Abstract
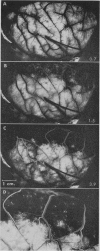
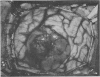
Patterns of blood flow were examined in the surface vessels of the surgically exposed brain by intracarotid injection of 1% fluorescein and rapid serial photographs timed by a photo-cell signal. Matching colour filters were used for black and white or Ektachrome film.
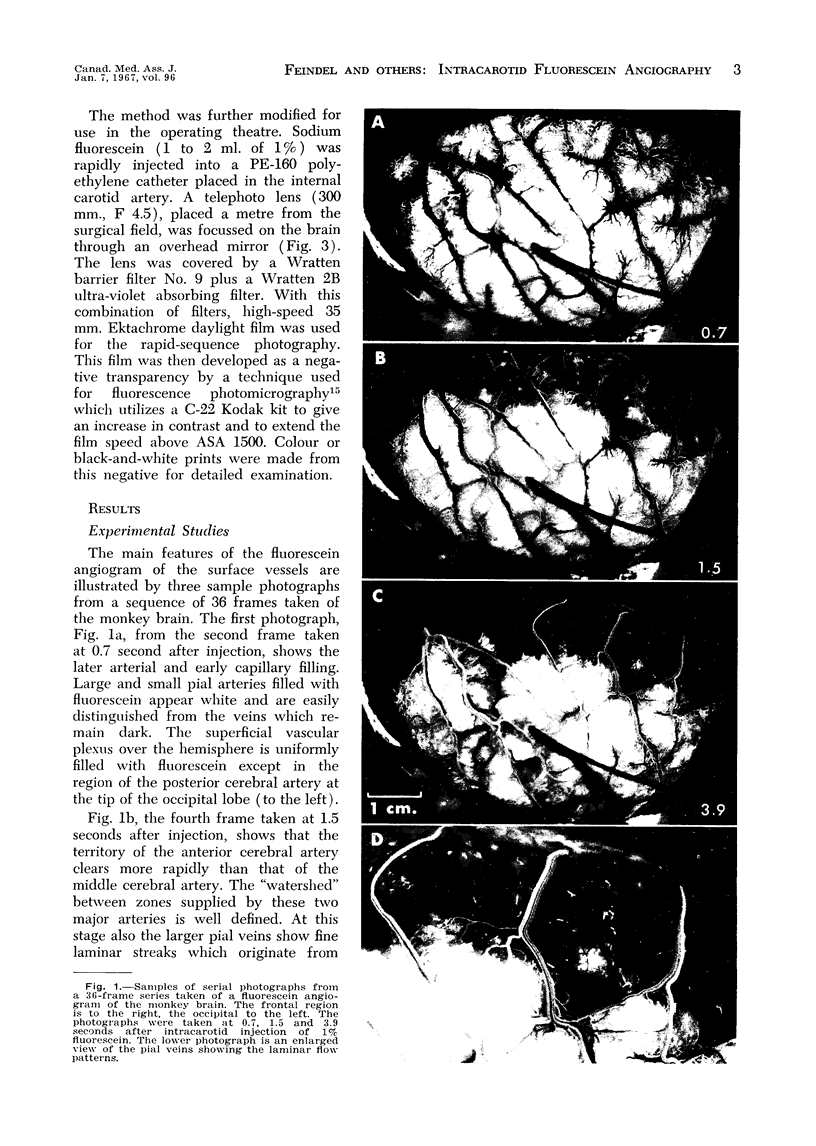
As developed in cats and monkeys, and applied in five patients during craniotomy, the technique gave a picture of flow patterns in the pial and cortical vascular bed, demonstrating “water-shed” areas bordering major arterial territories, laminar flow in veins, and, in particular, the details of filling and clearing in the fine pial vessels, the superficial cortical capillary bed and in the vascular beds of tumours.
