Abstract
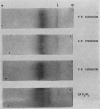
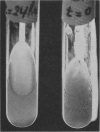
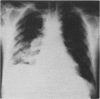
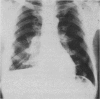
A method which will reduce significantly the viscosity of epithelial mucus is essential to the physiological mechanisms involved in the mobilization and removal of such secretions. The life expectancy of patients with chronic pulmonary conditions and cystic fibrosis has been considerably increased and consequently the problem of liquefying mucin acquires new importance. In view of these considerations, as well as to facilitate research into the structural relationship of the glycoprotein macromolecule, a systematic investigation of mucolysis was undertaken using gastric mucin. Three amides, carbamide, acetamide and formamide, were found to dissolve gastric gel mucin with minimal degradation, and rapidly disperse the viscous secretions produced in pathological conditions of the tracheobronchial tree. Their effect on secretions from patients with cystic fibrosis and bronchiectasis is dramatic, and within five minutes of adding the reagent the flow time was reduced by at least 95%. Clinical studies were carried out with carbamide (urea in anhydrous, lyophilized, sterile powder form) in 32 patients with a variety of bronchial conditions, including chronic bronchitis, cystic fibrosis, asthma, bronchiectasis and emphysema. With the concentrations used, no irritant, bronchospastic or other reactions were observed.
It is concluded that amides of this type have at least two actions on the epithelial mucous secretion: (1) breakage of the three-dimensional gel structure and (2) a slower reduction in viscosity followed by solution of the solid material.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CURTAIN C. C. The action of urea on the urinary inhibitor of influenza virus haemagglutination. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1953 Dec;31(6):615–622. doi: 10.1038/icb.1953.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARD D. W., SKORYNA S. C. PROPERTIES OF GEL MUCIN OF HUMAN GASTRIC JUICE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Jul;116:794–799. doi: 10.3181/00379727-116-29376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINK A. I., BINKHORST R. D., FUNAHASHI T. Intraveous urea and angle-closure glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 1961 Dec;52:872–875. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(61)90331-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBONS R. A., MORGAN W. T., GIBBONS M. Studies in immunochemistry. 16. The isolation of blood-group active mucoids from ovarian cyst fluids. Biochem J. 1955 Jul;60(3):428–436. doi: 10.1042/bj0600428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBONS R. A., ROBERTS G. P. Some aspects of the structure of macromolecular constituents of epithelial mucus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Mar 30;106:218–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb16640.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTSCHALK A. The relation between structure and function in some glycoproteins. Perspect Biol Med. 1962;5:327–337. doi: 10.1353/pbm.1962.0014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAVID M., SETTLAGE P. Effect of urea on cerebrospinal fluid pressure in human subjects; preliminary report. J Am Med Assoc. 1956 Mar 17;160(11):943–949. doi: 10.1001/jama.1956.02960460021006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAHN D. S., PHILLIPS M. J., SKORYNA S. C. CHRONIC EXPERIMENTAL GASTRIC ULCER IN THE RAT RECEIVING INTERMITTENT CORTISONE ADMINISTRATION. Exp Mol Pathol. 1963 Oct;31:481–490. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(63)90024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYNCH B., CLIFFTON E. E., LEWIS J. Tracheitis sicca; successful enzymatic treatment with pancreatic desoxyribosenuclease (dornase). N Engl J Med. 1957 Mar 14;256(11):495–498. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195703142561104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. T., King H. K. Studies in immunochemistry: 7. The isolation from hog gastric mucin of the polysaccharide-amino acid complex possessing blood group A specificity. Biochem J. 1943;37(5):640–651. doi: 10.1042/bj0370640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLGAR G., DENTON R. Cystic fibrosis in adults. Studies of pulmonary function and some physical properties of bronchial mucus. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1962 Mar;85:319–327. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1962.85.3.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEGAL M. S., GOLDSTEIN M. Pancreatic dornase aerosols in bronchopulmonary disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1957 Aug 30;68(1):138–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1957.tb42617.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEFFNER A. L. The reduction in vitro in viscosity of mucoprotein solutions by a new mucolytic agent, N-acetyl-L-cysteine. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Mar 30;106:298–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb16647.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPIER R., WITEBSKY E., PAINE J. R. Aerosolized pancreatic dornase and antibiotics in pulmonary infections: use in patients with postoperative and nonoperative infections. JAMA. 1961 Dec 2;178:878–886. doi: 10.1001/jama.1961.03040480008003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TARTER R. C., LINN J. G., Jr A clinical study of the use of intravenous urea in glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 1961 Sep;52:323–330. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(61)90728-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBB W. R. Clinical evaluaton of a new mucolytic agent, acetyl-cysteine. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1962 Sep;44:330–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldron-Edward D. The micro determination of acid and base dissociation constants by paper electrophoresis. J Chromatogr. 1965 Dec;20(3):556–562. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)97458-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]