Abstract
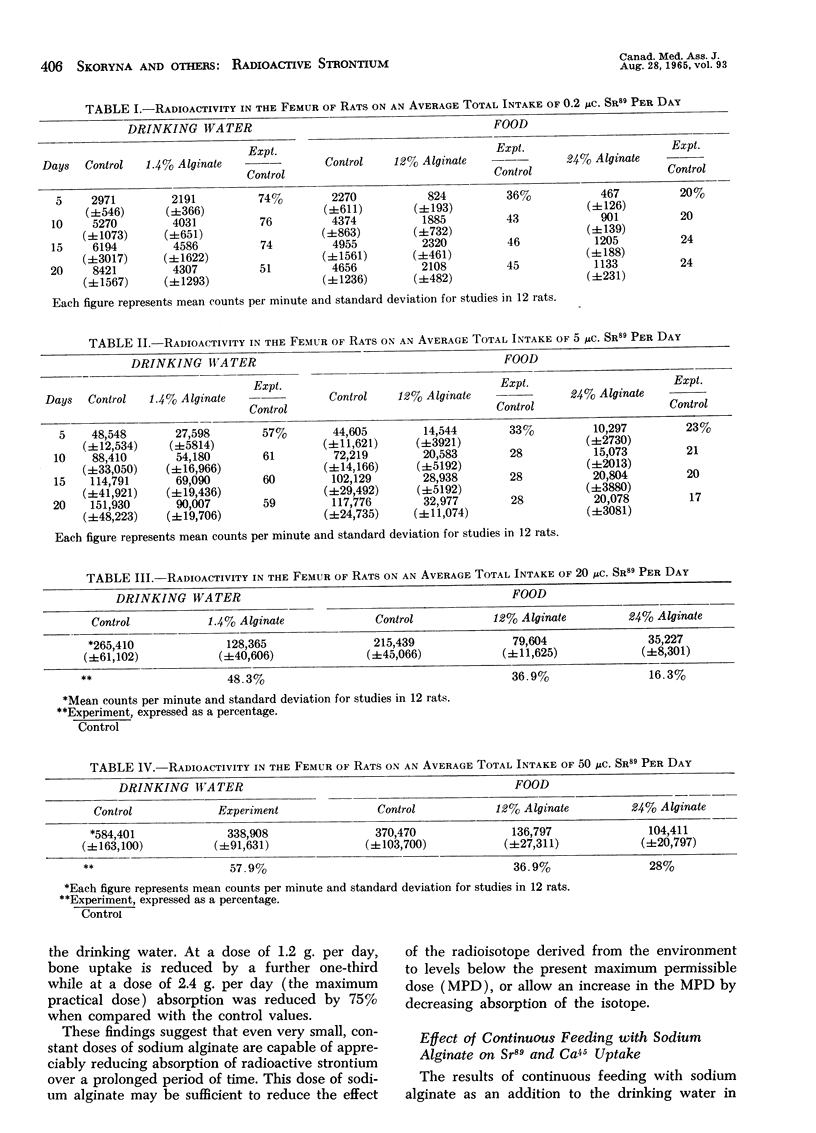
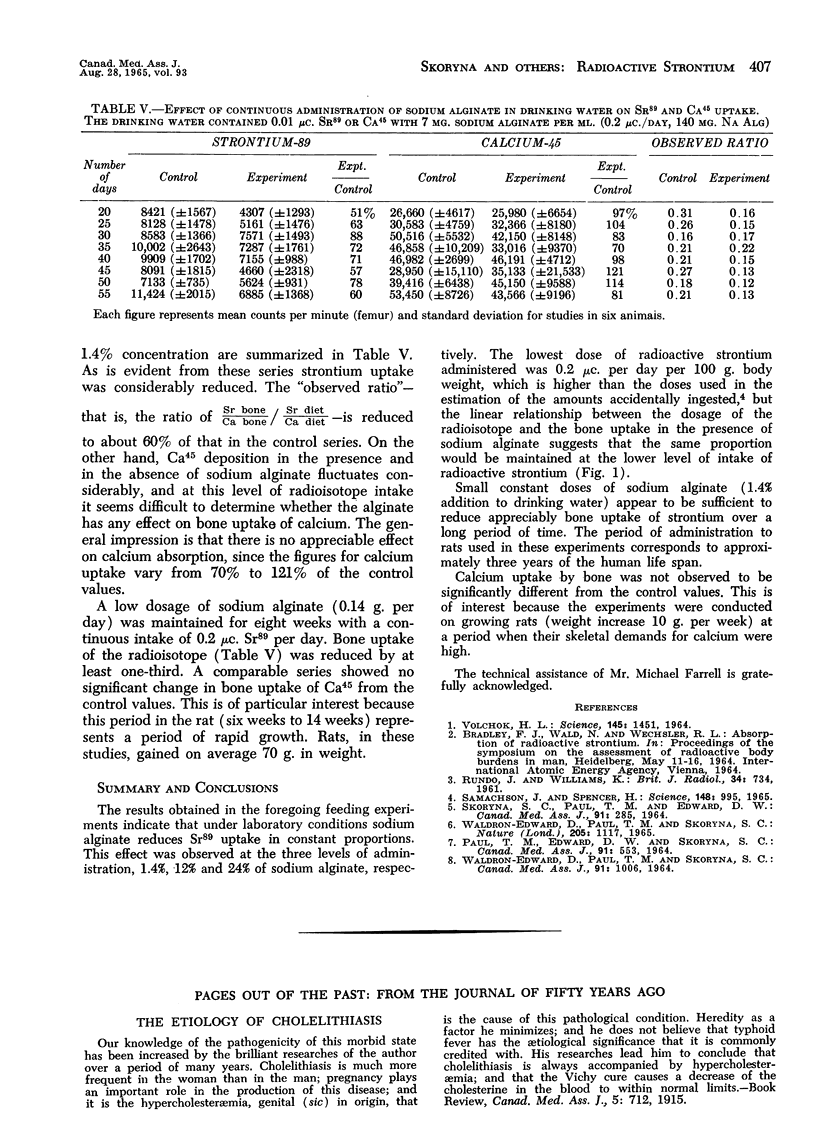
A method is reported which permits selective suppression of absorption of radioactive strontium from ingested food material, allowing calcium to be available to the body. Studies were carried out on the inhibitory effect of various amounts of sodium alginate and the dose-response relationship of Sr89 and bone uptake. The results obtained indicated that under laboratory conditions sodium alginate effectively reduces Sr89 uptake in a constant proportion. This effect was observed at the three levels of administration of 1.4%, 12% and 24% of sodium alginate. The linear relationship between the dosage of the radioisotope and the bone uptake in the presence of sodium alginate suggests that the same proportion is maintained at the lower levels of intake of radioactive strontium.
Previous studies with small constant doses of sodium alginate were extended in rats to a period corresponding approximately to three years of human life span. Low doses were sufficient to reduce appreciably bone uptake of radiostrontium.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- PAUL T. M., EDWARD D. W., SKORYNA S. C. STUDIES ON INHIBITION OF INTESTINAL ABSORPTION OF RADIOACTIVE STRONTIUM. II. EFFECTS OF ADMINISTRATION OF SODIUM ALGINATE BY OROGASTRIC INTUBATION AND FEEDING. Can Med Assoc J. 1964 Sep 5;91:553–557. