Abstract
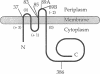
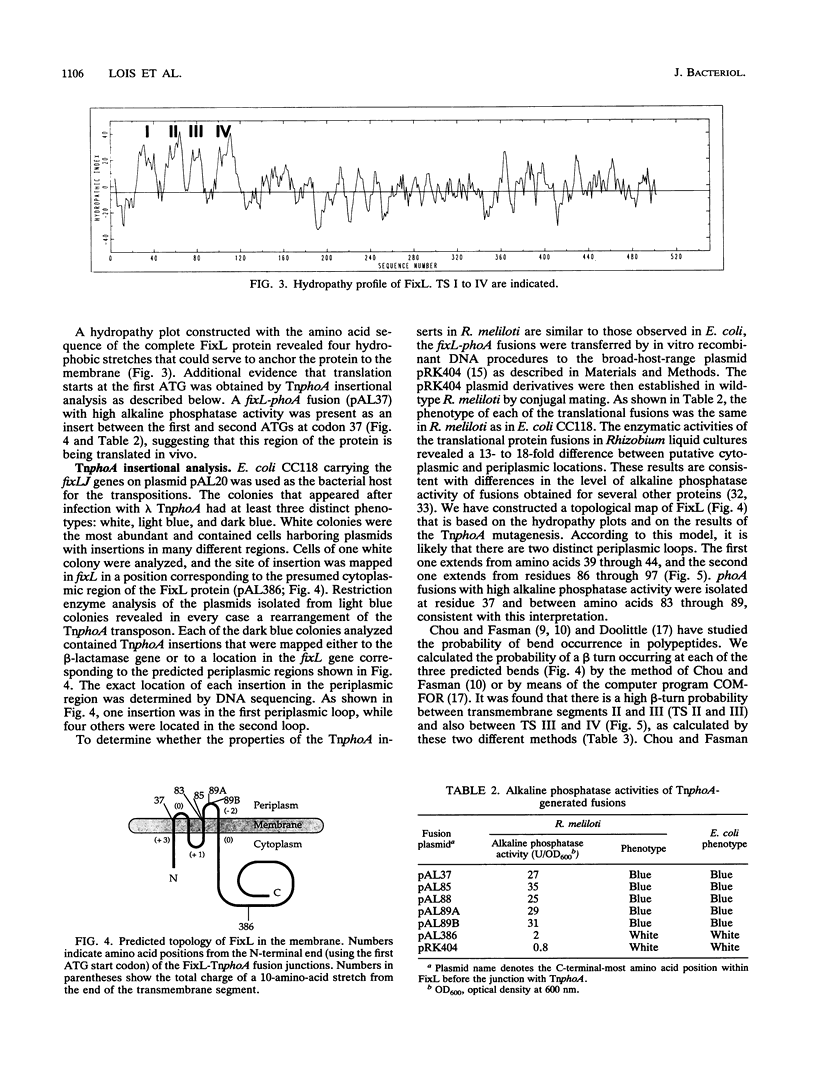
Regulation of nitrogen fixation genes in Rhizobium meliloti is mediated by two proteins, FixL and FixJ, in response to oxygen availability. FixL is an oxygen-binding hemoprotein with kinase and phosphatase activities that is thought to sense oxygen levels directly and to transmit this signal to FixJ via phosphorylation-dephosphorylation reactions. FixJ controls the expression of other regulatory genes, including nifA, that regulate the transcription of genes required for symbiotic nitrogen fixation. We have been studying the structural and functional features of FixL that are required for oxygen sensing. We constructed mutant derivatives and confirmed that FixL consists of 505 amino acids instead of 464, as originally reported. Hydropathy plots of the full-length protein, together with TnphoA insertional analysis, lead us to propose that FixL is likely to be a polytopic integral membrane protein containing four membrane-spanning segments. We have also constructed an N-terminal deletion of the FixL protein whose in vivo activity indicates that the hydrophobic membrane-spanning regions are not absolutely required for oxygen sensing in vivo. We also report that FixL shares homology in its N terminus with other sensor proteins, including KinA from Bacillus subtilis and NtrB from Bradyrhizobium parasponia. The region of homology comprises a 70-amino-acid residue stretch that is also conserved in two oxygenases, P-450 and isopenicillin synthase.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin T. O., Berends T., Bunch T. A., Holzman T. F., Rausch S. K., Shamansky L., Treat M. L., Ziegler M. M. Cloning of the luciferase structural genes from Vibrio harveyi and expression of bioluminescence in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 31;23(16):3663–3667. doi: 10.1021/bi00311a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batut J., Daveran-Mingot M. L., David M., Jacobs J., Garnerone A. M., Kahn D. fixK, a gene homologous with fnr and crp from Escherichia coli, regulates nitrogen fixation genes both positively and negatively in Rhizobium meliloti. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1279–1286. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03502.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Better M., Ditta G., Helinski D. R. Deletion analysis of Rhizobium meliloti symbiotic promoters. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2419–2424. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03950.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd D., Beckwith J. Positively charged amino acid residues can act as topogenic determinants in membrane proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9446–9450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd D., Beckwith J. The role of charged amino acids in the localization of secreted and membrane proteins. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1031–1033. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90378-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brickman E., Beckwith J. Analysis of the regulation of Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase synthesis using deletions and phi80 transducing phages. J Mol Biol. 1975 Aug 5;96(2):307–316. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90350-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burbulys D., Trach K. A., Hoch J. A. Initiation of sporulation in B. subtilis is controlled by a multicomponent phosphorelay. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):545–552. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90238-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):222–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G., Shiffman D., Mevarech M., Aharonowitz Y. Microbial isopenicillin N synthase genes: structure, function, diversity and evolution. Trends Biotechnol. 1990 Apr;8(4):105–111. doi: 10.1016/0167-7799(90)90148-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin D., Ditta G., Helinski D. R. Clustering of nitrogen fixation (nif) genes in Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):221–228. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.221-228.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David M., Daveran M. L., Batut J., Dedieu A., Domergue O., Ghai J., Hertig C., Boistard P., Kahn D. Cascade regulation of nif gene expression in Rhizobium meliloti. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):671–683. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Schmidhauser T., Yakobson E., Lu P., Liang X. W., Finlay D. R., Guiney D., Helinski D. R. Plasmids related to the broad host range vector, pRK290, useful for gene cloning and for monitoring gene expression. Plasmid. 1985 Mar;13(2):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Virts E., Palomares A., Kim C. H. The nifA gene of Rhizobium meliloti is oxygen regulated. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3217–3223. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3217-3223.