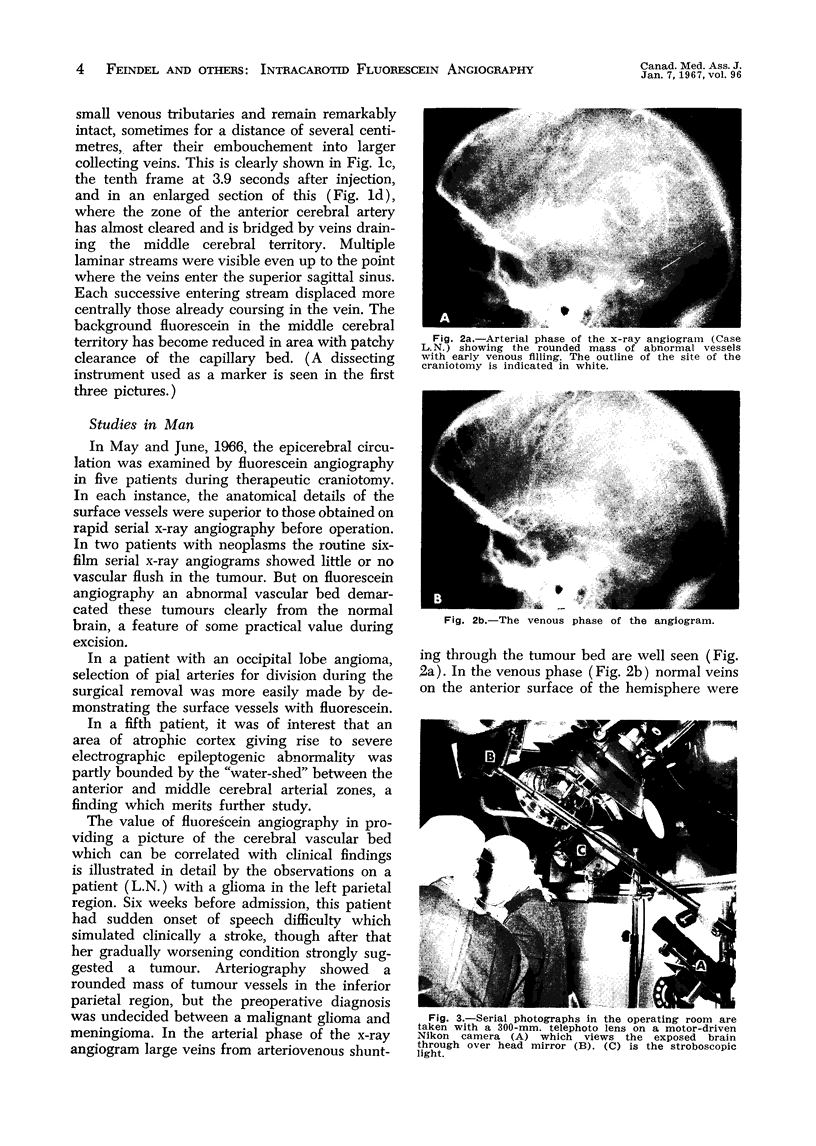
Since these features are rendered in finer detail and sharper contrast than by standard x-ray angiography, the method affords a new means of more adequately examining the epicerebral circulation in man during craniotomy for a variety of lesions.
Full text
PDF

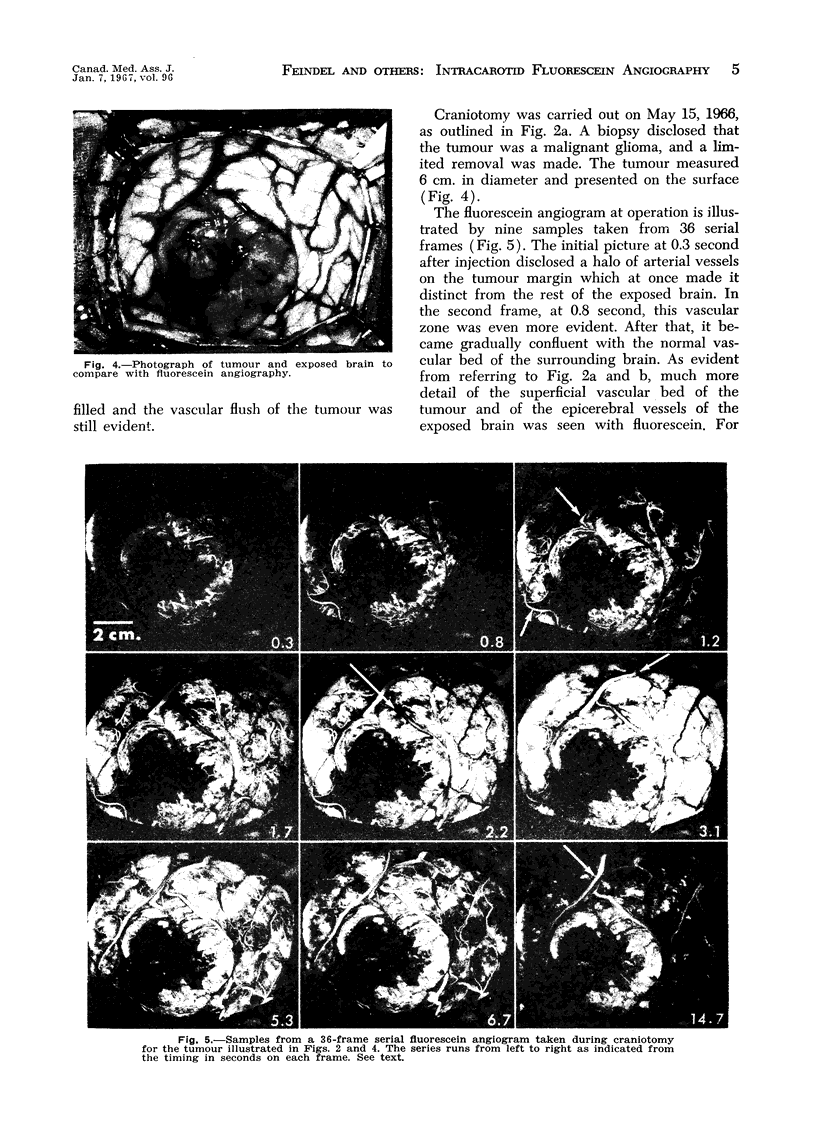


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DOLLERY C. T., HODGE J. V., ENGEL M. Studies of the retinal circulation with flourescein. Br Med J. 1962 Nov 10;2(5314):1210–1215. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5314.1210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollery C. T., Henkind P., Paterson J. W., Ramalho P. S., Hill D. W. I. Ophthalmoscopic and circulatory changes in focal retinal ischaemia. Br J Ophthalmol. 1966 Jun;50(6):285–324. doi: 10.1136/bjo.50.6.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEINDEL W., PEROT P. RED CEREBRAL VEINS: A REPORT ON ARTERIOVENOUS SHUNTS IN TUMORS AND CEREBRAL SCARS. J Neurosurg. 1965 Apr;22:315–325. doi: 10.3171/jns.1965.22.4.0315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEINDEL W., ROVIT R. L., STEPHENS-NEWSHAM L. Localization of intracranial vascular lesions by radioactive isotopes and an automatic contour brain scanner. J Neurosurg. 1961 Nov;18:811–821. doi: 10.3171/jns.1961.18.6.0811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feindel W., Garretson H., Yamamoto L., Perot P., Rumin N. Blood flow patterns in the cerebral vessels and cortex in man studies by intracarotid injection of radioisotopes and Coomassie Blue dye. J Neurosurg. 