HOROWITZ P. L., SWADEY J. G. Coccidioidomycosis and its treatment with amphotericin B. Am J Med. 1958 Apr;24(4):568–592. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(58)90297-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peto T. E., Bull R., Millard P. R., Mackenzie D. W., Campbell C. K., Haines M. E., Mitchell R. G. Systemic mycosis due to Penicillium marneffei in a patient with antibody to human immunodeficiency virus. J Infect. 1988 May;16(3):285–290. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(88)97700-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piehl M. R., Kaplan R. L., Haber M. H. Disseminated penicilliosis in a patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1988 Dec;112(12):1262–1264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sathapatayavongs B., Damrongkitchaiporn S., Saengditha P., Kiatboonsri S., Jayanetra P. Disseminated penicilliosis associated with HIV infection. J Infect. 1989 Jul;19(1):84–85. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(89)95136-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekhon A. S., Padhye A. A., Garg A. K. In vitro sensitivity of Penicillium marneffei and Pythium insidiosum to various antifungal agents. Eur J Epidemiol. 1992 May;8(3):427–432. doi: 10.1007/BF00158578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shadomy S. In vitro studies with 5-fluorocytosine. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Jun;17(6):871–877. doi: 10.1128/am.17.6.871-877.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So S. Y., Chau P. Y., Jones B. M., Wu P. C., Pun K. K., Lam W. K., Lawton J. W. A case of invasive penicilliosis in Hong Kong with immunologic evaluation. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Apr;131(4):662–665. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.4.662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Supparatpinyo K., Chiewchanvit S., Hirunsri P., Uthammachai C., Nelson K. E., Sirisanthana T. Penicillium marneffei infection in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Apr;14(4):871–874. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.4.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang D. N., Li P. C., Tsui M. S., Lau Y. T., Ma K. F., Yeoh E. K. Penicillium marneffei: another pathogen to consider in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Jul-Aug;13(4):766–767. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.4.766-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsui W. M., Ma K. F., Tsang D. N. Disseminated Penicillium marneffei infection in HIV-infected subject. Histopathology. 1992 Apr;20(4):287–293. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1992.tb00985.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitzman I., Gordon M. A., Henderson R. W., Lapa E. W. Phialophora parasitica, an emerging pathogen. Sabouraudia. 1984;22(4):331–339. doi: 10.1080/00362178485380541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



