Full text
PDF















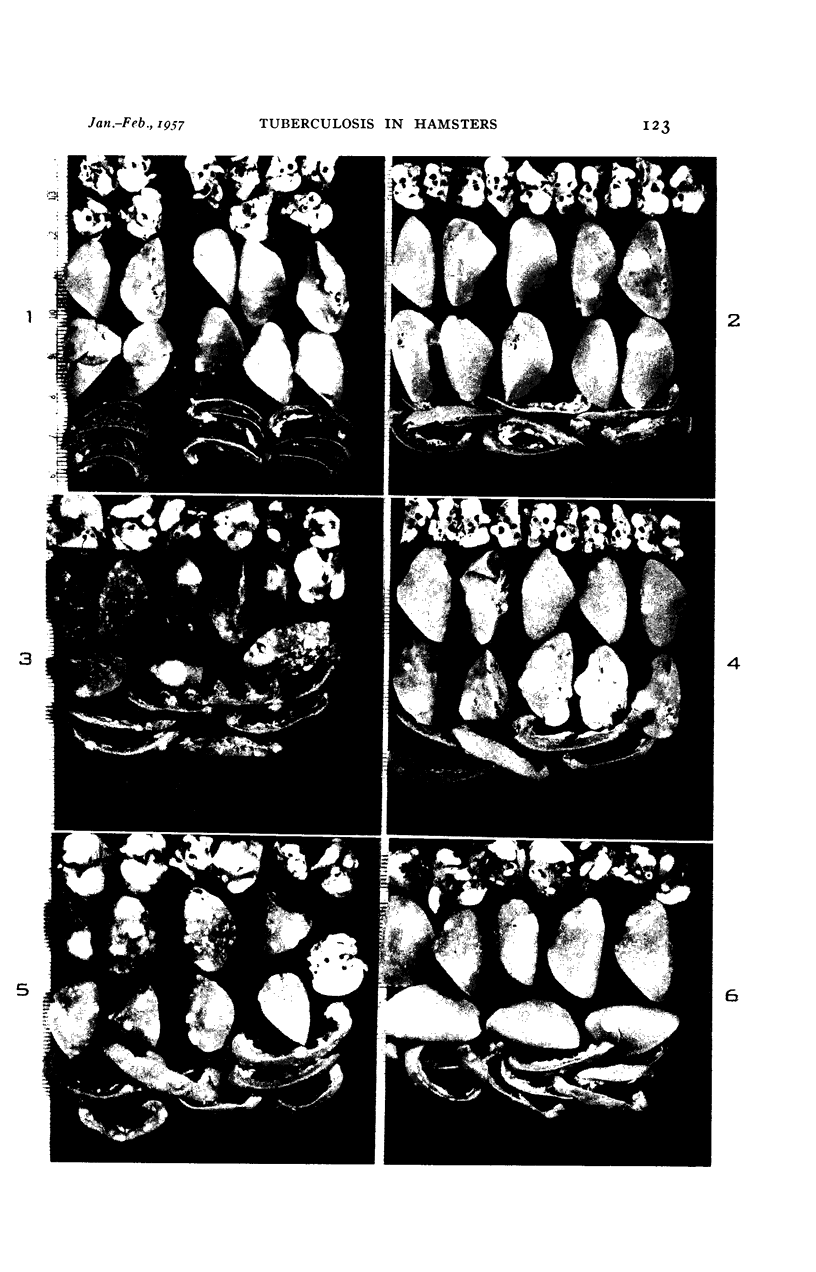

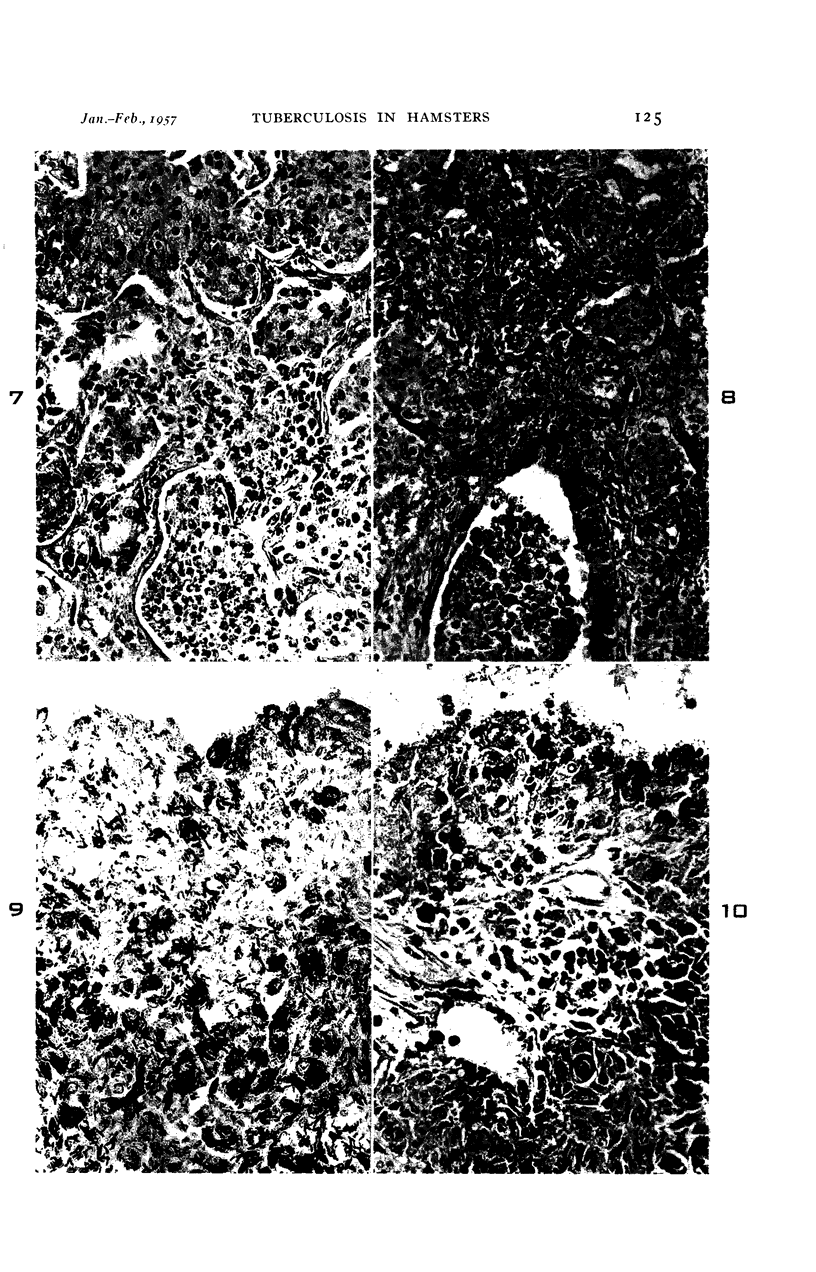

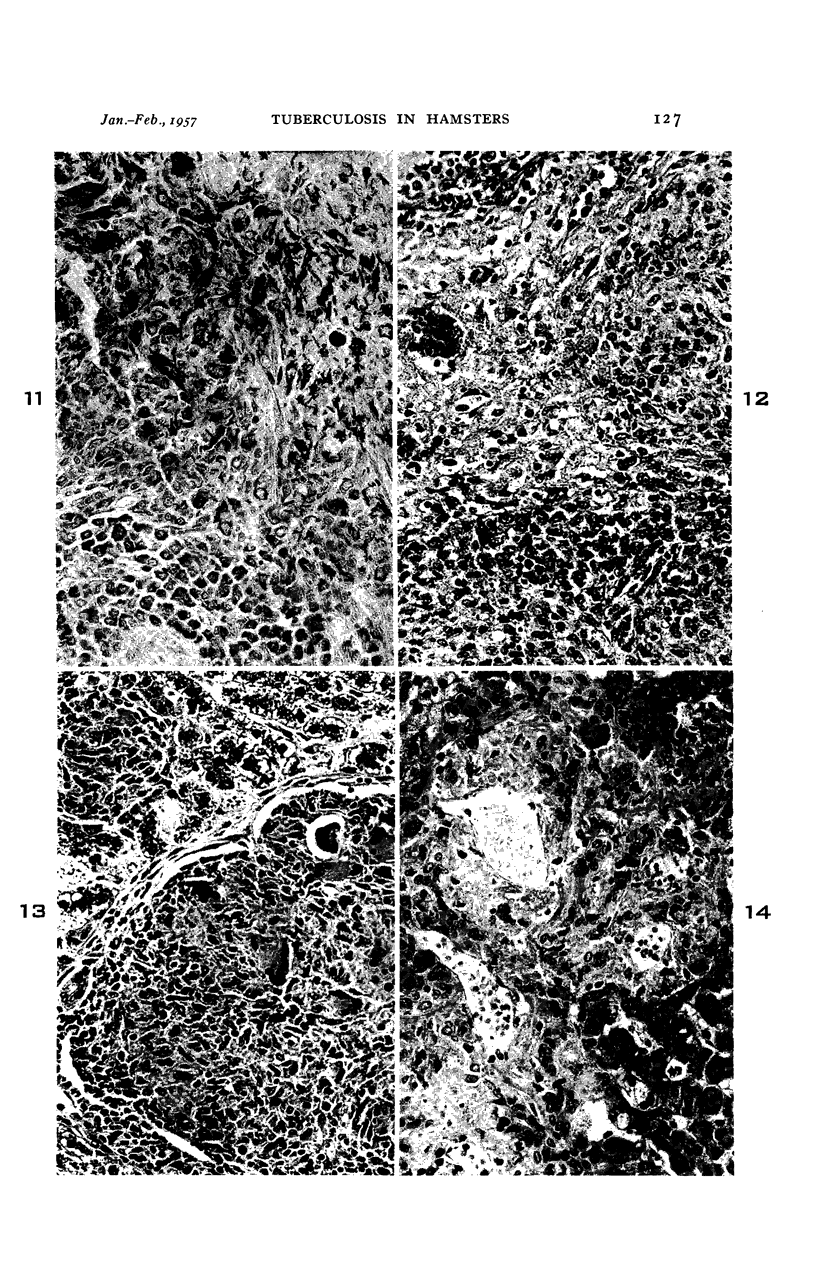

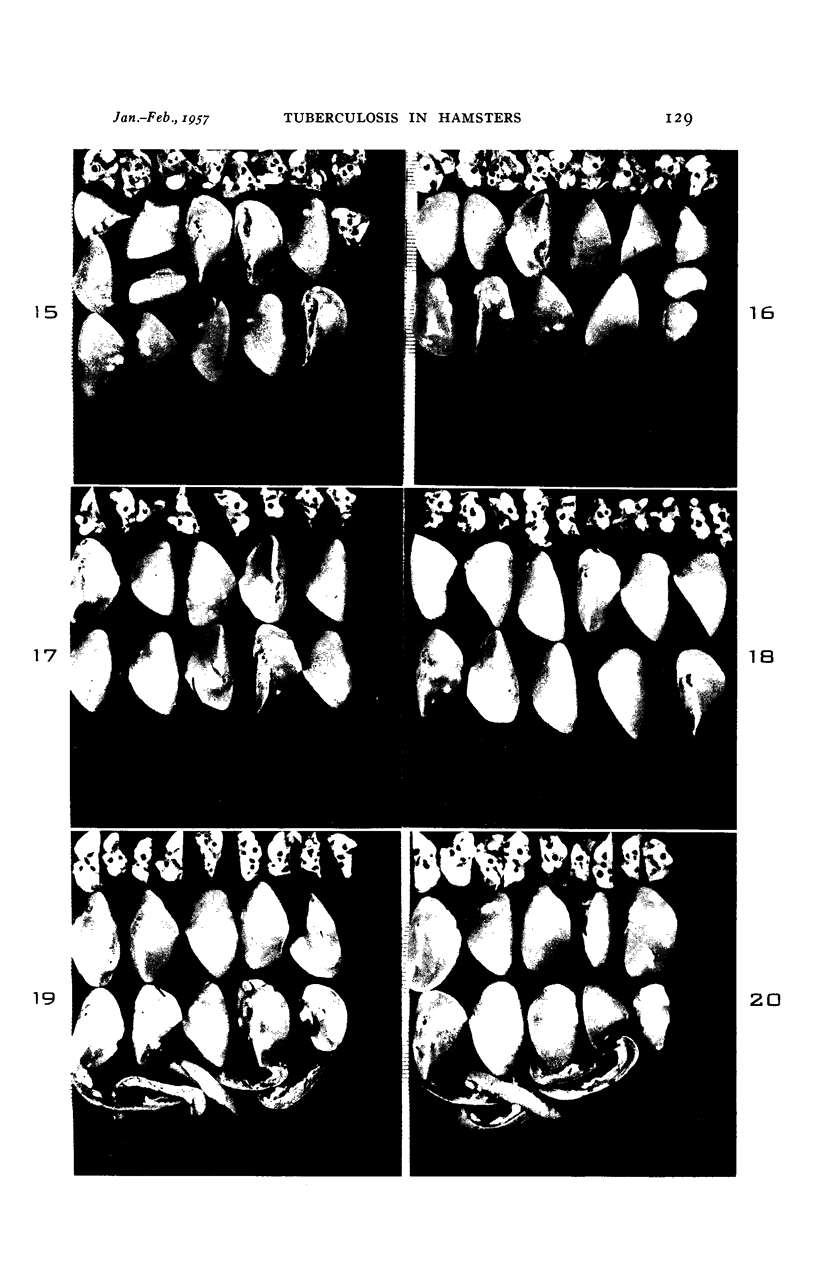
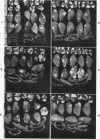
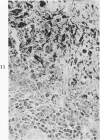
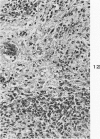
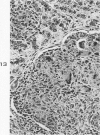
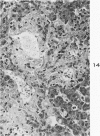
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GETZ H. R., LONG E. R., HENDERSON H. J. A study of the relation of nutrition to the development of tuberculosis; influence of ascorbic acid and vitamin A. Am Rev Tuberc. 1951 Oct;64(4):381–393. doi: 10.1164/art.1951.64.4.