Abstract
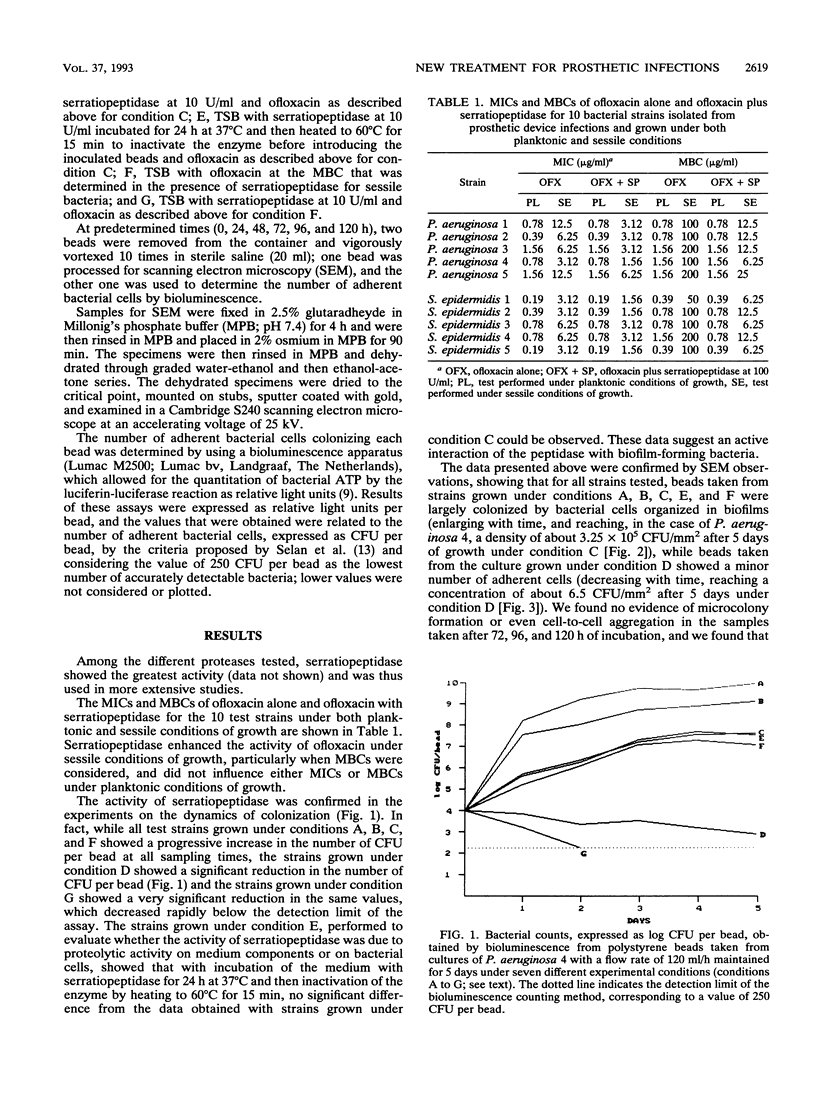
Among the different mechanisms of bacterial resistance to antimicrobial agents that have been studied, biofilm formation is one of the most widespread. This mechanism is frequently the cause of failure in the treatment of prosthetic device infections, and several attempts have been made to develop molecules and protocols that are able to inhibit biofilm-embedded bacteria. We present data suggesting the possibility that proteolytic enzymes could significantly enhance the activities of antibiotics against biofilms. Antibiotic susceptibility tests on both planktonic and sessile cultures, studies on the dynamics of colonization of 10 biofilm-forming isolates, and then bioluminescence and scanning electron microscopy under seven different experimental conditions showed that serratiopeptidase greatly enhances the activity of ofloxacin on sessile cultures and can inhibit biofilm formation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anwar H., Dasgupta M. K., Costerton J. W. Testing the susceptibility of bacteria in biofilms to antibacterial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Nov;34(11):2043–2046. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.11.2043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anwar H., Strap J. L., Costerton J. W. Establishment of aging biofilms: possible mechanism of bacterial resistance to antimicrobial therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Jul;36(7):1347–1351. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.7.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. R., Collier P. J., Gilbert P. Influence of growth rate on susceptibility to antimicrobial agents: modification of the cell envelope and batch and continuous culture studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Sep;34(9):1623–1628. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.9.1623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Cheng K. J., Geesey G. G., Ladd T. I., Nickel J. C., Dasgupta M., Marrie T. J. Bacterial biofilms in nature and disease. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:435–464. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.002251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert P., Brown M. R. Influence of growth rate and nutrient limitation on the gross cellular composition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its resistance to 3- and 4-chlorophenol. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1066–1072. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1066-1072.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giwercman B., Jensen E. T., Høiby N., Kharazmi A., Costerton J. W. Induction of beta-lactamase production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 May;35(5):1008–1010. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.5.1008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harber M. J., Mackenzie R., Asscher A. W. A rapid bioluminescence method for quantifying bacterial adhesion to polystyrene. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Mar;129(3):621–632. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-3-621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahama K., Yoshimura K., Marumoto R., Kikuchi M., Lee I. S., Hase T., Matsubara H. Cloning and sequencing of Serratia protease gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 25;14(14):5843–5855. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.14.5843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selan L., Berlutti F., Passariello C., Thaller M. C., Renzini G. Reliability of a bioluminescence ATP assay for detection of bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jul;30(7):1739–1742. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.7.1739-1742.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selan L., Thaller M. C., Berlutti F., Passariello C., Scazzocchio F., Renzini G. Effect of slime production on the antibiotic susceptibility of isolates from prosthetic infections. J Chemother. 1989 Dec;1(6):369–373. doi: 10.1080/1120009x.1989.11738925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki H., Tsuji H., Saeki K. [Anti-inflammatory action of a protease, TSP, produced by Serratia]. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1967 Jul 20;63(4):302–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loosdrecht M. C., Lyklema J., Norde W., Zehnder A. J. Influence of interfaces on microbial activity. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Mar;54(1):75–87. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.1.75-87.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




