Abstract
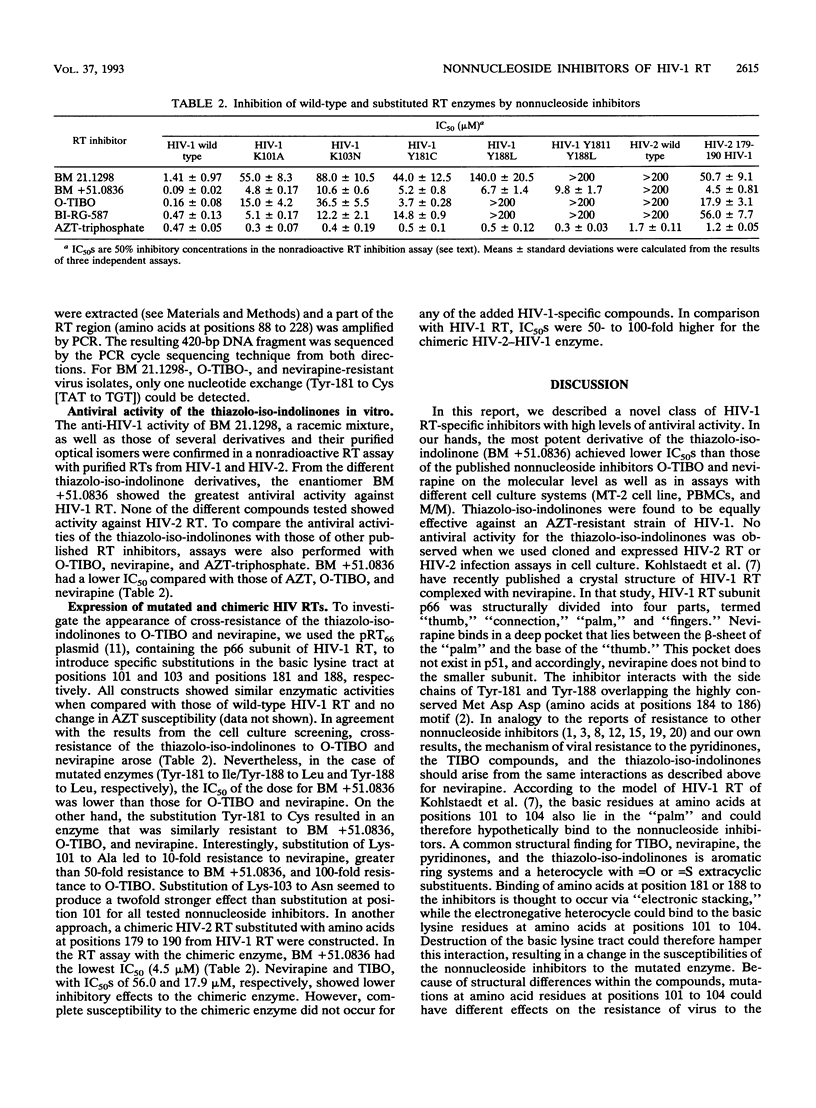
Thiazolo-iso-indolinone derivatives with high specificity toward the reverse transcriptase (RT) of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) were identified. The most potent compound, BM +51.0836, inhibited HIV-1 RT at a 50% inhibitory concentration of 90 nM in vitro. In cell culture assays, similar 50% inhibitory concentrations were obtained with high specificity for HIV-1. These substances were equally active against a zidovudine-resistant isolate. No antiviral effect was observed with an HIV-2 isolate. HIV-1 isolates resistant to the thiazolo-iso-indolinones were generated in cell culture, and the nucleotide sequences of the respective RT genes were analyzed subsequently. Comparison of the deduced amino acid sequences with the wild-type sequence showed an amino acid change at position 181 (Tyr to Cys). Substitutions of amino acid Lys-101 and Lys-103 as well as Tyr-181 and/or Tyr-188 by site-directed mutagenesis led to resistance against the thiazolo-iso-indolinones. A chimeric HIV-2 RT, substituted with amino acids at positions 179 to 190 from HIV-1, acquired only partial susceptibility to BM +51.0836.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balzarini J., Karlsson A., Pérez-Pérez M. J., Vrang L., Walbers J., Zhang H., Oberg B., Vandamme A. M., Camarasa M. J., De Clercq E. HIV-1-specific reverse transcriptase inhibitors show differential activity against HIV-1 mutant strains containing different amino acid substitutions in the reverse transcriptase. Virology. 1993 Jan;192(1):246–253. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber A. M., Hizi A., Maizel J. V., Jr, Hughes S. H. HIV-1 reverse transcriptase: structure predictions for the polymerase domain. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Sep;6(9):1061–1072. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.1061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberle J., Seibl R. A new method for measuring reverse transcriptase activity by ELISA. J Virol Methods. 1992 Dec 1;40(3):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(92)90092-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn B. H., Gonda M. A., Shaw G. M., Popovic M., Hoxie J. A., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Genomic diversity of the acquired immune deficiency syndrome virus HTLV-III: different viruses exhibit greatest divergence in their envelope genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4813–4817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada S., Koyanagi Y., Yamamoto N. Infection of HTLV-III/LAV in HTLV-I-carrying cells MT-2 and MT-4 and application in a plaque assay. Science. 1985 Aug 9;229(4713):563–566. doi: 10.1126/science.2992081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohlstaedt L. A., Wang J., Friedman J. M., Rice P. A., Steitz T. A. Crystal structure at 3.5 A resolution of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase complexed with an inhibitor. Science. 1992 Jun 26;256(5065):1783–1790. doi: 10.1126/science.1377403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellors J. W., Im G. J., Tramontano E., Winkler S. R., Medina D. J., Dutschman G. E., Bazmi H. Z., Piras G., Gonzalez C. J., Cheng Y. C. A single conservative amino acid substitution in the reverse transcriptase of human immunodeficiency virus-1 confers resistance to (+)-(5S)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-5-methyl-6-(3-methyl-2-butenyl)imidazo[4,5, 1- jk][1,4]benzodiazepin-2(1H)-thione (TIBO R82150). Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Jan;43(1):11–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merluzzi V. J., Hargrave K. D., Labadia M., Grozinger K., Skoog M., Wu J. C., Shih C. K., Eckner K., Hattox S., Adams J. Inhibition of HIV-1 replication by a nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor. Science. 