Full text
PDF









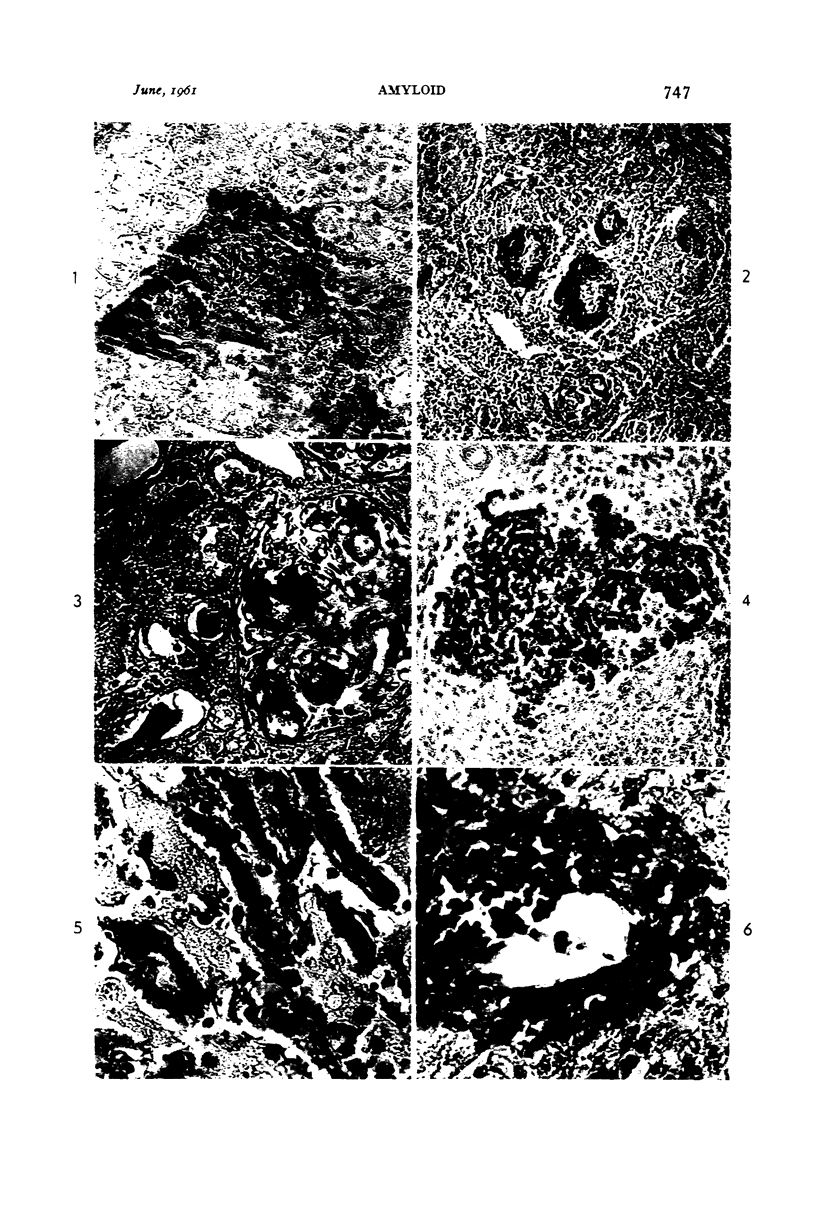
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADAMS C. W. A p-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde-nitrite method for the histochemical demonstration of tryptophane and related compounds. J Clin Pathol. 1957 Feb;10(1):56–62. doi: 10.1136/jcp.10.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN A. S., CALKINS E., LEVENE C. I. Studies on experimental amyloidosis. I. Analysis of histology and staining reactions of casein-induced amyloidosis in the rabbit. Am J Pathol. 1959 Sep-Oct;35:971–989. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANIELLI J. F. Studies on the cytochemistry of proteins. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1950;14:32–39. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1950.014.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON F. J., VAZQUEZ J. J. Immunohistochemical analysis of amyloid by the fluorescence technique. J Exp Med. 1956 Nov 1;104(5):727–736. doi: 10.1084/jem.104.5.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EHRICH W. E. Nature of collagen diseases. Am Heart J. 1952 Jan;43(1):121–156. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(52)90034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEER J. C., STRONG J. P., McGILL H. C., Jr, MUSLOW I. Electron microscopic observations on the localization of amyloid in the kidney in secondary amyloidosis. Lab Invest. 1958 Nov-Dec;7(6):554–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILES R. B., Jr, CALKINS E. Studies of the composition of secondary amyloid. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1476–1482. doi: 10.1172/JCI103198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES R. S., FRAZIER D. B. Primary cardiovascular amyloidosis; its clinical manifestations, pathology and histogenesis. Arch Pathol (Chic) 1950 Sep;50(3):366–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARSEN B. Relation between the affinity for congo red and the glycoprotein content of serum in rheumatoid arthritis and related diseases. Ann Rheum Dis. 1958 Jun;17(2):240–244. doi: 10.1136/ard.17.2.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORKIN S. A., WEITZEL R., CAMPAGNA-PINTO D., MACDONALD R. A., MALLORY G. K. "Alcoholic" hyalin in human cirrhosis histochemical studies. Am J Pathol. 1960 Jul;37:49–61. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REECE J. M., REYNOLDS T. B. Amyloidosis complicating rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Med Sci. 1954 Nov;228(5):554–559. doi: 10.1097/00000441-195411000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SYMMERS W. S. Primary amyloidosis: a review. J Clin Pathol. 1956 Aug;9(3):187–211. doi: 10.1136/jcp.9.3.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEILUM G. Cortisone-ascorbic acid interaction and the pathogenesis of amyloidosis; mechanism of action of cortisone on mesenchymal tissue. Ann Rheum Dis. 1952 Jun;11(2):119–136. doi: 10.1136/ard.11.2.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEILUM G. Periodic acid-Schiff-positive reticulo-endothelial cells producing glycoprotein; functional significance during formation of amyloid. Am J Pathol. 1956 Sep-Oct;32(5):945–959. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON S. W., 2nd, WIEGAND R. G., THOMASSEN R. W., HARRISON M., TURBYFILL C. L. The protein nature of acidophilic of dogs. Am J Pathol. 1959 Nov-Dec;35:1105–1115. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VASSAR P. S., CULLING C. F. Fluorescent stains, with special reference to amyloid and connective tissues. Arch Pathol. 1959 Nov;68:487–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINDRUM G. M., KRAMER H. Some observations on the histochemical reactions of amyloid. AMA Arch Pathol. 1957 Apr;63(4):373–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]