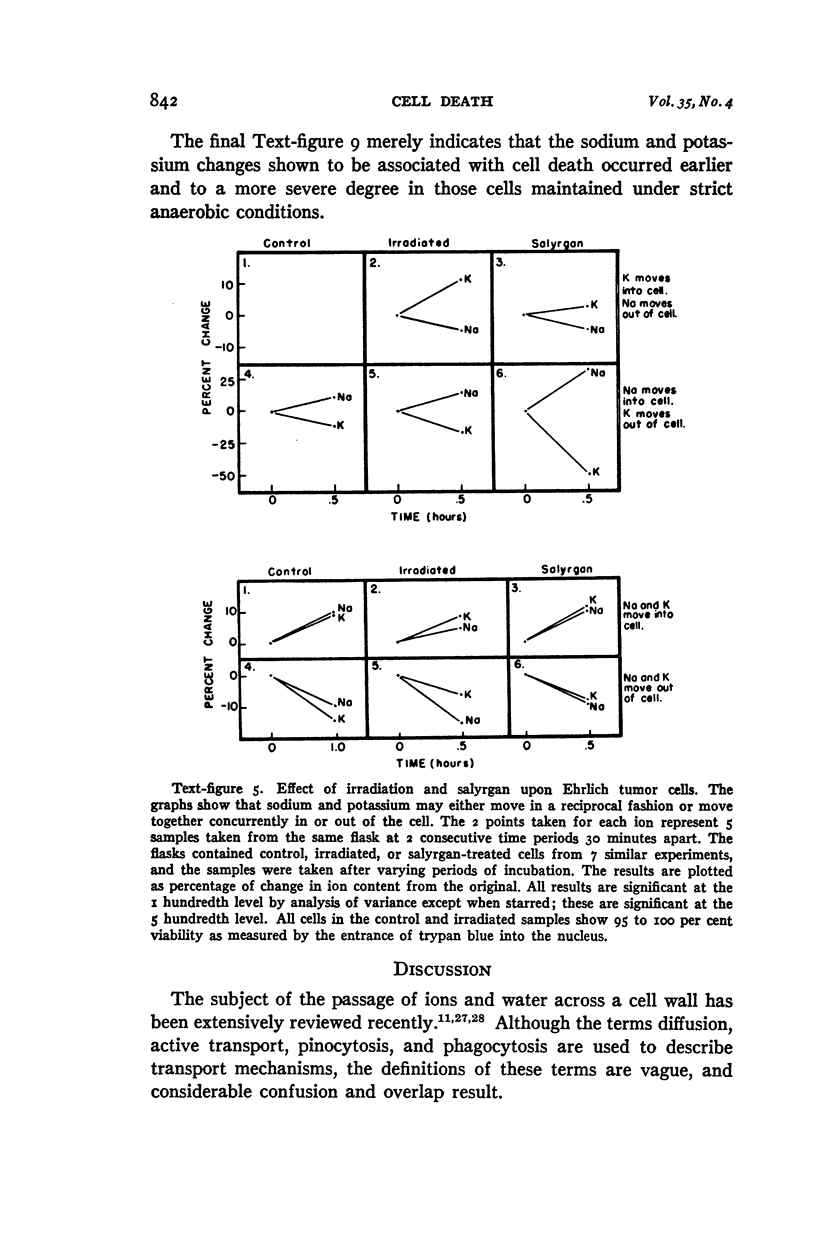
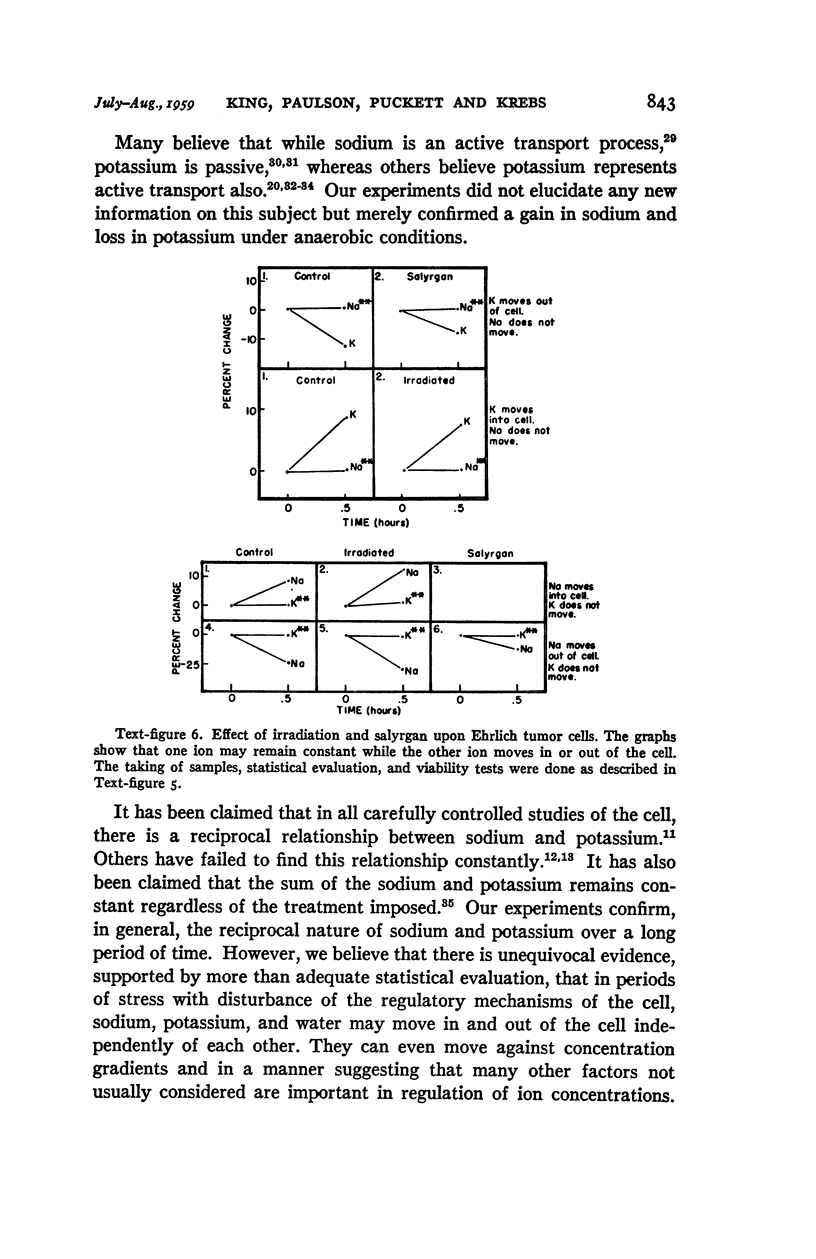
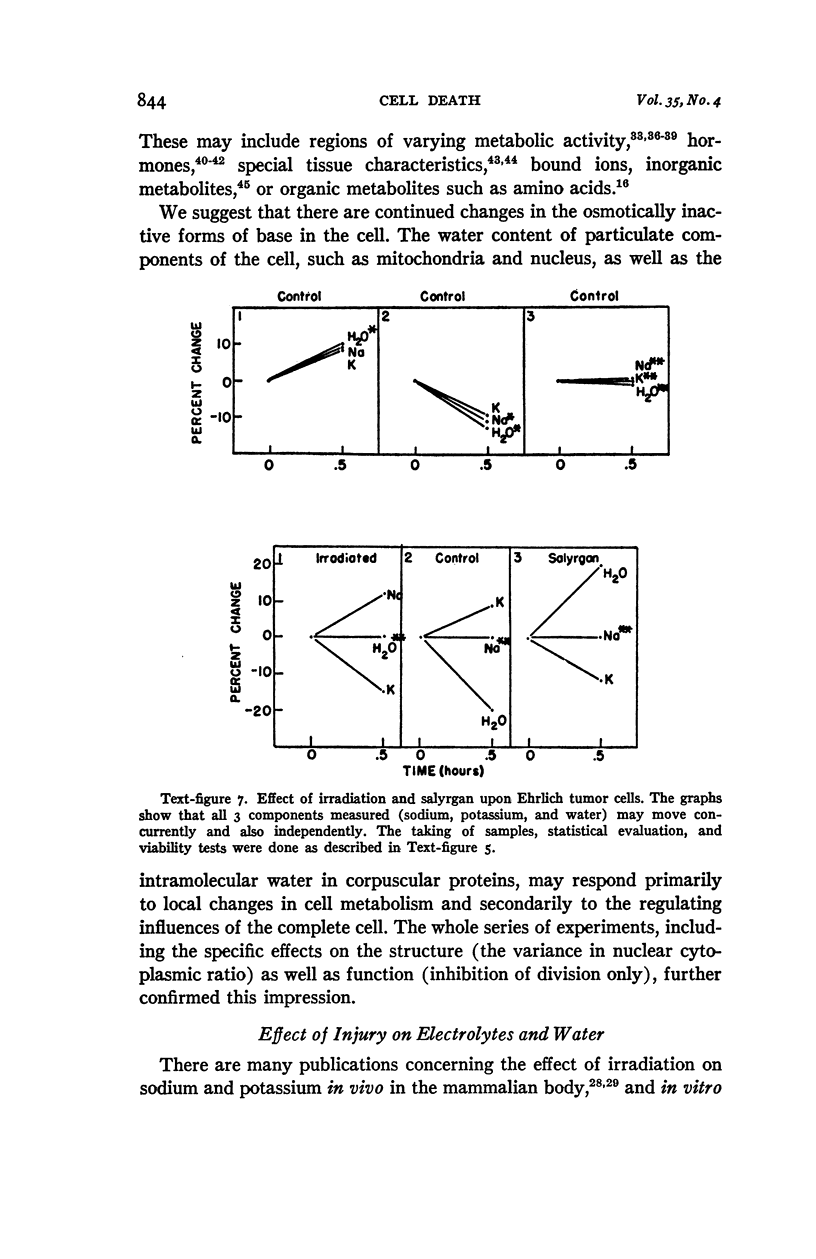
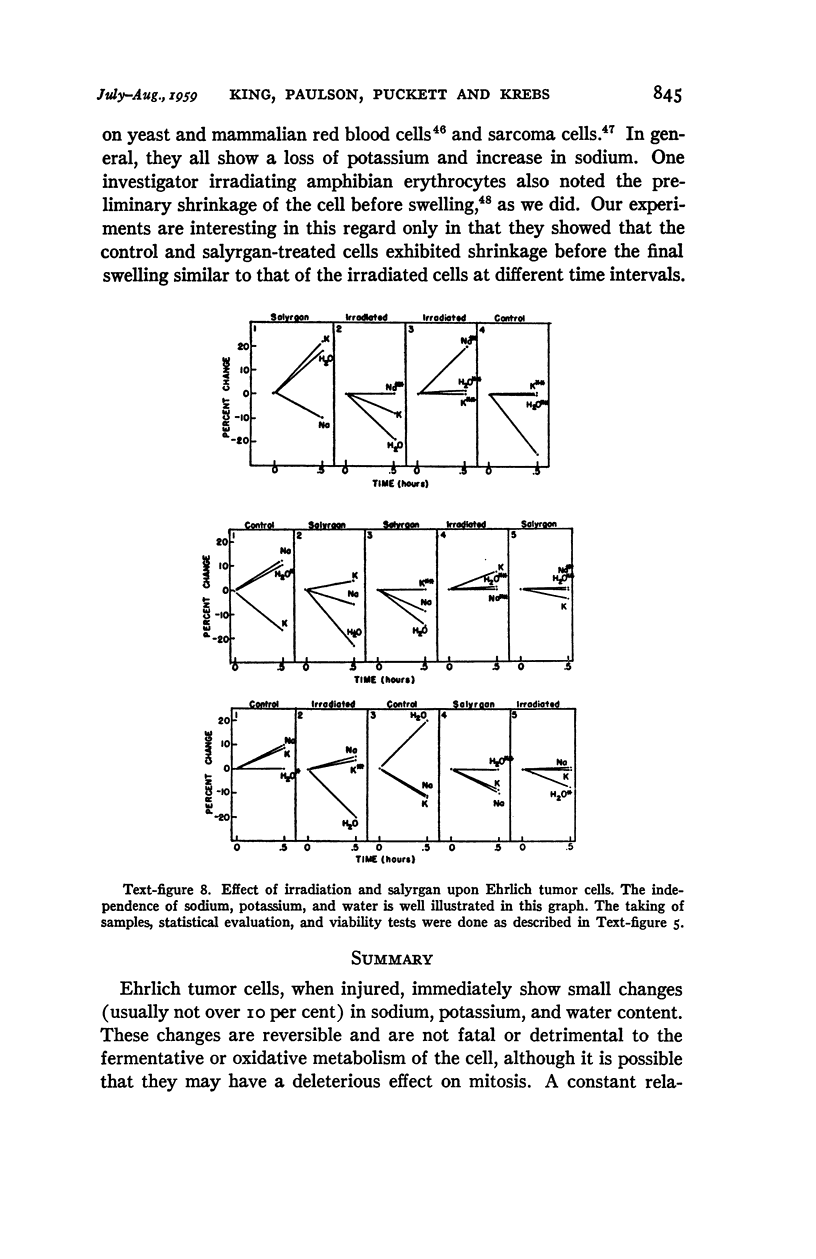
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashford C. A., Dixon K. C. The effect of potassium on the glucolysis of brain tissue with reference to the Pasteur effect. Biochem J. 1935;29(1):157–168. doi: 10.1042/bj0290157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTENSEN H. N., RIGGS T. R. Concentrative uptake of amino acids by the Ehrlich mouse ascites carcinoma cell. J Biol Chem. 1952 Jan;194(1):57–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANOWSKI T. S. Newer concepts of the role of sodium in disease. Am J Med. 1951 Apr;10(4):468–480. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(51)90293-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon K. C. Anaerobic leakage of potassium from brain. Biochem J. 1949;44(2):187–190. doi: 10.1042/bj0440187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDELMAN I. S. Exchange of water between blood and tissues; characteristics of deuterium oxidases equilibration in body water. Am J Physiol. 1952 Nov;171(2):279–296. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1952.171.2.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkinton J. R., Winkler A. W., Danowski T. S. TRANSFERS OF CELL SODIUM AND POTASSIUM IN EXPERIMENTAL AND CLINICAL CONDITIONS. J Clin Invest. 