Abstract
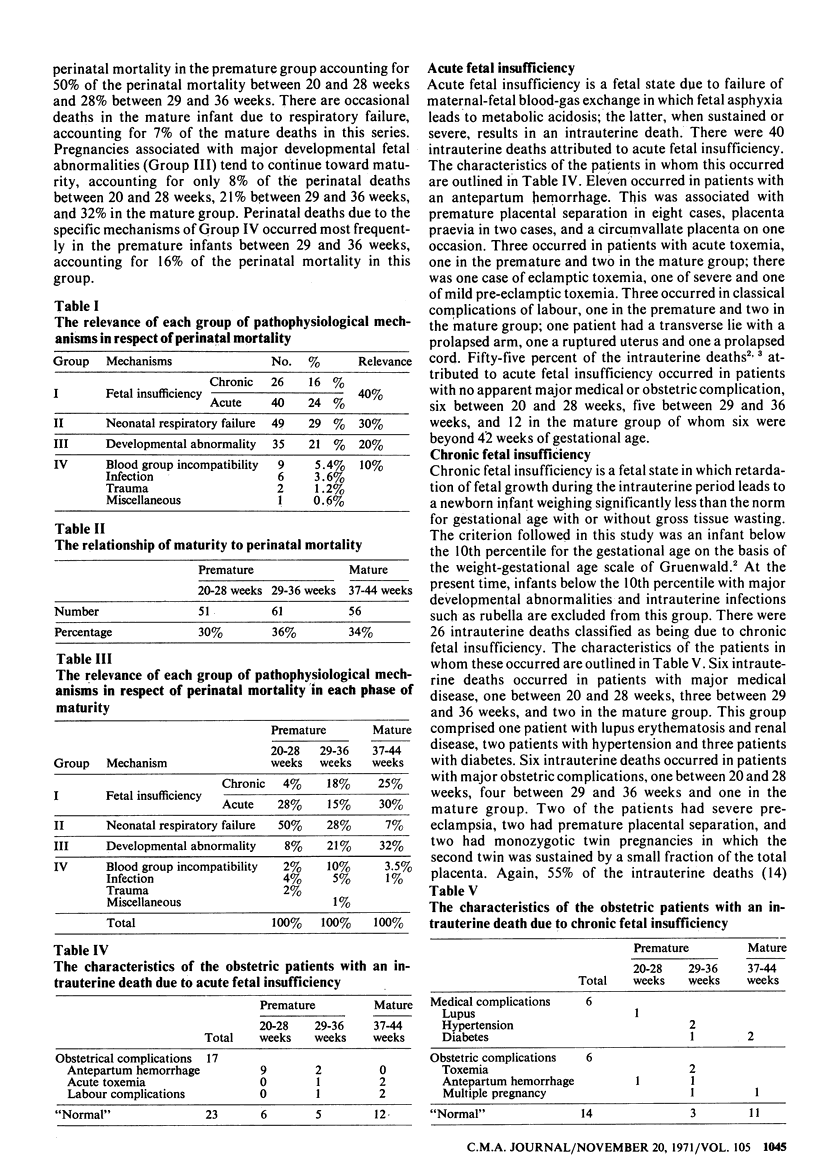
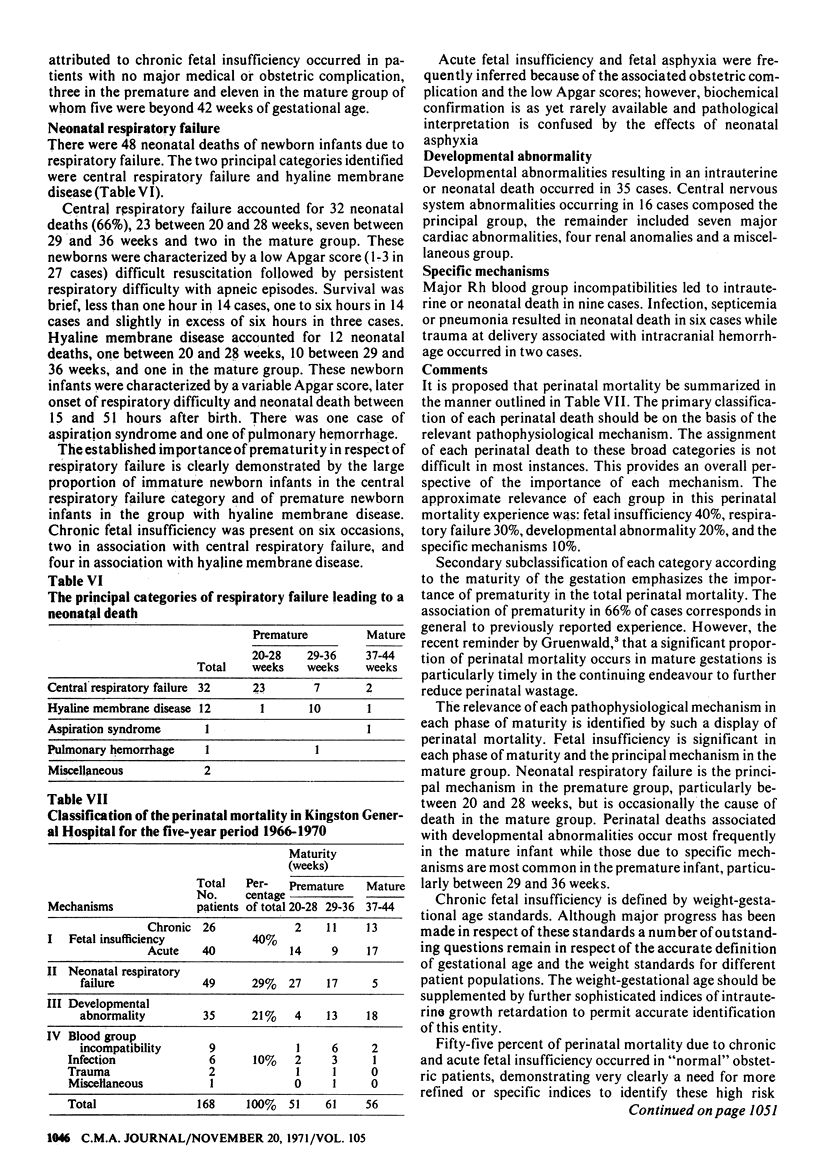
A classification based upon pathophysiological mechanisms has been applied to perinatal mortality. The approximate relevance of each group was: fetal insufficiency 40%, respiratory failure 30%, developmental abnormality 20%, and the specific mechanisms 10%. Secondary subclassification of each category according to the maturity of the gestation emphasizes the importance of prematurity in the total perinatal mortality (66%) and the relevance of each pathophysiological mechanism in each phase of maturity. The principal mechanism in the mature group is fetal insufficiency and in the premature group, particularly between 20 and 28 weeks, it is neonatal respiratory failure. Perinatal death due to developmental abnormalities occurs most frequently in the mature infant and due to specific mechanisms in the premature infant, particularly between 29 and 36 weeks. It is suggested that greater emphasis should be placed on perinatal mortality rather than the separate consideration of stillbirth and neonatal mortality.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gruenwald P. Growth of the human fetus. I. Normal growth and its variation. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1966 Apr 15;94(8):1112–1119. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(66)90774-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low J. A., Boston R. W., Cervenko F. W. A clinical classification of the mechanisms of perinatal wastage. Can Med Assoc J. 1970 Feb 28;102(4):365–368. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