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LURIE M. B. Native and acquired resistance to tuberculosis. Am J Med. 1950 Nov;9(5):591–610. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(50)90210-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LURIE M. B., ZAPPASODI P., TICKNER C. On the nature of genetic resistance to tuberculosis in the light of the host-parasite relationships in natively resistant and susceptible rabbits. Am Rev Tuberc. 1955 Sep;72(3):297–329. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1955.72.3.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. R., Holley S. W., Vorwald A. J. A Comparison of the Cellular Reaction in Experimental Tuberculosis of the Cornea in Animals of Varying Resistance. Am J Pathol. 1933 May;9(3):329–336.1. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. The growth of tubercle bacilli in monocytes from normal and vaccinated rabbits. Am Rev Tuberc. 1954 Apr;69(4):495–504. doi: 10.1164/art.1954.69.4.495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RATCLIFFE H. L., PALLADINO V. S. Tuberculosis induced by droplet nuclei infection; initial homogeneous response of small mammals (rats, mice, guinea pigs, and hamsters) to human and to bovine bacilli, and the rate and pattern of tubercle development. J Exp Med. 1953 Jan;97(1):61–68. doi: 10.1084/jem.97.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RATCLIFFE H. L. Tuberculosis induced by droplet nuclei infection; pulmonary tuberculosis of predetermined initial intensity in mammals. Am J Hyg. 1952 Jan;55(1):36–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTER E. Multiplication of tubercle bacilli within mononuclear phagocytes in tissue cultures derived from normal animals and animals vaccinated with BCG. J Exp Med. 1953 Feb 1;97(2):235–245. doi: 10.1084/jem.97.2.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff C. E. A Free Growth Period of Tubercle Bacilli in the Guinea Pig Omentum as Related to the Hypersensitive State. Am J Pathol. 1934 Nov;10(6):739–756.13. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]