1948 Jan;27(1):74–81. doi: 10.1172/JCI101926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLYNN F., MAIZELS M. Cation control in human erythrocytes. J Physiol. 1949 Dec;110(3-4):301–318. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOULKES E. C., MILLER B. F. Action protamine on electrolyte transport in kidney slices. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 Feb;73(2):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90279-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAUDINO M., LEVITT M. F. Influence of the adrenal cortex on body water distribution and renal function. J Clin Invest. 1949 Nov;28(6 Pt 2):1487–1497. doi: 10.1172/JCI102214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING D. W., PAULSON S. R., HANNAFORD N. C., KREBS A. T. Cell death. I. The effect of injury on the proteins and deoxyribonucleic acid of Ehrlich tumor cells. Am J Pathol. 1959 Mar-Apr;35(2):369–381. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING D. W., PAULSON S. R., HANNAFORD N. C., KREBS A. T. Cell death. II. The effect of injury on the enzymatic protein of Ehrlich tumor cells. Am J Pathol. 1959 May-Jun;35(3):575–589. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREBS H. A., EGGLESTON L. V., TERNER C. In vitro measurements of the turnover rate of potassium in brain and retina. Biochem J. 1951 May;48(5):530–537. doi: 10.1042/bj0480530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUCKE B., PARPART A. K. Osmotic properties and permeability of cancer cells. I. Relative permeability of Ehrlich mouse ascites tumor cells and of mouse erythrocytes to polyhydric alcohols and to sodium chloride. Cancer Res. 1954 Jan;14(1):75–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasnitzki A., Szörényi E. The influence of alkali cations on the fermentation capacity of yeast. Biochem J. 1935 Mar;29(3):580–587. doi: 10.1042/bj0290580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANERY J. F. Water and electrolyte metabolism. Physiol Rev. 1954 Apr;34(2):334–417. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1954.34.2.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MELCHIOR N. C. Sodium and potassium complexes of adenosinetriphosphate: equilibrium studies. J Biol Chem. 1954 Jun;208(2):615–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUDGE G. H. Electrolyte and water metabolism of rabbit kidney slices; effect of metabolic inhibitors. Am J Physiol. 1951 Oct;167(1):206–223. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.167.1.206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSTERHOUT W. J. Changes in resting potential due to a shift of electrolytes in the cell produced by non-electrolytes. J Gen Physiol. 1954 Mar;37(4):423–432. doi: 10.1085/jgp.37.4.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostern P., Herbert D., Holmes E. Formation and breakdown of glycogen in the liver. Biochem J. 1939 Nov;33(11):1858–1878. doi: 10.1042/bj0331858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PINSON E. A. Water exchanges and barriers as studied by the use of hydrogen isotopes 1. Physiol Rev. 1952 Apr;32(2):123–134. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1952.32.2.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON J. R., MCCANCE R. A. Water metabolism. Annu Rev Physiol. 1952;14:115–142. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.14.030152.000555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAWYER W. H. Effect of posterior pituitary extract on permeability of frog skin to water. Am J Physiol. 1951 Jan;164(1):44–48. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1950.164.1.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEPPARD C. W., MARTIN W. R. Cation exchange between cells and plasma of mammalian blood; methods and application to potassium exchange in human blood. J Gen Physiol. 1950 Jul 20;33(6):703–722. doi: 10.1085/jgp.33.6.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON R. C. Studies of metabolic turnover with tritium as a tracer. II. Gross studies on the rat. J Biol Chem. 1953 Feb;200(2):731–743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



