Abstract
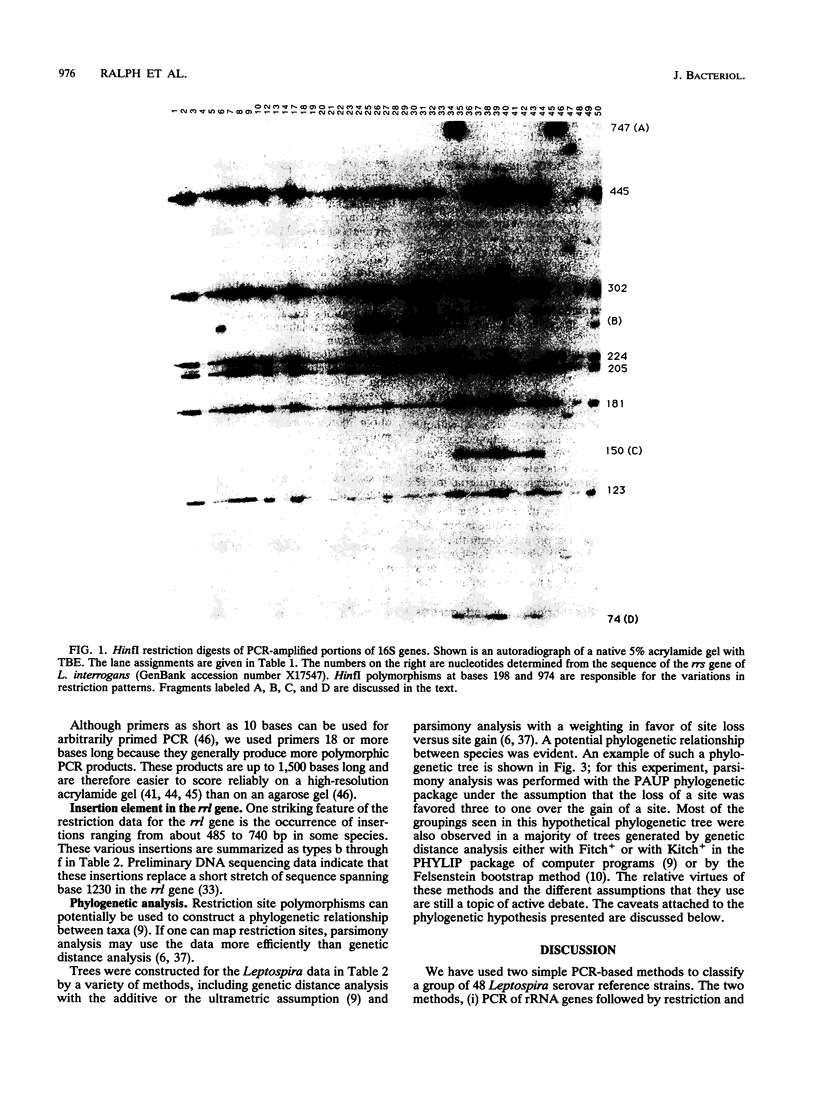
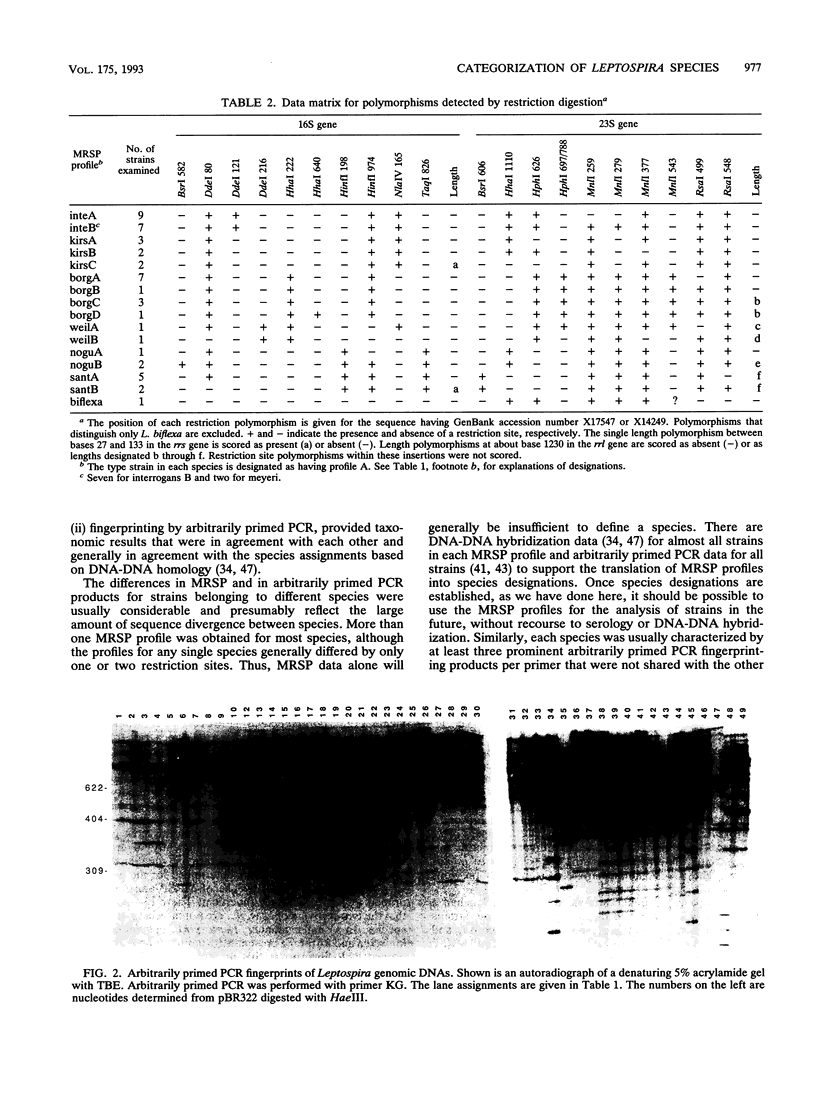
Reference strains from 48 selected serovars representing eight species of Leptospira were examined by two polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based strategies. First, mapped restriction site polymorphisms (MRSP) were examined in PCR products from portions of rrs (16S rRNA gene) and rrl (23S rRNA gene). Twenty MRSP and 2 length polymorphisms were used to group reference strains into 16 MRSP profiles. Species assignments were consistent with those obtained by a second method, genomic fingerprinting with arbitrarily primed PCR, in which strains within a species were characterized by many shared arbitrarily primed PCR products. The results of both of these methods were in general agreement with those of previous studies that used DNA-DNA relatedness and confirmed the high level of divergence among the recognized species of Leptospira. However, Leptospira meyeri serovar ranarum and evansi strains were indistinguishable from some strains of Leptospira interrogans sensu stricto. Intervening sequences of about 485 to 740 bp were located near base 1230 in rrl of some strains.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander A. D., Evans L. B., Baker M. F., Baker H. J., Ellison D., Marriapan M. Pathogenic leptospiras isolated from Malaysian surface waters. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jan;29(1):30–33. doi: 10.1128/am.29.1.30-33.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babudieri B. Systematics of a leptospira strain isolated from frog. Experientia. 1972 Oct 15;28(10):1252–1253. doi: 10.1007/BF01946207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgin A. B., Parodos K., Lane D. J., Pace N. R. The excision of intervening sequences from Salmonella 23S ribosomal RNA. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):405–414. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90592-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenstein J. Phylogenies from molecular sequences: inference and reliability. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:521–565. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.002513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Stackebrandt E., Hespell R. B., Gibson J., Maniloff J., Dyer T. A., Wolfe R. S., Balch W. E., Tanner R. S., Magrum L. J. The phylogeny of prokaryotes. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):457–463. doi: 10.1126/science.6771870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga M., Horie I., Mifuchi I. Nucleotide sequence of a 23S ribosomal RNA gene from Leptospira interrogans serovar canicola strain Moulton. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):2123–2123. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.2123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga M., Mifuchi I. Unique organization of Leptospira interrogans rRNA genes. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):5763–5767. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.5763-5767.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga M., Sohnaka M. Tandem repeat of the 23S and 5S ribosomal RNA genes in Borrelia burgdorferi, the etiological agent of Lyme disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Mar 31;183(3):952–957. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80282-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann J. L., Baril C., Bellenger E., Perolat P., Baranton G., Saint Girons I. Genome conservation in isolates of Leptospira interrogans. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7582–7588. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7582-7588.