1990 Dec 7;250(4986):1411–1413. doi: 10.1126/science.1701568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller B., Restle T., Kühnel H., Goody R. S. Expression of the heterodimeric form of human immunodeficiency virus type 2 reverse transcriptase in Escherichia coli and characterization of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14709–14713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller B., Restle T., Weiss S., Gautel M., Sczakiel G., Goody R. S. Co-expression of the subunits of the heterodimer of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):13975–13978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunberg J. H., Schleif W. A., Boots E. J., O'Brien J. A., Quintero J. C., Hoffman J. M., Emini E. A., Goldman M. E. Viral resistance to human immunodeficiency virus type 1-specific pyridinone reverse transcriptase inhibitors. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4887–4892. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4887-4892.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauwels R., Andries K., Desmyter J., Schols D., Kukla M. J., Breslin H. J., Raeymaeckers A., Van Gelder J., Woestenborghs R., Heykants J. Potent and selective inhibition of HIV-1 replication in vitro by a novel series of TIBO derivatives. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):470–474. doi: 10.1038/343470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauwels R., Balzarini J., Baba M., Snoeck R., Schols D., Herdewijn P., Desmyter J., De Clercq E. Rapid and automated tetrazolium-based colorimetric assay for the detection of anti-HIV compounds. J Virol Methods. 1988 Aug;20(4):309–321. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(88)90134-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D., Shih C. K., Lowy I., Rose J., Prodanovich P., Goff S., Griffin J. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 mutants resistant to nonnucleoside inhibitors of reverse transcriptase arise in tissue culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11241–11245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardana V. V., Emini E. A., Gotlib L., Graham D. J., Lineberger D. W., Long W. J., Schlabach A. J., Wolfgang J. A., Condra J. H. Functional analysis of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase amino acids involved in resistance to multiple nonnucleoside inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17526–17530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih C. K., Rose J. M., Hansen G. L., Wu J. C., Bacolla A., Griffin J. A. Chimeric human immunodeficiency virus type 1/type 2 reverse transcriptases display reversed sensitivity to nonnucleoside analog inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9878–9882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S., König B., Müller H. J., Seidel H., Goody R. S. Synthetic human tRNA(UUULys3) and natural bovine tRNA(UUULys3) interact with HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and serve as specific primers for retroviral cDNA synthesis. Gene. 1992 Feb 15;111(2):183–197. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90686-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vreese K., Debyser Z., Vandamme A. M., Pauwels R., Desmyter J., de Clercq E., Anné J. Resistance of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase to TIBO derivatives induced by site-directed mutagenesis. Virology. 1992 Jun;188(2):900–904. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90550-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