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forst S., Comeau D., Norioka S., Inouye M. Localization and membrane topology of EnvZ, a protein involved in osmoregulation of OmpF and OmpC in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16433–16438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilles-Gonzalez M. A., Ditta G. S., Helinski D. R. A haemoprotein with kinase activity encoded by the oxygen sensor of Rhizobium meliloti. Nature. 1991 Mar 14;350(6314):170–172. doi: 10.1038/350170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Vilbois F., Hardwick J. P., McBride O. W., Nebert D. W., Gelboin H. V., Meyer U. A. Human debrisoquine 4-hydroxylase (P450IID1): cDNA and deduced amino acid sequence and assignment of the CYP2D locus to chromosome 22. Genomics. 1988 Feb;2(2):174–179. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R., Aricò B., Rappuoli R. Families of bacterial signal-transducing proteins. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Nov;3(11):1661–1667. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00152.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez C., Barondess J., Manoil C., Beckwith J. The use of transposon TnphoA to detect genes for cell envelope proteins subject to a common regulatory stimulus. Analysis of osmotically regulated genes in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 20;195(2):289–297. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90650-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heijne G. The distribution of positively charged residues in bacterial inner membrane proteins correlates with the trans-membrane topology. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):3021–3027. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04601.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn M., Ow D., Sauer B., Rabinowitz A., Calendar R. Genetic analysis of bacteriophage P4 using P4-plasmid ColE1 hybrids. Mol Gen Genet. 1980 Feb;177(3):399–412. doi: 10.1007/BF00271478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long S., McCune S., Walker G. C. Symbiotic loci of Rhizobium meliloti identified by random TnphoA mutagenesis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4257–4265. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4257-4265.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino K., Shinagawa H., Amemura M., Nakata A. Nucleotide sequence of the phoR gene, a regulatory gene for the phosphate regulon of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 5;192(3):549–556. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90275-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. A genetic approach to analyzing membrane protein topology. Science. 1986 Sep 26;233(4771):1403–1408. doi: 10.1126/science.3529391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. TnphoA: a transposon probe for protein export signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8129–8133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Boyd D., Beckwith J. Molecular genetic analysis of membrane protein topology. Trends Genet. 1988 Aug;4(8):223–226. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90154-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehdi H., Ono E., Gupta K. C. Initiation of translation at CUG, GUG, and ACG codons in mammalian cells. Gene. 1990 Jul 16;91(2):173–178. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90085-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchers L. S., Regensburg-Tuïnk T. J., Bourret R. B., Sedee N. J., Schilperoort R. A., Hooykaas P. J. Membrane topology and functional analysis of the sensory protein VirA of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):1919–1925. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03595.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monson E. K., Weinstein M., Ditta G. S., Helinski D. R. The FixL protein of Rhizobium meliloti can be separated into a heme-binding oxygen-sensing domain and a functional C-terminal kinase domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4280–4284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutoh N., Simon M. I. Nucleotide sequence corresponding to five chemotaxis genes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jan;165(1):161–166. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.1.161-166.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nixon B. T., Ronson C. W., Ausubel F. M. Two-component regulatory systems responsive to environmental stimuli share strongly conserved domains with the nitrogen assimilation regulatory genes ntrB and ntrC. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7850–7854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Ninfa A. J., Stock A. M. Protein phosphorylation and regulation of adaptive responses in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):450–490. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.450-490.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szeto W. W., Zimmerman J. L., Sundaresan V., Ausubel F. M. A Rhizobium meliloti symbiotic regulatory gene. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1035–1043. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virts E. L., Stanfield S. W., Helinski D. R., Ditta G. S. Common regulatory elements control symbiotic and microaerobic induction of nifA in Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3062–3065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]