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann J. L., Bellenger E., Perolat P., Baranton G., Saint Girons I. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of NotI digests of leptospiral DNA: a new rapid method of serovar identification. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jul;30(7):1696–1702. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.7.1696-1702.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu D., Pan M. J., Zee Y. C., LeFebvre R. B. Unique ribosome structure of Leptospira interrogans is composed of four rRNA components. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3478–3480. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3478-3480.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. G., Ochman H., Hartl D. L. Molecular and evolutionary relationships among enteric bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Aug;137(8):1911–1921. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-8-1911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeFebvre R. B. DNA probe for detection of the Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo genotype hardjo-bovis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2236–2238. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2236-2238.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liesack W., Stackebrandt E. Evidence for unlinked rrn operons in the Planctomycete Pirellula marina. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):5025–5030. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.5025-5030.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. B., Wilton B. E., Robinson A. J. Identification of Leptospira serovars by restriction-endonuclease analysis. J Med Microbiol. 1981 Feb;14(1):163–166. doi: 10.1099/00222615-14-1-163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland M., Petersen C., Welsh J. Length polymorphisms in tRNA intergenic spacers detected by using the polymerase chain reaction can distinguish streptococcal strains and species. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jun;30(6):1499–1504. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.6.1499-1504.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mylvaganam S., Dennis P. P. Sequence heterogeneity between the two genes encoding 16S rRNA from the halophilic archaebacterium Haloarcula marismortui. Genetics. 1992 Mar;130(3):399–410. doi: 10.1093/genetics/130.3.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J. N., Armstrong C. H., Nielsen N. C. Relationship among selected Leptospira interrogans serogroups as determined by nucleic acid hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2724–2729. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2724-2729.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacciarini M. L., Savio M. L., Tagliabue S., Rossi C. Repetitive sequences cloned from Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo genotype hardjoprajitno and their application to serovar identification. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 May;30(5):1243–1249. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.5.1243-1249.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paster B. J., Dewhirst F. E., Weisburg W. G., Tordoff L. A., Fraser G. J., Hespell R. B., Stanton T. B., Zablen L., Mandelco L., Woese C. R. Phylogenetic analysis of the spirochetes. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(19):6101–6109. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.19.6101-6109.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérolat P., Grimont F., Regnault B., Grimont P. A., Fournié E., Thevenet H., Baranton G. rRNA gene restriction patterns of Leptospira: a molecular typing system. Res Microbiol. 