1965 Jul;23(1):12–22. doi: 10.3171/jns.1965.23.1.0012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feindel W., Garretson M., Yamamoto L. Y., Haslam C., Heuff M. Analysis of the blood flow pattern in the pial and cortical circulation in man. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 1965;14:187–189. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1965.tb01984.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GURDJIAN E. S., THOMAS L. M. Human pial circulation. Arch Neurol. 1961 Jul;5:111–118. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1961.00450130113013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAKIM S., FISHER C. M. A new technique for the microscopic examination of cerebral vessels in vivo. J Neurosurg. 1957 Jul;14(4):405–412. doi: 10.3171/jns.1957.14.4.0405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVOTNY H. R., ALVIS D. L. A method of photographing fluorescence in circulating blood in the human retina. Circulation. 1961 Jul;24:82–86. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.24.1.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. W., Simcock J. P. A new technique for examining the leptomeningeal circulation. Lancet. 1966 Oct 29;2(7470):942–943. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)90540-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders R. L., Feindel W. H., Carvalho V. R. X-ray microscopy of the blood vessels of the human brain. II. Med Biol Illus. 1965 Oct;15(4):234–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMAMOTO Y. L., FEINDEL W., ZANELLI J. COMPARATIVE STUDY OF RADIOACTIVE CHLORMERODRIN (NEOHYDRIN) TAGGED WITH MERCURY 197 AND MERCURY 203 FOR BRAIN SCANNING. Neurology. 1964 Sep;14:815–820. doi: 10.1212/wnl.14.9.815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]