Abstract
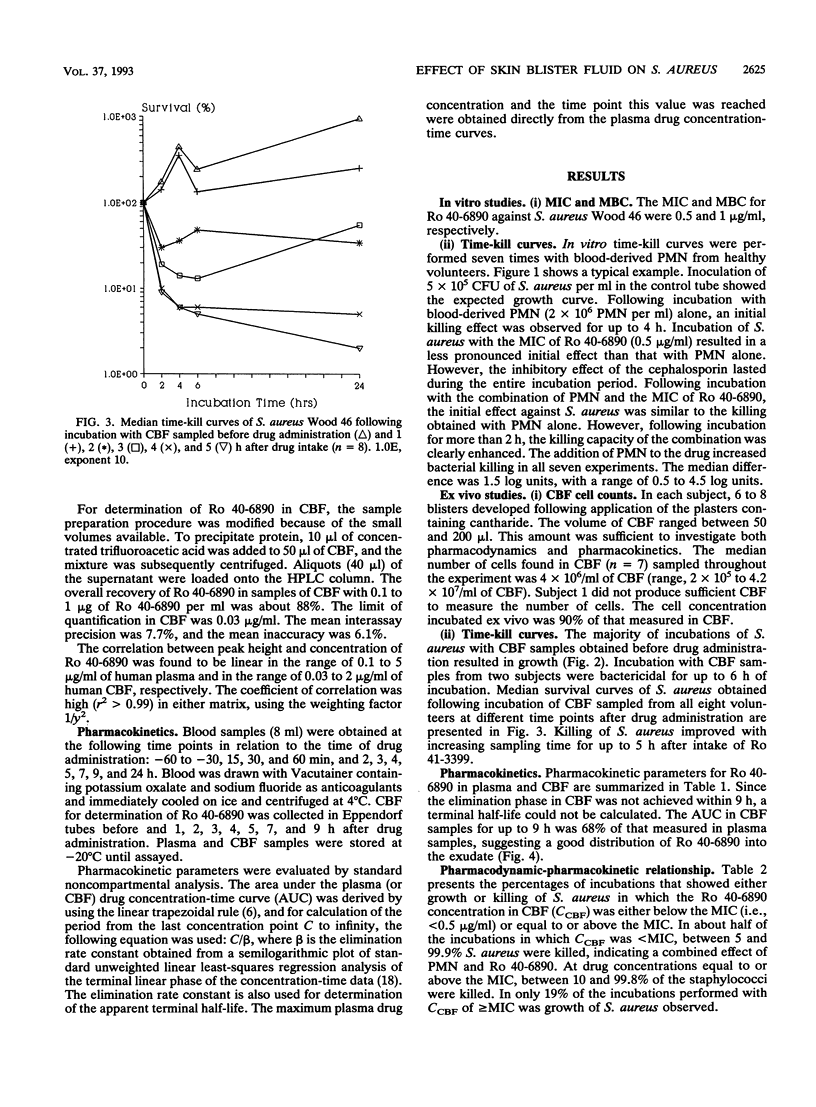
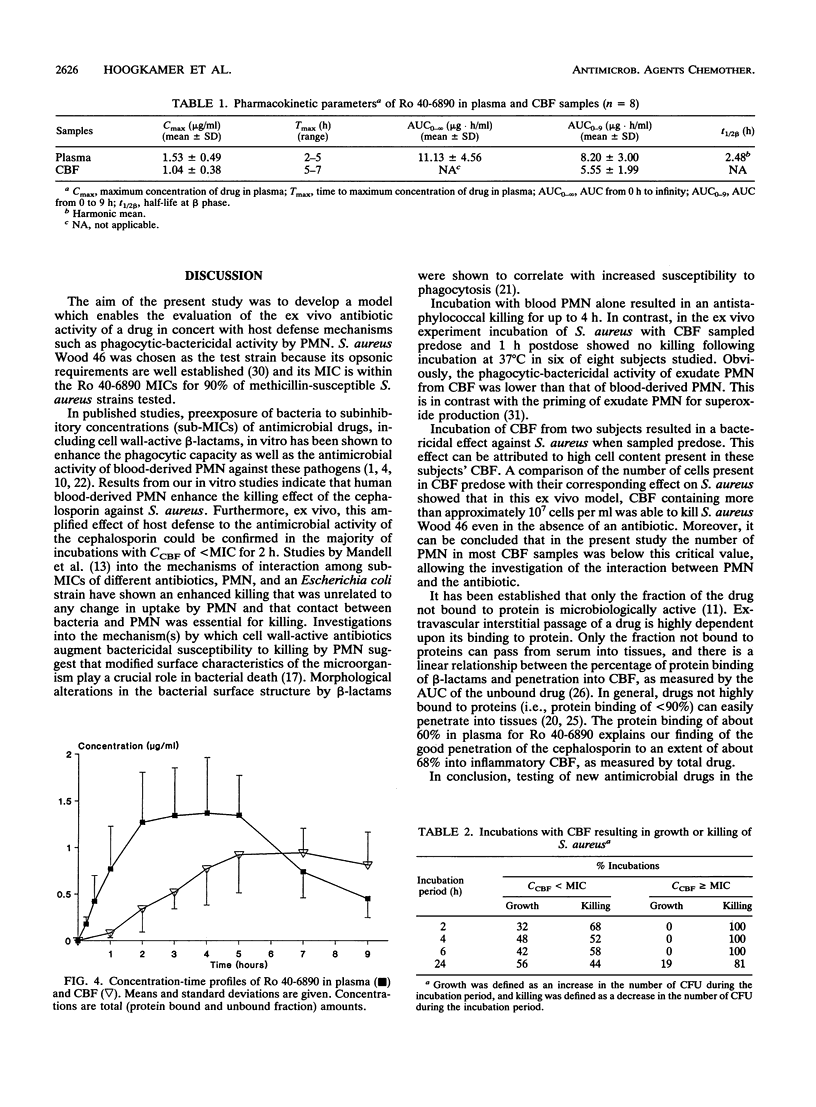
The pharmacokinetics of an antimicrobial drug in human plasma and in vitro susceptibility testing of an antimicrobial drug do not necessarily predict its efficacy in vivo. Therefore, the combined activity of an antimicrobial drug and blood-derived polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN) against Staphylococcus aureus were investigated in vitro. In addition, a pharmacological model allowing analysis of the bactericidal activity of a drug-containing exudate against S. aureus ex vivo was developed. For this purpose, a phagocytic-bactericidal assay was miniaturized to a volume of 100 microliters in order to test the bactericidal activities of an antimicrobial drug with blood PMN in vitro and with skin blister fluid (CBF) ex vivo. Ro 40-6890, the active metabolite of the ester prodrug Ro 41-3399, was used as the test drug. Killing of S. aureus was clearly enhanced when Ro 41-6890 was combined in vitro with a suboptimal number of blood-derived PMN. In eight healthy volunteers, skin blisters were provoked by plasters containing cantharidin. Following a single oral dose of Ro 41-3399, CBF containing PMN was sampled at regular intervals and incubated ex vivo with S. aureus (5 x 10(5) CFU/ml) for 2, 4, 6, and 24 h at 37 degrees C. Concentrations of Ro 40-6890 were measured in CBF (CCBF) and plasma. Ro 40-6890 distributed well from plasma into CBF. When CCBF was below the MIC, an enhanced effect of Ro 40-6890 and host defense factors present in CBF against S. aureus was observed. In conclusion, the present model can provide additional information on human plasma drug concentrations and MICs established in vitro.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adinolfi L. E., Bonventre P. F. Enhanced phagocytosis, killing, and serum sensitivity of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus treated with sub-MICs of imipenem. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jul;32(7):1012–1018. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.7.1012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angehrn P., Hohl P., Hubschwerlen C., Page M., Then R. Antibacterial properties of Ro 40-6890, a broad-spectrum cephalosporin, and its novel orally absorbable ester, Ro 41-3399. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Dec;36(12):2825–2834. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.12.2825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buggy B. P., Schaberg D. R., Swartz R. D. Intraleukocytic sequestration as a cause of persistent Staphylococcus aureus peritonitis in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Am J Med. 1984 Jun;76(6):1035–1040. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90854-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daschner F. D. Antibiotics and host defence with special reference to phagocytosis by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Aug;16(2):135–141. doi: 10.1093/jac/16.2.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drusano G. L. Role of pharmacokinetics in the outcome of infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Mar;32(3):289–297. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.3.