1990 Feb;141(2):159–171. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(90)90025-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramadass P., Jarvis B. D., Corner R. J., Penny D., Marshall R. B. Genetic characterization of pathogenic Leptospira species by DNA hybridization. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;42(2):215–219. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-2-215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. J., Gazumyan A., Schwartz I. rRNA gene organization in the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3757–3765. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3757-3765.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm L. V., Charon N. W. Sensitivity of pathogenic and free-living Leptospira spp. to UV radiation and mitomycin C. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Mar;54(3):728–733. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.3.728-733.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Eys G. J., Gerritsen M. J., Korver H., Schoone G. J., Kroon C. C., Terpstra W. J. Characterization of serovars of the genus Leptospira by DNA hybridization with hardjobovis and icterohaemorrhagiae recombinant probes with special attention to serogroup sejroe. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 May;29(5):1042–1048. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.5.1042-1048.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilgalys R., Hester M. Rapid genetic identification and mapping of enzymatically amplified ribosomal DNA from several Cryptococcus species. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4238–4246. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4238-4246.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisburg W. G., Barns S. M., Pelletier D. A., Lane D. J. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):697–703. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.697-703.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J., McClelland M. Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7213–7218. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J., McClelland M. PCR-amplified length polymorphisms in tRNA intergenic spacers for categorizing staphylococci. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jun;6(12):1673–1680. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00892.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J., Petersen C., McClelland M. Polymorphisms generated by arbitrarily primed PCR in the mouse: application to strain identification and genetic mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 25;19(2):303–306. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.2.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J., Pretzman C., Postic D., Saint Girons I., Baranton G., McClelland M. Genomic fingerprinting by arbitrarily primed polymerase chain reaction resolves Borrelia burgdorferi into three distinct phyletic groups. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;42(3):370–377. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-3-370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Kubelik A. R., Livak K. J., Rafalski J. A., Tingey S. V. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6531–6535. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuerner R. L., Bolin C. A. Nucleic acid probe characterizes Leptospira interrogans serovars by restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Vet Microbiol. 1990 Sep;24(3-4):355–366. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(90)90183-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]