Abstract
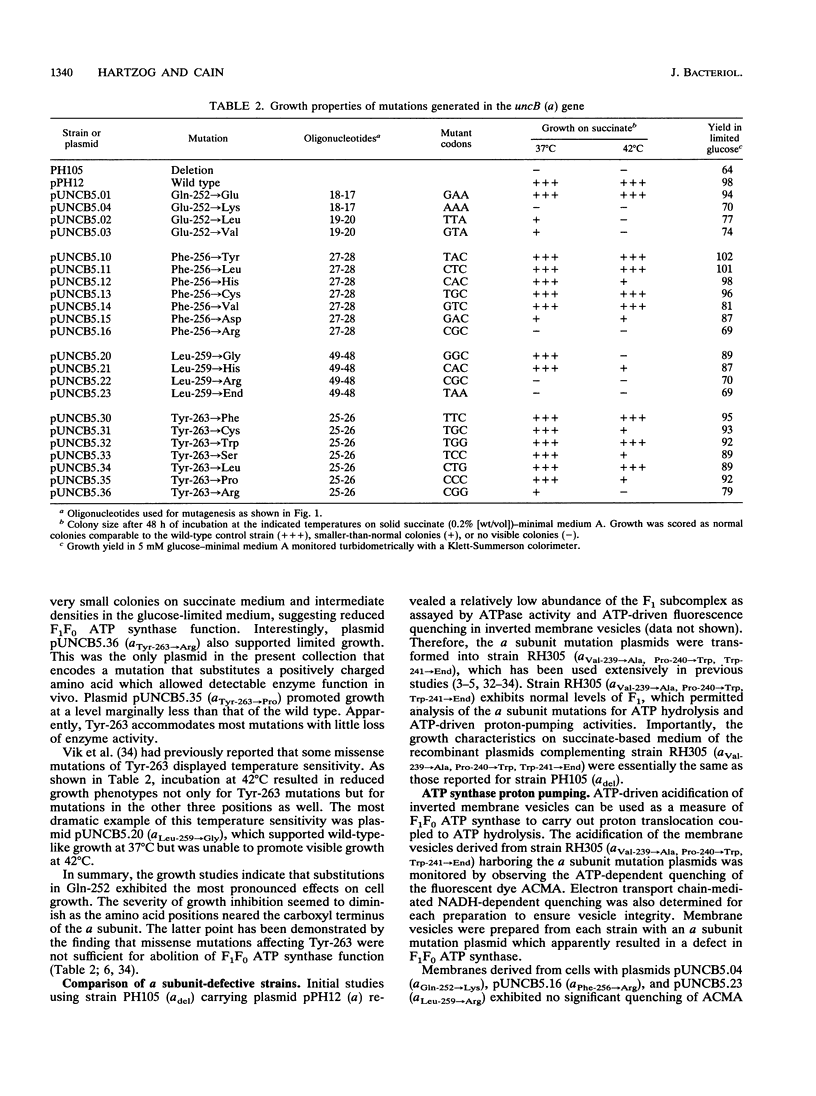
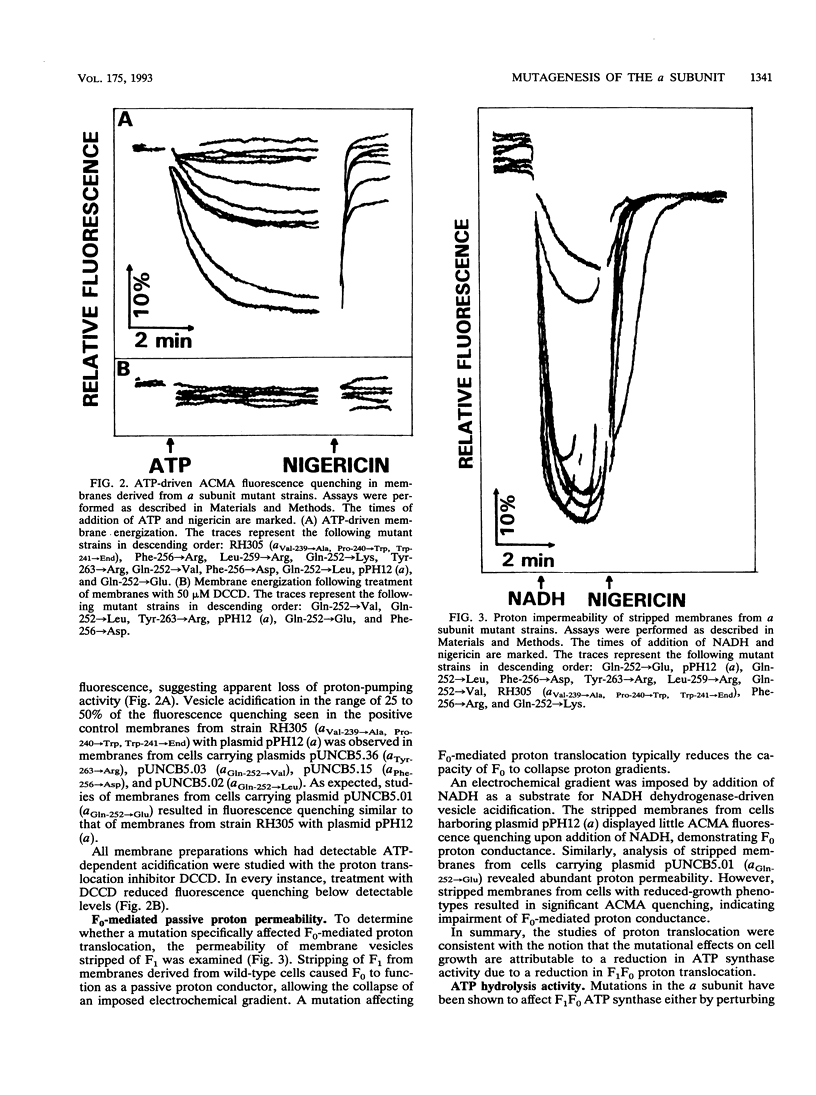
The a subunit of F1F0 ATP synthase contains a highly conserved region near its carboxyl terminus which is thought to be important in proton translocation. Cassette site-directed mutagenesis was used to study the roles of four conserved amino acids Gln-252, Phe-256, Leu-259, and Tyr-263. Substitution of basic amino acids at each of these four sites resulted in marked decreases in enzyme function. Cells carrying a subunit mutations Gln-252-->Lys, Phe-256-->Arg, Leu-259-->Arg, and Tyr-263-->Arg all displayed growth characteristics suggesting substantial loss of ATP synthase function. Studies of both ATP-driven proton pumping and proton permeability of stripped membranes indicated that proton translocation through F0 was affected by the mutations. Other mutations, such as the Phe-256-->Asp mutation, also resulted in reduced enzyme activity. However, more conservative amino acid substitutions generated at these same four positions produced minimal losses of F1F0 ATP synthase. The effects of mutations and, hence, the relative importance of the amino acids for enzyme function appeared to decrease with proximity to the carboxyl terminus of the a subunit. The data are most consistent with the hypothesis that the region between Gln-252 and Tyr-263 of the a subunit has an important structural role in F1F0 ATP synthase.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aris J. P., Klionsky D. J., Simoni R. D. The Fo subunits of the Escherichia coli F1Fo-ATP synthase are sufficient to form a functional proton pore. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11207–11215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cain B. D., Simoni R. D. Impaired proton conductivity resulting from mutations in the a subunit of F1F0 ATPase in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10043–10050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cain B. D., Simoni R. D. Interaction between Glu-219 and His-245 within the a subunit of F1F0-ATPase in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6606–6612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cain B. D., Simoni R. D. Proton translocation by the F1F0ATPase of Escherichia coli. Mutagenic analysis of the a subunit. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3292–3300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eya S., Maeda M., Futai M. Role of the carboxyl terminal region of H(+)-ATPase (F0F1) a subunit from Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Jan;284(1):71–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90265-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eya S., Noumi T., Maeda M., Futai M. Intrinsic membrane sector (Fo) of H+-ATPase (FoF1) from Escherichia coli. Mutations in the alpha subunit give Fo with impaired proton translocation and F1 binding. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10056–10062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fillingame R. H. Subunit c of F1F0 ATP synthase: structure and role in transmembrane energy transduction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jul 17;1101(2):240–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futai M., Noumi T., Maeda M. ATP synthase (H+-ATPase): results by combined biochemical and molecular biological approaches. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:111–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.000551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garger S. J., Griffith O. M., Grill L. K. Rapid purification of plasmid DNA by a single centrifugation in a two-step cesium chloride-ethidium bromide gradient. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Dec 28;117(3):835–842. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91672-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton C. M., Aldea M., Washburn B. K., Babitzke P., Kushner S. R. New method for generating deletions and gene replacements in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4617–4622. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4617-4622.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermolin J., Fillingame R. H. H+-ATPase activity of Escherichia coli F1F0 is blocked after reaction of dicyclohexylcarbodiimide with a single proteolipid (subunit c) of the F0 complex. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):3896–3903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howitt S. M., Gibson F., Cox G. B. The proton pore of the F0F1-ATPase of Escherichia coli: Ser-206 is not required for proton translocation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Oct 26;936(1):74–80. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(88)90253-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humbert R., Brusilow W. S., Gunsalus R. P., Klionsky D. J., Simoni R. D. Escherichia coli mutants defective in the uncH gene. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):416–422. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.416-422.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klionsky D. J., Brusilow W. S., Simoni R. D. Assembly of a functional F0 of the proton-translocating ATPase of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):10136–10143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumamoto C. A., Simoni R. D. Genetic evidence for interaction between the a and b subunits of the F0 portion of the Escherichia coli proton translocating ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10037–10042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis M. J., Chang J. A., Simoni R. D. A topological analysis of subunit alpha from Escherichia coli F1F0-ATP synthase predicts eight transmembrane segments. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10541–10550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightowlers R. N., Howitt S. M., Hatch L., Gibson F., Cox G. B. The proton pore in the Escherichia coli F0F1-ATPase: a requirement for arginine at position 210 of the a-subunit. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Dec 17;894(3):399–406. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(87)90118-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightowlers R. N., Howitt S. M., Hatch L., Gibson F., Cox G. The proton pore in the Escherichia coli F0F1-ATPase: substitution of glutamate by glutamine at position 219 of the alpha-subunit prevents F0-mediated proton permeability. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Apr 22;933(2):241–248. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(88)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick K. A., Cain B. D. Targeted mutagenesis of the b subunit of F1F0 ATP synthase in Escherichia coli: Glu-77 through Gln-85. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(22):7240–7248. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.22.7240-7248.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paule C. R., Fillingame R. H. Mutations in three of the putative transmembrane helices of subunit a of the Escherichia coli F1F0-ATPase disrupt ATP-driven proton translocation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Oct;274(1):270–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90439-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter A. C., Kumamoto C., Aldape K., Simoni R. D. Role of the b subunit of the Escherichia coli proton-translocating ATPase. A mutagenic analysis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):8182–8187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider E., Altendorf K. All three subunits are required for the reconstitution of an active proton channel (F0) of Escherichia coli ATP synthase (F1F0). EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):515–518. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03658.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior A. E. The proton-translocating ATPase of Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1990;19:7–41. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.19.060190.000255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon K. A., Brusilow W. S. Effect of an uncE ribosome-binding site mutation on the synthesis and assembly of the Escherichia coli proton-translocating ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5402–5407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vik S. B., Cain B. D., Chun K. T., Simoni R. D. Mutagenesis of the alpha subunit of the F1Fo-ATPase from Escherichia coli. Mutations at Glu-196, Pro-190, and Ser-199. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6599–6605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vik S. B., Lee D., Curtis C. E., Nguyen L. T. Mutagenesis of the a subunit of the F1F0-ATP synthase from Escherichia coli in the region of Asn-192. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Oct;282(1):125–131. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90095-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vik S. B., Lee D., Marshall P. A. Temperature-sensitive mutations at the carboxy terminus of the alpha subunit of the Escherichia coli F1F0 ATP synthase. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4544–4548. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4544-4548.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Gay N. J. The unc operon. Nucleotide sequence, regulation and structure of ATP-synthase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 6;768(2):164–200. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(84)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


