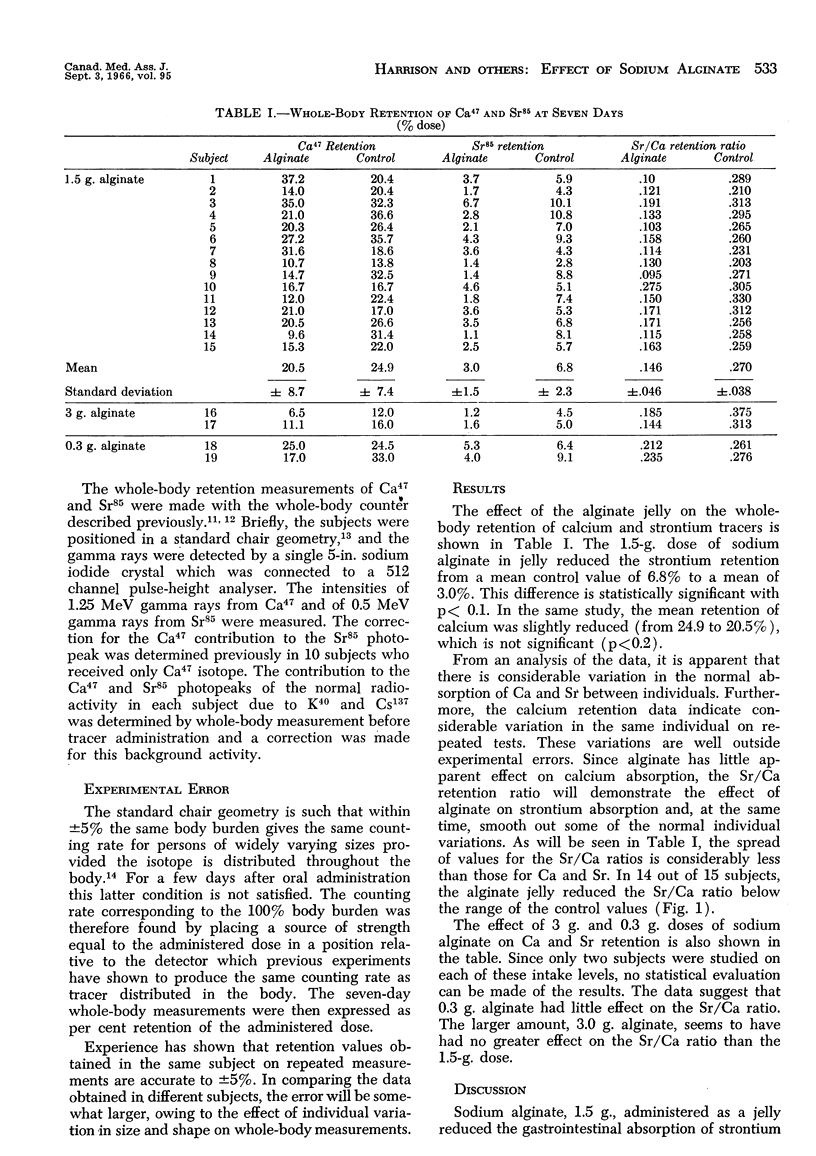
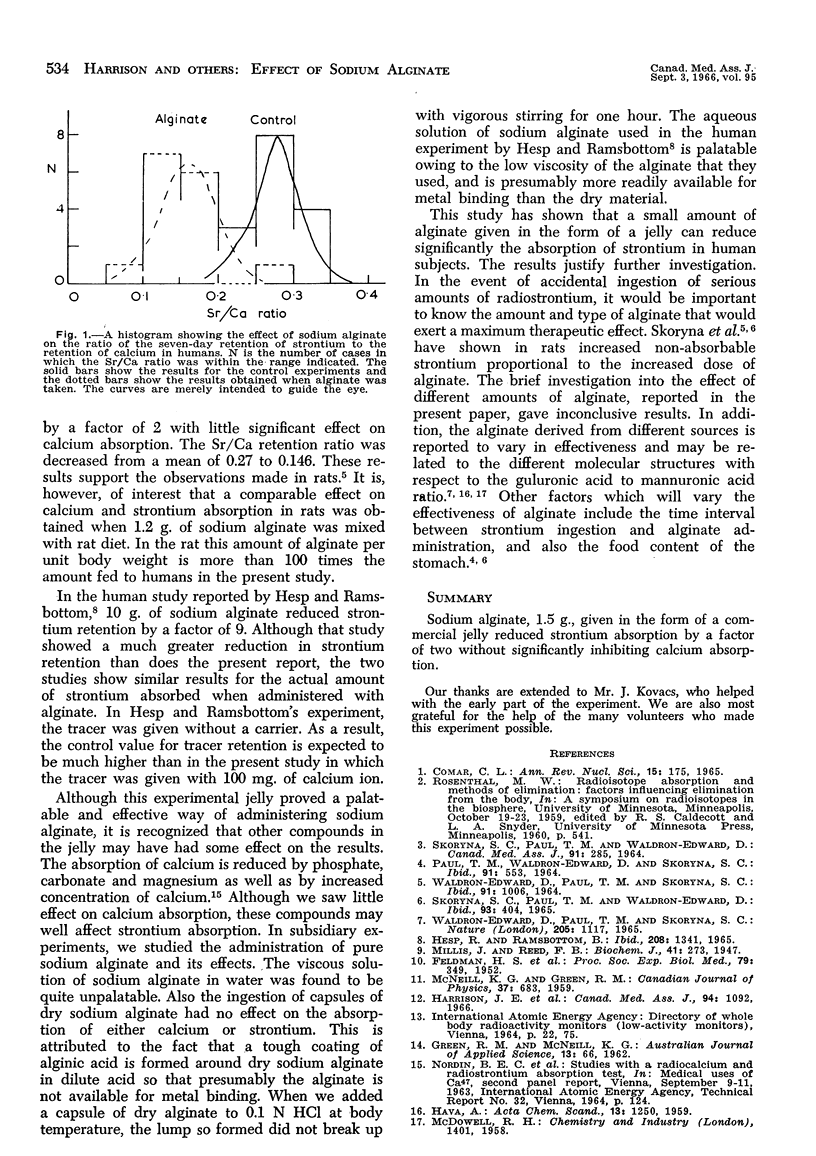
Abstract
The effect of sodium alginate on the gastrointestinal absorption of the tracers strontium-85 and calcium-47 was investigated in 19 human subjects. The tracers were administered orally with 100 mg. of a calcium carrier—calcium chloride. At the same time, sodium alginate was given in a commercial jelly. The sevenday per cent retentions of tracers were measured with a whole-body counter. After one month, the experiments were repeated without alginate so that each subject acted as his own control. Fifteen volunteers were given 1.5 g. of alginate, two were given 3.0 g. and two 0.3 g. 1.5 g. of alginate reduced the absorption of strontium by a factor of two with no significant effect on calcium absorption. The smaller dose of alginate (0.3 g.) appeared to have no effect on strontium or calcium absorption and the larger dose (3.0 g.) had no greater effect than the 1.5 g. dose.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Comar C. L. Movement of fallout radionuclides through the biosphere and man. Annu Rev Nucl Sci. 1965;15:175–206. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ns.15.120165.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesp R., Ramsbottom B. Effect of sodium alginate in inhibiting uptake of radiostrontium by the human body. Nature. 