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUNDO J., WILLIAMS K. A case of accidental inhalation of 90SrCO3. Br J Radiol. 1961 Nov;34:734–740. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-34-407-734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKORYNA S. C., PAUL T. M., EDWARD D. W. STUDIES ON INHIBITION OF INTESTINAL ABSORPTION OF RADIOACTIVE STRONTIUM. I. PREVENTION OF ABSORPTION FROM LIGATED INTESTINAL SEGMENTS. Can Med Assoc J. 1964 Aug 8;91:285–288. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOLCHOK H. L. STRONTIUM 90: ESTIMATION OF WORLDWIDE DEPOSITION. Science. 1964 Sep 25;145(3639):1451–1452. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3639.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALDRON-EDWARD D., SKORYNA S. C., PAUL T. M. STUDIES ON THE INHIBITION OF INTESTINAL ABSORPTION OF RADIOACTIVE STRONTIUM. 3. THE EFFECT OF ADMINISTRATION OF SODIUM ALGINATE IN FOOD AND IN DRINKING WATER. Can Med Assoc J. 1964 Nov 7;91:1006–1010. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldron-Edward D., Paul T. M., Skoryna S. C. Suppression of intestinal absorption of radioactive strontium by naturally occurring non-absorbable polyelectrolytes. Nature. 1965 Mar 13;205(976):1117–1118. doi: 10.1038/2051117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


