Abstract
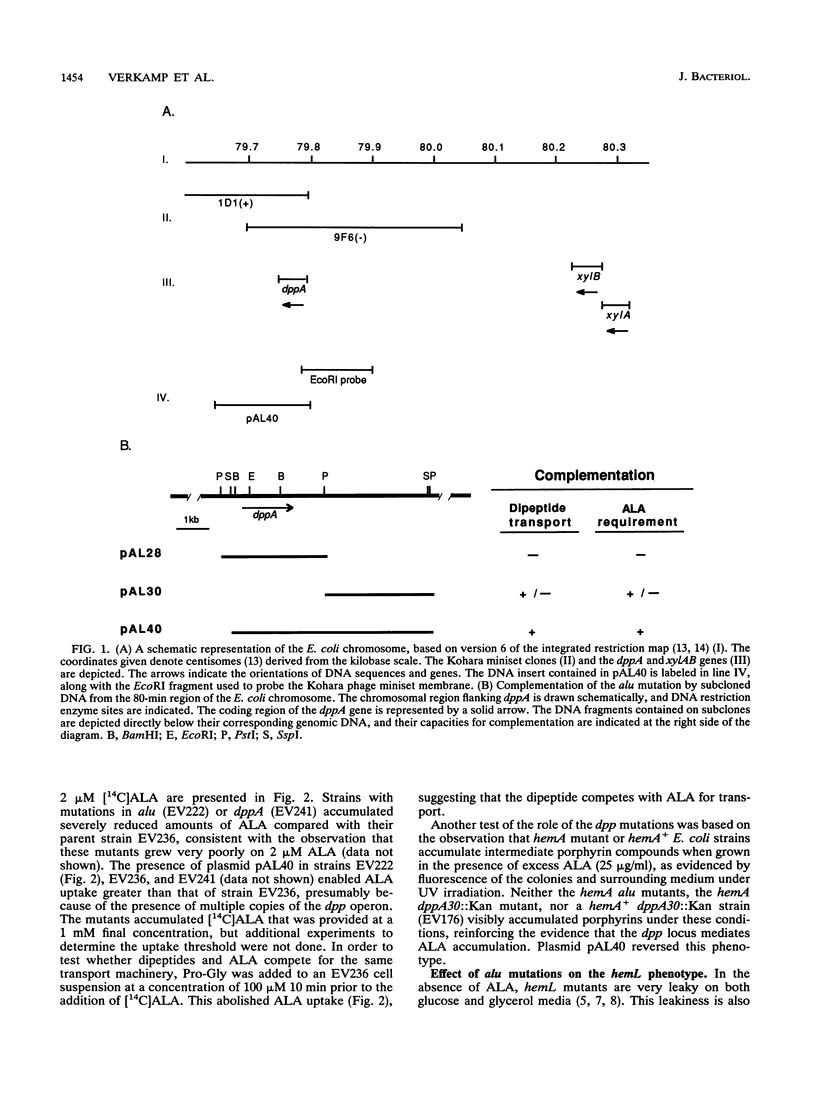
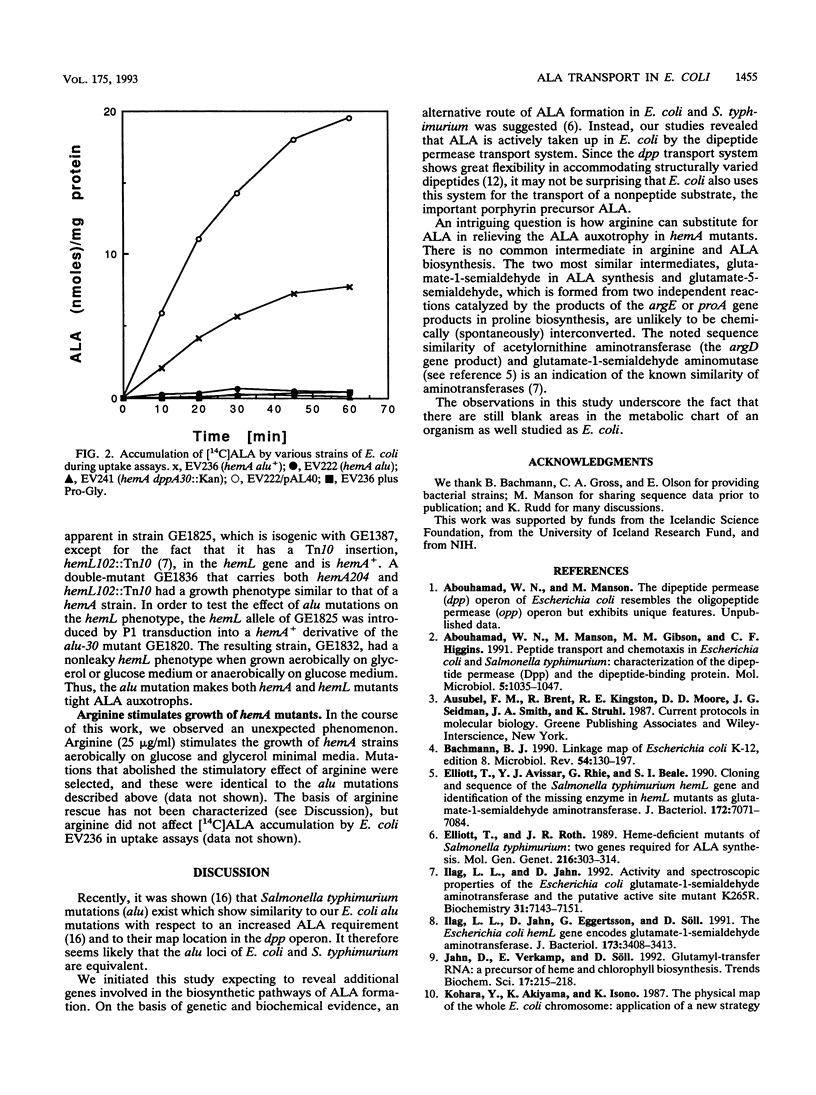
In a genetic screen designed to generate Escherichia coli strains completely devoid of the heme precursor 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA), we isolated a class of mutants which were defective for exogenous ALA uptake. The mutations, designated alu (ALA uptake), mapped to the 80-min region of the E. coli chromosome. They were complemented by a recombinant plasmid containing the dpp operon, which encodes a dipeptide permease transport system. Alu mutants displayed a severe reduction in ALA import, as did a strain with a chromosomal insertion in the first gene of the dpp operon. A recognized substrate of Dpp transport, prolyl-glycine, effectively competed with ALA for uptake. E. coli strains defective in ALA biosynthesis (hemA or hemL) require exogenous ALA to achieve wild-type growth but show limited aerobic and anaerobic growth in the absence of ALA. The presence of an alu or dpp mutation in hemA or hemL strains abolishes growth in the absence of ALA and requires increased levels of ALA for normal growth. We conclude that the alu mutations are within the dpp operon and that the dipeptide transport system mediates uptake of the important metabolite ALA.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abouhamad W. N., Manson M., Gibson M. M., Higgins C. F. Peptide transport and chemotaxis in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: characterization of the dipeptide permease (Dpp) and the dipeptide-binding protein. Mol Microbiol. 1991 May;5(5):1035–1047. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01876.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 8. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jun;54(2):130–197. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.2.130-197.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott T., Avissar Y. J., Rhie G. E., Beale S. I. Cloning and sequence of the Salmonella typhimurium hemL gene and identification of the missing enzyme in hemL mutants as glutamate-1-semialdehyde aminotransferase. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7071–7084. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7071-7084.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott T., Roth J. R. Heme-deficient mutants of Salmonella typhimurium: two genes required for ALA synthesis. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Apr;216(2-3):303–314. doi: 10.1007/BF00334369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilag L. L., Jahn D. Activity and spectroscopic properties of the Escherichia coli glutamate 1-semialdehyde aminotransferase and the putative active site mutant K265R. Biochemistry. 1992 Aug 11;31(31):7143–7151. doi: 10.1021/bi00146a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilag L. L., Jahn D., Eggertsson G., Söll D. The Escherichia coli hemL gene encodes glutamate 1-semialdehyde aminotransferase. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3408–3413. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3408-3413.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn D., Verkamp E., Söll D. Glutamyl-transfer RNA: a precursor of heme and chlorophyll biosynthesis. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Jun;17(6):215–218. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90380-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. R., Dunyak D. S., Jurss L. M., Poorman R. A. Identification and characterization of dppA, an Escherichia coli gene encoding a periplasmic dipeptide transport protein. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(1):234–244. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.1.234-244.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd K. E., Miller W., Werner C., Ostell J., Tolstoshev C., Satterfield S. G. Mapping sequenced E.coli genes by computer: software, strategies and examples. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 11;19(3):637–647. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.3.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkamp E., Chelm B. K. Isolation, nucleotide sequence, and preliminary characterization of the Escherichia coli K-12 hemA gene. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4728–4735. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4728-4735.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu K., Delling J., Elliott T. The genes required for heme synthesis in Salmonella typhimurium include those encoding alternative functions for aerobic and anaerobic coproporphyrinogen oxidation. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(12):3953–3963. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.12.3953-3963.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



