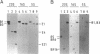Abstract
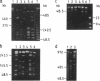
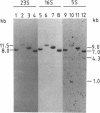
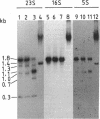
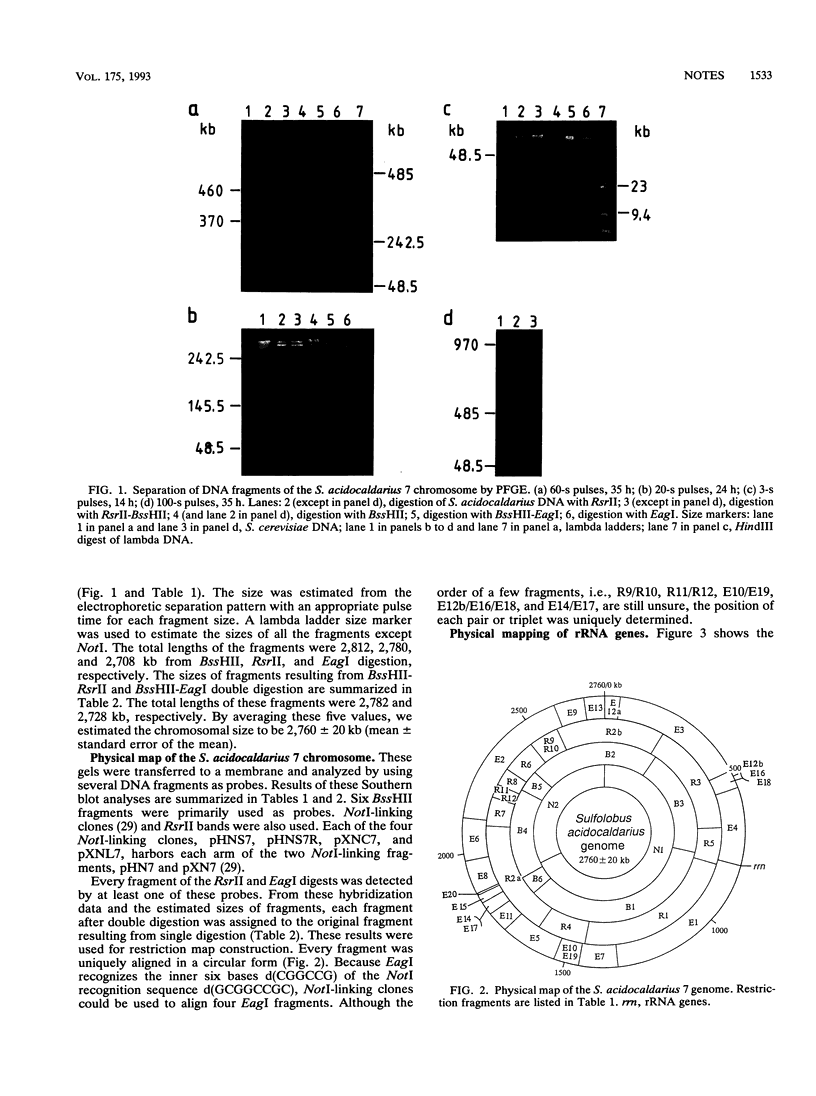
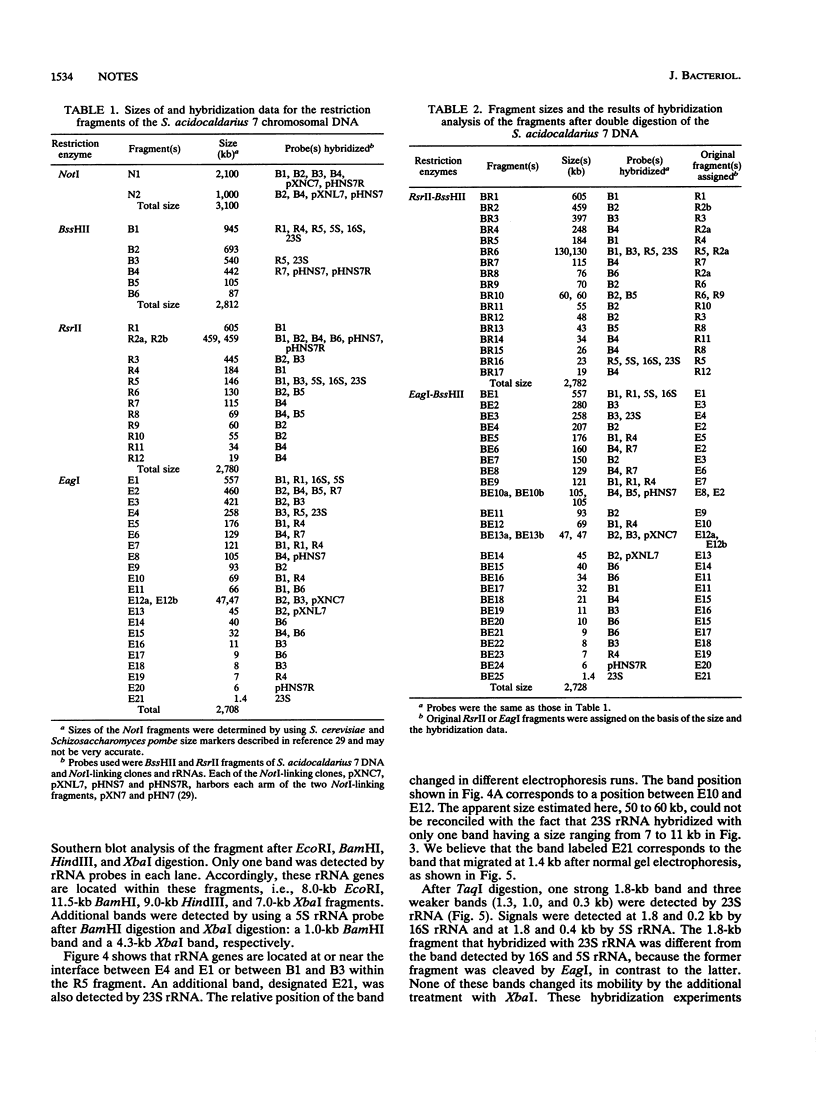
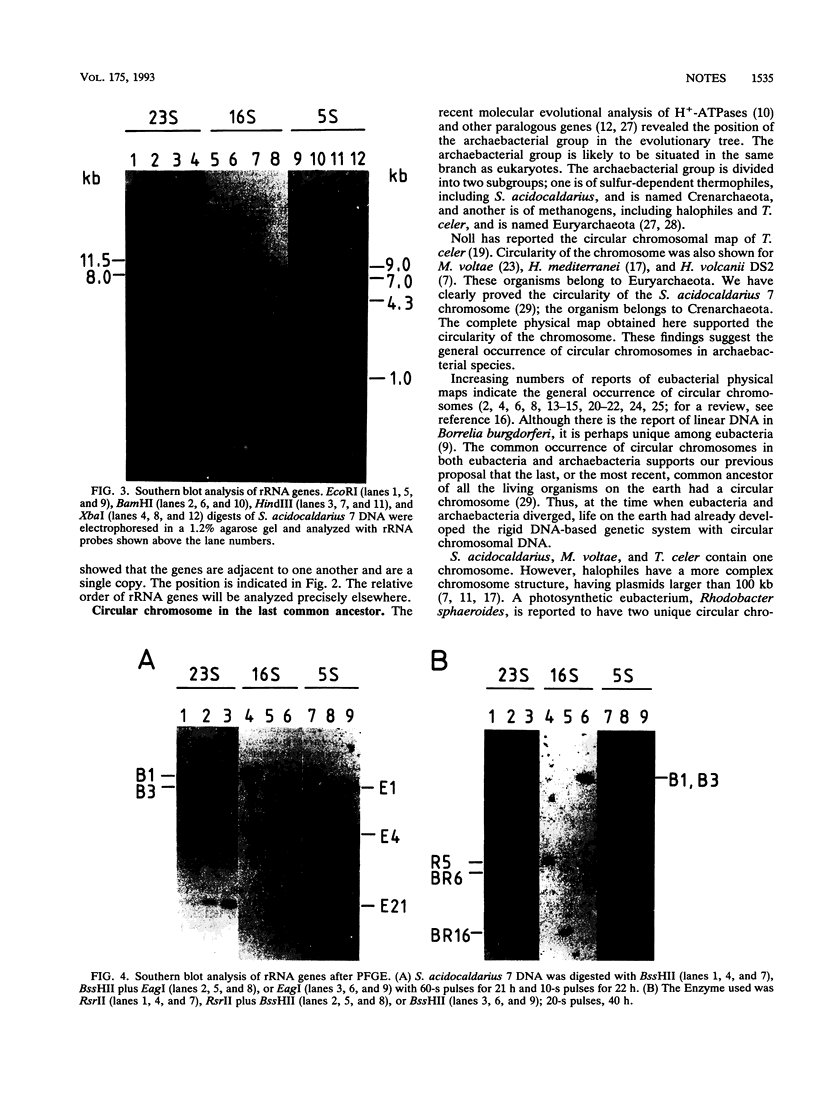
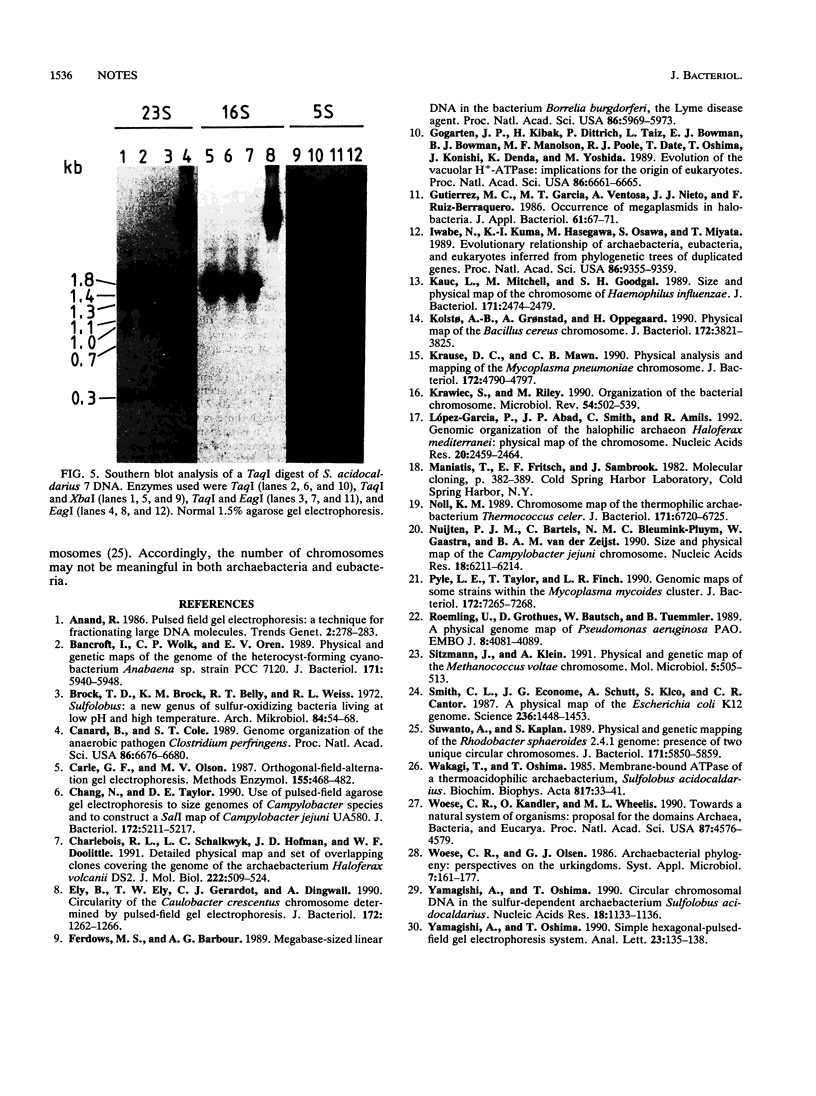
A chromosomal map of the sulfur-dependent thermoacidophilic archaebacterium Sulfolobus acidocaldarius 7 was constructed with four restriction enzymes: NotI, BssHII, RsrII, and EagI. The map indicated that the chromosome is a single circular DNA of 2,760 +/- 20 kb (mean +/- standard error of the mean). rRNA genes were also mapped. They were located at one site in the genome.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bancroft I., Wolk C. P., Oren E. V. Physical and genetic maps of the genome of the heterocyst-forming cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):5940–5948. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.5940-5948.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. D., Brock K. M., Belly R. T., Weiss R. L. Sulfolobus: a new genus of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria living at low pH and high temperature. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;84(1):54–68. doi: 10.1007/BF00408082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canard B., Cole S. T. Genome organization of the anaerobic pathogen Clostridium perfringens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6676–6680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Orthogonal-field-alternation gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:468–482. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55031-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang N., Taylor D. E. Use of pulsed-field agarose gel electrophoresis to size genomes of Campylobacter species and to construct a SalI map of Campylobacter jejuni UA580. