Abstract
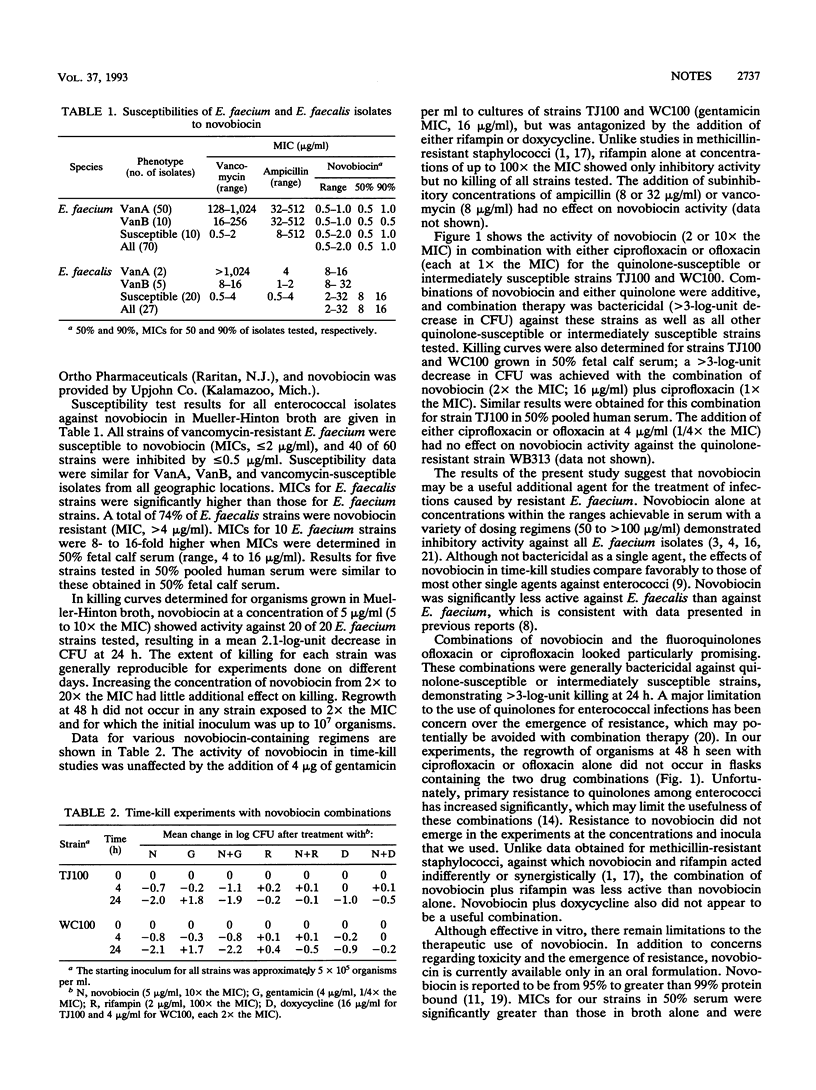
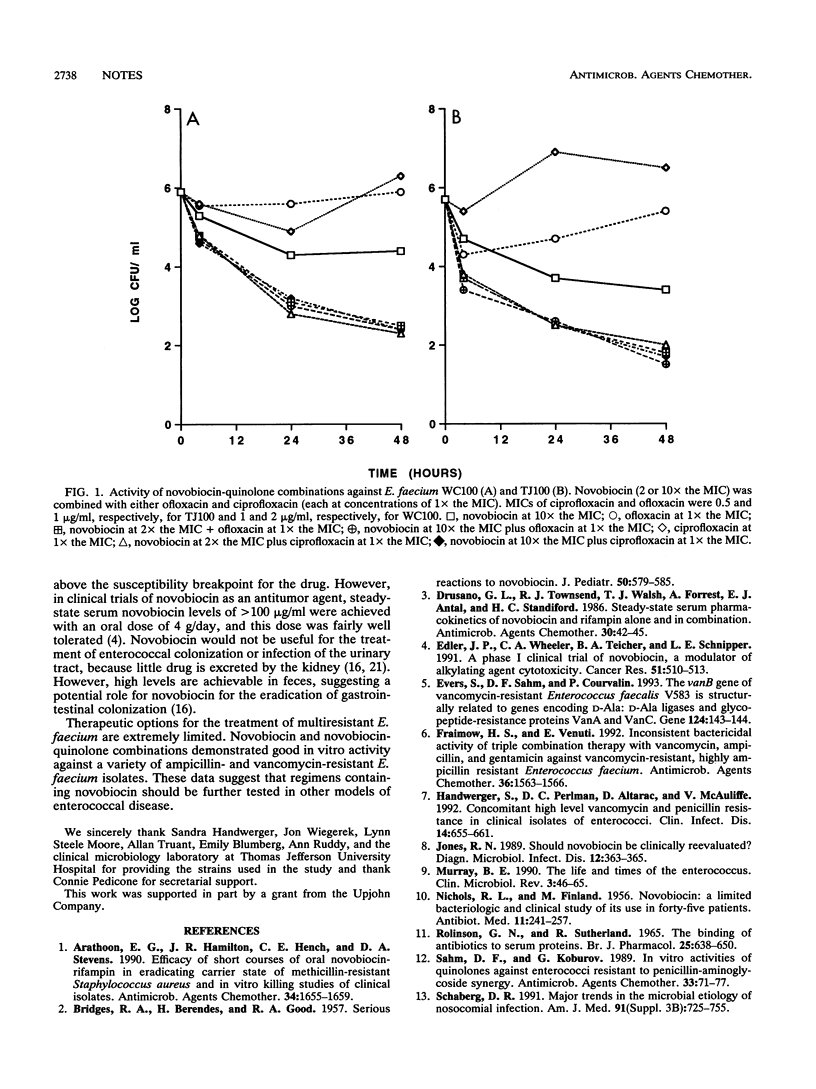
Sixty strains of vancomycin- and ampicillin-resistant Enterococcus faecium were evaluated for their susceptibilities to novobiocin in vitro. In Mueller-Hinton broth, novobiocin inhibited all strains when it was used at a concentration of < or = 2 microgram/ml and 40 of 60 strains when it was used at a concentration of < or = 0.5 micrograms/ml. MICs were 8- to 16-fold higher in 50% serum. Novobiocin alone resulted in 2-log-unit killing at 24 h. Combinations of novobiocin and a fluoroquinolone (either ciprofloxacin or ofloxacin) were additive and bactericidal for quinolone-susceptible strains in either broth or 50% serum. Gentamicin did not affect novobiocin activity, and rifampin and doxycycline were antagonistic.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arathoon E. G., Hamilton J. R., Hench C. E., Stevens D. A. Efficacy of short courses of oral novobiocin-rifampin in eradicating carrier state of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and in vitro killing studies of clinical isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Sep;34(9):1655–1659. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.9.1655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRIDGES R. A., BERENDES H., GOOD R. A. Serious reactions to novobiocin. J Pediatr. 1957 May;50(5):579–585. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(57)80222-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drusano G. L., Townsend R. J., Walsh T. J., Forrest A., Antal E. J., Standiford H. C. Steady-state serum pharmacokinetics of novobiocin and rifampin alone and in combination. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jul;30(1):42–45. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.1.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eder J. P., Wheeler C. A., Teicher B. A., Schnipper L. E. A phase I clinical trial of novobiocin, a modulator of alkylating agent cytotoxicity. Cancer Res. 1991 Jan 15;51(2):510–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evers S., Sahm D. F., Courvalin P. The vanB gene of vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis V583 is structurally related to genes encoding D-Ala:D-Ala ligases and glycopeptide-resistance proteins VanA and VanC. Gene. 1993 Feb 14;124(1):143–144. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90779-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraimow H. S., Venuti E. Inconsistent bactericidal activity of triple-combination therapy with vancomycin, ampicillin, and gentamicin against vancomycin-resistant, highly ampicillin-resistant Enterococcus faecium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Jul;36(7):1563–1566. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.7.1563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handwerger S., Perlman D. C., Altarac D., McAuliffe V. Concomitant high-level vancomycin and penicillin resistance in clinical isolates of enterococci. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Mar;14(3):655–661. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.3.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N. Should novobiocin be clinically re-evaluated? Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Jul-Aug;12(4):363–365. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(89)90105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E. The life and times of the Enterococcus. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jan;3(1):46–65. doi: 10.1128/cmr.3.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICHOLS R. L., FINLAND M. Novobiocin; a limited bacteriologic and clinical study of its use in forty-five patients. Antibiotic Med Clin Ther (New York) 1956 Apr;2(4):241–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolinson G. N., Sutherland R. The binding of antibiotics to serum proteins. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1965 Dec;25(3):638–650. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1965.tb01788.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahm D. F., Koburov G. T. In vitro activities of quinolones against enterococci resistant to penicillin-aminoglycoside synergy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jan;33(1):71–77. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaberg D. R., Dillon W. I., Terpenning M. S., Robinson K. A., Bradley S. F., Kauffman C. A. Increasing resistance of enterococci to ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Nov;36(11):2533–2535. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.11.2533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spera R. V., Jr, Farber B. F. Multiply-resistant Enterococcus faecium. The nosocomial pathogen of the 1990s. JAMA. 1992 Nov 11;268(18):2563–2564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRIGHT W. W., PUTNAM L. E., WELCH H. Novobiocin; serum concentrations and urinary excretion following oral administration in man. Antibiotic Med Clin Ther (New York) 1956 May;2(5):311–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh T. J., Auger F., Tatem B. A., Hansen S. L., Standiford H. C. Novobiocin and rifampicin in combination against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: an in-vitro comparison with vancomycin plus rifampicin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Jan;17(1):75–82. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh T. J., Standiford H. C., Reboli A. C., John J. F., Mulligan M. E., Ribner B. S., Montgomerie J. Z., Goetz M. B., Mayhall C. G., Rimland D. Randomized double-blinded trial of rifampin with either novobiocin or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus colonization: prevention of antimicrobial resistance and effect of host factors on outcome. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Jun;37(6):1334–1342. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.6.1334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Kitayama R., Hayashi T., Nakashima Y., Noguchi M., Yasuda T., Saikawa I., Shimizu K. Studies on protein binding of antibiotics. IV. Effect of the binding of drug to 100,000 X g supernatant fluid of rabbit liver homogenates on urinary excretion. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1982 Nov;35(11):1603–1609. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.35.1603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