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood D. In vitro veritas? Antimicrobial susceptibility tests and their clinical relevance. J Infect Dis. 1981 Oct;144(4):380–385. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.4.380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gristina A. G., Jennings R. A., Naylor P. T., Myrvik Q. N., Webb L. X. Comparative in vitro antibiotic resistance of surface-colonizing coagulase-negative staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jun;33(6):813–816. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.6.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohl P., Buser U., Frei R. Fatal Legionella pneumophila pneumonia: treatment failure despite early sequential oral-parenteral amoxicillin-clavulanic acid therapy. Infection. 1992 Mar-Apr;20(2):99–100. doi: 10.1007/BF01711076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labro M. T., Babin-Chevaye C., Hakim J. Influence of subinhibitory concentrations of ceftriaxone on opsonization and killing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by human neutrophils. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Sep;22(3):341–352. doi: 10.1093/jac/22.3.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam Y. W., Duroux M. H., Gambertoglio J. G., Barriere S. L., Guglielmo B. J. Effect of protein binding on serum bactericidal activities of ceftazidime and cefoperazone in healthy volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Mar;32(3):298–302. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.3.298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell G. L. Interaction of intraleukocytic bacteria and antibiotics. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jul;52(7):1673–1679. doi: 10.1172/JCI107348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell L. A., Afnan M. Mechanisms of interaction among subinhibitory concentrations of antibiotics, human polymorphonuclear neutrophils, and gram-negative bacilli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jul;35(7):1291–1297. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.7.1291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. H., Mroczkowski T. F., Dalu Z. A., McCarty J., Jones R. B., Hopkins S. J., Johnson R. B. A controlled trial of a single dose of azithromycin for the treatment of chlamydial urethritis and cervicitis. The Azithromycin for Chlamydial Infections Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1992 Sep 24;327(13):921–925. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199209243271304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nightingale J. Clinical limitations of in vitro testing of microorganism susceptibility. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1987 Jan;44(1):131–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root R. K., Isturiz R., Molavi A., Metcalf J. A., Malech H. L. Interactions between antibiotics and human neutrophils in the killing of staphylococci. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jan;67(1):247–259. doi: 10.1172/JCI110020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyu W. C., Quintiliani R., Nightingale C. H., Dudley M. N. Effect of protein binding on drug penetration into blister fluid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jan;32(1):128–130. