Abstract
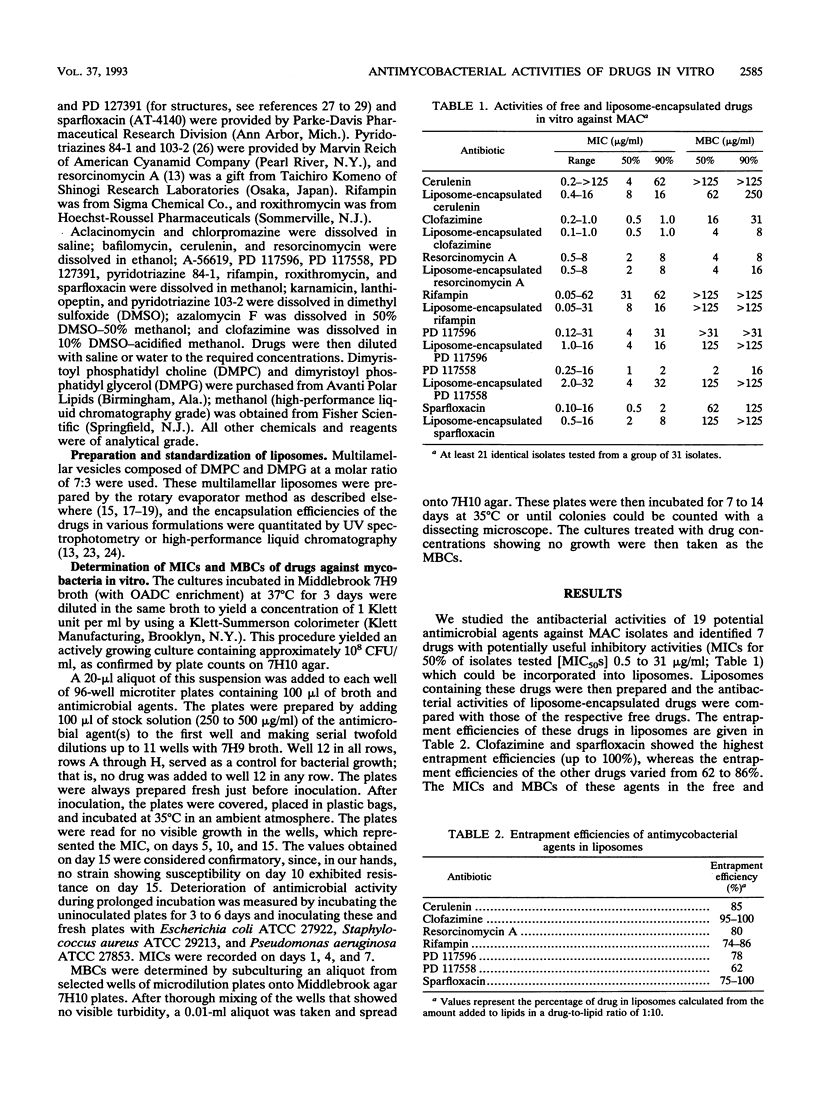
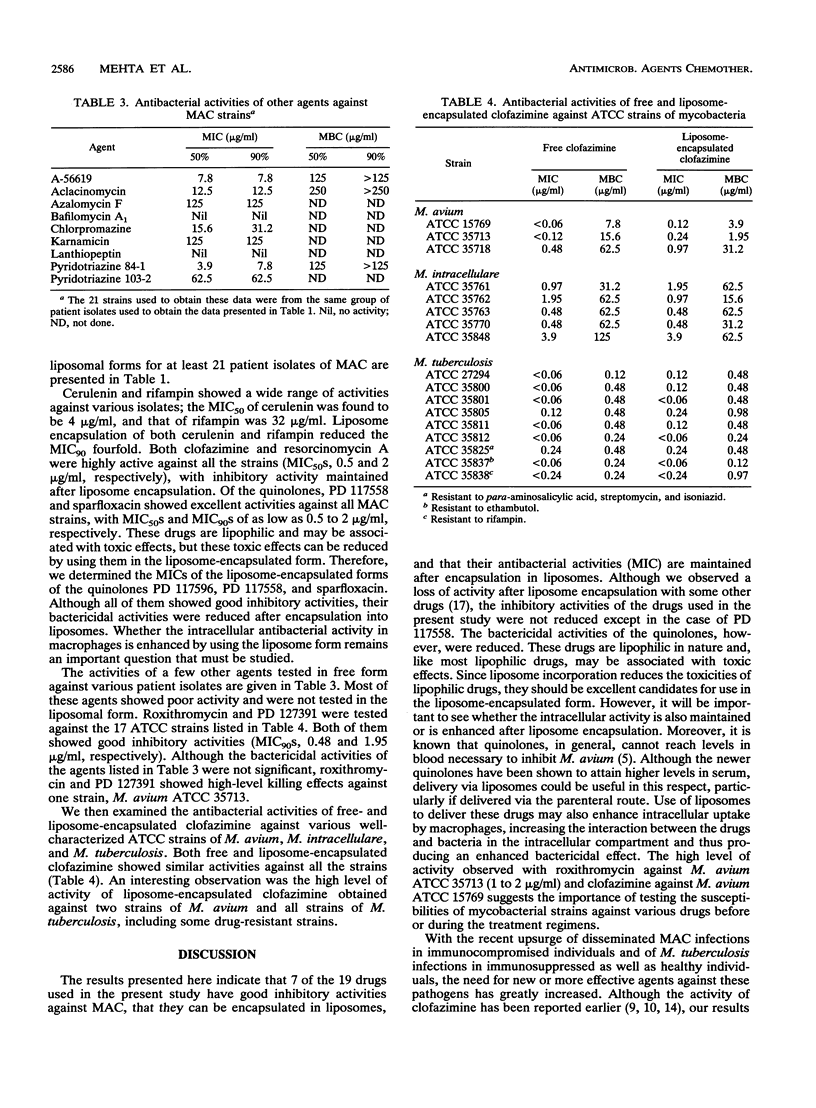
We compared MICs and MBCs of various free- and liposome-incorporated antimicrobial agents against several patient isolates of Mycobacterium avium-M. intracellulare complex and certain American Type Culture Collection strains of M. avium, M. intracellulare, and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Seven of 19 agents were selected for incorporation into liposomes. The MICs of these agents for 50 and 90% of isolates tested (MIC50s and MIC90s, respectively) ranged from 0.5 to 62 micrograms/ml. Members of the M. avium-M. intracellulare complex were resistant to killing by most of the other agents tested in the free form. However, clofazimine, resorcinomycin A, and PD 117558 showed complete killing of bacteria at concentrations ranging from 8 to 31 micrograms/ml, represented as MBC90s. Among the liposome-incorporated agents, clofazimine and resorcinomycin A had the highest killing effects (MBC90s, 8 and 16 micrograms/ml, respectively). Furthermore, both free and liposome-incorporated clofazimine had equivalent growth-inhibitory and killing effects on all American Type Culture Collection strains of M. avium, M. intracellulare, and M. tuberculosis tested. These results show that the antibacterial activities of certain drugs, particularly those of clofazimine and resorcinomycin, were maintained after the drugs were incorporated into liposomes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong D., Gold J. W., Dryjanski J., Whimbey E., Polsky B., Hawkins C., Brown A. E., Bernard E., Kiehn T. E. Treatment of infections in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Nov;103(5):738–743. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-5-738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashtekar D., Düzgünes N., Gangadharam P. R. Activity of free and liposome encapsulated streptomycin against Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) inside peritoneal macrophages. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Oct;28(4):615–617. doi: 10.1093/jac/28.4.615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bermudez L. E., Wu M., Young L. S. Intracellular killing of Mycobacterium avium complex by rifapentine and liposome-encapsulated amikacin. J Infect Dis. 1987 Sep;156(3):510–513. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.3.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman E. J., Siebers A., Altendorf K. Bafilomycins: a class of inhibitors of membrane ATPases from microorganisms, animal cells, and plant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7972–7976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casal M., Rodriguez F., Villalba R., Benavente M. C., Gonzalez A. I. In vitro susceptibility of Mycobacterium fortuitum, Mycobacterium chelonae and Mycobacterium avium against some quinolones. Chemioterapia. 1987 Dec;6(6):431–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David H. L. Basis for lack of drug susceptibility of atypical mycobacteria. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Sep-Oct;3(5):878–884. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.5.878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliopoulos G. M., Moellering A. E., Reiszner E., Moellering R. C., Jr In vitro activities of the quinolone antimicrobial agents A-56619 and A-56620. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Oct;28(4):514–520. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.4.514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Macher A. M., Longo D. L., Lane H. C., Rook A. H., Masur H., Gelmann E. P. NIH conference. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: epidemiologic, clinical, immunologic, and therapeutic considerations. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Jan;100(1):92–106. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-1-92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene J. B., Sidhu G. S., Lewin S., Levine J. F., Masur H., Simberkoff M. S., Nicholas P., Good R. C., Zolla-Pazner S. B., Pollock A. A. Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare: a cause of disseminated life-threatening infection in homosexuals and drug abusers. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Oct;97(4):539–546. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-4-539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khardori N., Rolston K., Rosenbaum B., Hayat S., Bodey G. P. Comparative in-vitro activity of twenty antimicrobial agents against clinical isolates of Mycobacterium avium complex. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 Nov;24(5):667–673. doi: 10.1093/jac/24.5.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo E., Katayama T., Kawamura Y., Yasuda Y., Matsumoto K., Ishii K., Tanimoto T., Hinoo H., Kato T., Kyotani H. Isolation and characterization of new antibiotics resorcinomycins A and B. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1989 Jan;42(1):1–6. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.42.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindholm-Levy P. J., Heifets L. B. Clofazimine and other rimino-compounds: minimal inhibitory and minimal bactericidal concentrations at different pHs for Mycobacterium avium complex. Tubercle. 1988 Sep;69(3):179–186. doi: 10.1016/0041-3879(88)90019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Berestein G., Mehta R., Hopfer R. L., Mills K., Kasi L., Mehta K., Fainstein V., Luna M., Hersh E. M., Juliano R. Treatment and prophylaxis of disseminated infection due to Candida albicans in mice with liposome-encapsulated amphotericin B. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):939–945. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGARA M., AMINO E., ITO H., TAKASE Z., NAKAMURA J., SENDA C., KATO T. Laboratory and clinical studies on azalomycin F. Antibiot Chemother (Northfield) 1962 Aug;12:554–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta R. T., Hopfer R. L., Gunner L. A., Juliano R. L., Lopez-Berestein G. Formulation, toxicity, and antifungal activity in vitro of liposome-encapsulated nystatin as therapeutic agent for systemic candidiasis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Dec;31(12):1897–1900. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.12.1897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta R. T., Hopfer R. L., Juliano R. L., Lopez-Berestein G. A comparison of in vitro toxicity and antifungal efficacy of membrane-active drugs after liposome encapsulation. Sel Cancer Ther. 1989;5(3):113–117. doi: 10.1089/sct.1989.5.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta R. T., McQueen T. J., Keyhani A., Lopez-Berestein G. Liposomal hamycin: reduced toxicity and improved antifungal efficacy in vitro and in vivo. J Infect Dis. 1991 Nov;164(5):1003–1006. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.5.1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Minami A., Nakata K., Kurobe N., Kouno K., Sakaguchi Y., Kashimoto S., Yoshida H., Kojima T., Ohue T. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities of AT-4140, a new broad-spectrum quinolone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Aug;33(8):1167–1173. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.8.1167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naruse N., Tenmyo O., Tomita K., Konishi M., Miyaki T., Kawaguchi H., Fukase K., Wakamiya T., Shiba T. Lanthiopeptin, a new peptide antibiotic. Production, isolation and properties of lanthiopeptin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1989 Jun;42(6):837–845. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.42.837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishio M., Tomatsu K., Konishi M., Tomita K., Oki T., Kawaguchi H., Clardy J. Karnamicin, a complex of new antifungal antibiotics. I. Taxonomy, fermentation, isolation and physico-chemical and biological properties. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1989 Jun;42(6):852–868. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.42.852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omura S. The antibiotic cerulenin, a novel tool for biochemistry as an inhibitor of fatty acid synthesis. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Sep;40(3):681–697. doi: 10.1128/br.40.3.681-697.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J. H., Hamme K. J., Gordon G. R. Determination of clofazimine in plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1982 May 14;229(2):503–508. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)84299-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poznansky M. J., Juliano R. L. Biological approaches to the controlled delivery of drugs: a critical review. Pharmacol Rev. 1984 Dec;36(4):277–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich M. F., Fabio P. F., Lee V. J., Kuck N. A., Testa R. T. Pyrido[3,4-e]-1,2,4-triazines and related heterocycles as potential antifungal agents. J Med Chem. 1989 Nov;32(11):2474–2485. doi: 10.1021/jm00131a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolston K. V., Ho D. H., LeBlanc B., Bodey G. P. In vitro activity of PD127,391, a new quinolone against bacterial isolates from cancer patients. Chemotherapy. 1990;36(5):365–372. doi: 10.1159/000238789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolston K. V., Ho D. H., LeBlanc B., Bodey G. P. In vitro evaluation of difloxacin (A-56619), A-56620, and other 4-quinolones against isolates from cancer patients. Chemotherapy. 1987;33(6):419–427. doi: 10.1159/000238530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolston K. V., LeBlanc B., Gooch G., Ho D. H., Bodey G. P. In-vitro activity of PD 117558, a new quinolone against bacterial isolates from cancer patients. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 Mar;23(3):363–371. doi: 10.1093/jac/23.3.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolston K. V., LeBlanc B., Ho D. H., Bodey G. P. In-vitro activity of PD 117 596, a new quinolone, against bacterial isolates from cancer patients. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Jul;26(1):39–44. doi: 10.1093/jac/26.1.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson C. E., Popescu M. C., Ginsberg R. S. Preparation and use of liposomes in the treatment of microbial infections. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1988;15 (Suppl 1):S1–31. doi: 10.3109/10408418809104463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Inderlied C. B., Berlin O. G., Gottlieb M. S. Mycobacterial infections in AIDS patients, with an emphasis on the Mycobacterium avium complex. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Nov-Dec;8(6):1024–1033. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.6.1024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakowski P., Fligiel S., Berlin G. W., Johnson L., Jr Disseminated Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare infection in homosexual men dying of acquired immunodeficiency. JAMA. 1982 Dec 10;248(22):2980–2982. doi: 10.1001/jama.1982.03330220024029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