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5211–5217. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5211-5217.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlebois R. L., Schalkwyk L. C., Hofman J. D., Doolittle W. F. Detailed physical map and set of overlapping clones covering the genome of the archaebacterium Haloferax volcanii DS2. J Mol Biol. 1991 Dec 5;222(3):509–524. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90493-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely B., Ely T. W., Gerardot C. J., Dingwall A. Circularity of the Caulobacter crescentus chromosome determined by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Mar;172(3):1262–1266. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.3.1262-1266.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferdows M. S., Barbour A. G. Megabase-sized linear DNA in the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, the Lyme disease agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5969–5973. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogarten J. P., Kibak H., Dittrich P., Taiz L., Bowman E. J., Bowman B. J., Manolson M. F., Poole R. J., Date T., Oshima T. Evolution of the vacuolar H+-ATPase: implications for the origin of eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6661–6665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwabe N., Kuma K., Hasegawa M., Osawa S., Miyata T. Evolutionary relationship of archaebacteria, eubacteria, and eukaryotes inferred from phylogenetic trees of duplicated genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9355–9359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauc L., Mitchell M., Goodgal S. H. Size and physical map of the chromosome of Haemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2474–2479. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2474-2479.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolstø A. B., Grønstad A., Oppegaard H. Physical map of the Bacillus cereus chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3821–3825. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3821-3825.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause D. C., Mawn C. B. Physical analysis and mapping of the Mycoplasma pneumoniae chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):4790–4797. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.4790-4797.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawiec S., Riley M. Organization of the bacterial chromosome. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):502–539. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.4.502-539.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-García P., Abad J. P., Smith C., Amils R. Genomic organization of the halophilic archaeon Haloferax mediterranei: physical map of the chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 25;20(10):2459–2464. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.10.2459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll K. M. Chromosome map of the thermophilic archaebacterium Thermococcus celer. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6720–6725. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6720-6725.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuijten P. J., Bartels C., Bleumink-Pluym N. M., Gaastra W., van der Zeijst B. A. Size and physical map of the Campylobacter jejuni chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6211–6214. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyle L. E., Taylor T., Finch L. R. Genomic maps of some strains within the Mycoplasma mycoides cluster. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7265–7268. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7265-7268.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Römling U., Grothues D., Bautsch W., Tümmler B. A physical genome map of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4081–4089. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08592.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitzmann J., Klein A. Physical and genetic map of the Methanococcus voltae chromosome. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):505–513. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02134.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Econome J. G., Schutt A., Klco S., Cantor C. R. A physical map of the Escherichia coli K12 genome. Science. 1987 Jun 12;236(4807):1448–1453. doi: 10.1126/science.3296194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suwanto A., Kaplan S. Physical and genetic mapping of the Rhodobacter sphaeroides 2.4.1 genome: presence of two unique circular chromosomes. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):5850–5859. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.5850-5859.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakagi T., Oshima T. Membrane-bound ATPase of a thermoacidophilic archaebacterium, Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jul 11;817(1):33–41. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90065-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Kandler O., Wheelis M. L. Towards a natural system of organisms: proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4576–4579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Olsen G. J. Archaebacterial phylogeny: perspectives on the urkingdoms. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1986;7:161–177. doi: 10.1016/s0723-2020(86)80001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagishi A., Oshima T. Circular chromosomal DNA in the sulfur-dependent archaebacterium Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 11;18(5):1133–1136. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.5.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]