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stübner G., Dalhoff A., Voigt W. H. Bacteriological and ultrastructural studies on the effect of subinhibitory beta-lactam concentrations on intraphagocytic killing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Arzneimittelforschung. 1986 Jun;36(6):899–904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widmer A. F., Wiestner A., Frei R., Zimmerli W. Killing of nongrowing and adherent Escherichia coli determines drug efficacy in device-related infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Apr;35(4):741–746. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.4.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Gillett A. P., Cadge B., Durham S. R., Baker S. The influence of protein binding upon tissue fluid levels of six beta-lactam antibiotics. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jul;142(1):77–82. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R. Methods for evaluating the penetration of beta-lactam antibiotics into tissues. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Jul-Aug;8 (Suppl 3):S325–S332. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.supplement_3.s325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R. The clinical relevance of protein binding and tissue concentrations in antimicrobial therapy. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1986 Nov-Dec;11(6):470–482. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198611060-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancey R. J., Sanchez M. S., Ford C. W. Activity of antibiotics against Staphylococcus aureus within polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991 Feb;10(2):107–113. doi: 10.1007/BF01964421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zak O., Tosch W., Sande M. A. Correlation of antibacterial activities of antibiotics in vitro and in animal models of infection. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jan;15 (Suppl A):273–282. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.suppl_a.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerli W., Lew P. D., Suter S., Wyss M., Waldvogel F. A. In vitro efficacy of several antibiotics against intracellular S. aureus in chronic granulomatous disease. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1983 Mar;38(1):51–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerli W., Schaffner A., Scheidegger C., Scherz R., Späth P. J. Humoral immune response to pneumococcal antigen 23-F in an asplenic patient with recurrent fulminant pneumococcaemia. J Infect. 1991 Jan;22(1):59–69. doi: 10.1016/0163-4453(91)91010-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerli W., Seligmann B., Gallin J. I. Exudation primes human and guinea pig neutrophils for subsequent responsiveness to the chemotactic peptide N-formylmethionylleucylphenylalanine and increases complement component C3bi receptor expression. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):925–933. doi: 10.1172/JCI112391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Broek P. J. Antimicrobial drugs, microorganisms, and phagocytes. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Mar-Apr;11(2):213–245. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.2.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


