Full text
PDF
















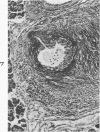
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DEL GRECO F., OLMSTED F., MASSON G. M., CORCORAN A. C. Graphic measurement of arterial pressure in the unanesthetized rat; an improved method. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 May;41(5):729–737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUSTAN H. P., TAYLOR R. D., CORCORAN A. C. Rheumatic and febrile syndrome during prolonged hydralazine treatment. J Am Med Assoc. 1954 Jan 2;154(1):23–29. doi: 10.1001/jama.1954.02940350025006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAUNT R., ANTONCHAK N., MILLER G. J., RENZI A. A. Effect of reserpine (serpasil) and hydralazine (apresoline) on experimental steroid hypertension. Am J Physiol. 1955 Jul;182(1):63–68. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1955.182.1.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN D. M., SAUNDERS F. J., WAHLGREN N., CRAIG R. L. Self-sustaining, post-DCA hypertensive cardiovascular disease. Am J Physiol. 1952 Jul;170(1):94–106. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1952.170.1.94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOLETSKY S. Necrotizing vascular disease in rat. I. Observations on pathogenesis. AMA Arch Pathol. 1955 Mar;59(3):312–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEEFE J. R., GAMBESCIA J. M., KURTZ C. H., SMITH H. D., BEEBE G. W., JABLON S., REINHOLD J. G., WILLIAMS S. C. Prevalence and nature of hepatic disturbance following acute viral hepatitis with jaundice. Ann Intern Med. 1955 Jul;43(1):1–32. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-43-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR R. D., CORCORAN A. C., DUSTAN H. P., PAGE I. H. Further evaluation of hydralazine in treatment of hypertensive disease. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1954 May;93(5):705–712. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1954.00240290063007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]