1965 Dec 25;208(5017):1341–1342. doi: 10.1038/2081341a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millis J., Reed F. B. The effect of sodium alginate on the absorption of calcium. Biochem J. 1947;41(2):273–275. doi: 10.1042/bj0410273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKORYNA S. C., PAUL T. M., EDWARD D. W. STUDIES ON INHIBITION OF INTESTINAL ABSORPTION OF RADIOACTIVE STRONTIUM. I. PREVENTION OF ABSORPTION FROM LIGATED INTESTINAL SEGMENTS. Can Med Assoc J. 1964 Aug 8;91:285–288. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKORYNA S. C., PAUL T. M., WALDRON-EDWARD D. STUDIES OF INHIBITION OF INTESTINAL ABSORPTION OF RADIOACTIVE STRONTIUM. IV. ESTIMATION OF THE SUPPRESSANT EFFECT OF SODIUM ALGINATE. Can Med Assoc J. 1965 Aug 28;93:404–407. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALDRON-EDWARD D., SKORYNA S. C., PAUL T. M. STUDIES ON THE INHIBITION OF INTESTINAL ABSORPTION OF RADIOACTIVE STRONTIUM. 3. THE EFFECT OF ADMINISTRATION OF SODIUM ALGINATE IN FOOD AND IN DRINKING WATER. Can Med Assoc J. 1964 Nov 7;91:1006–1010. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldron-Edward D., Paul T. M., Skoryna S. C. Suppression of intestinal absorption of radioactive strontium by naturally occurring non-absorbable polyelectrolytes. Nature. 1965 Mar 13;205(976):1117–1118. doi: 10.1038/2051117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


