Full text
PDF























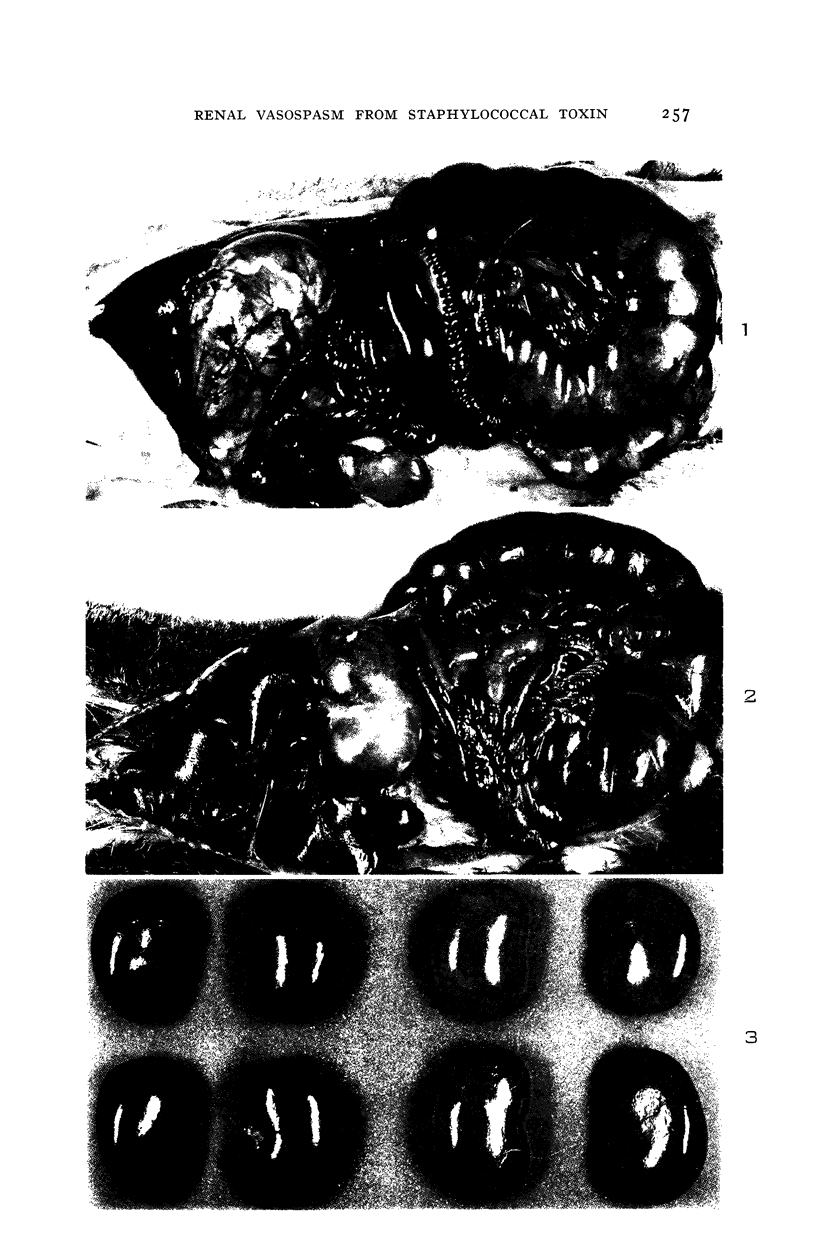


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Glynn J. H. The Pathogenesis of Cortical Necrosis of the Kidneys in Rabbits Following the Injection of Staphylococcus Toxin. Am J Pathol. 1937 Jul;13(4):593–604.5. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAUSMAN R., DREYFUS P. M. Intra-capillary precipitates produced in rabbits by means of sodium polyanetholsulfonate. AMA Arch Pathol. 1953 Dec;56(6):597–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFF E. C., KELL J. F., Jr, HASTINGS N., SHOLES D. M., GRAY E. H. Vasomotor, cellular and functional changes produced in kidney by brain stimulation. J Neurophysiol. 1951 Jul;14(4):317–332. doi: 10.1152/jn.1951.14.4.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLIVER J., MacDOWELL M., TRACY A. The pathogenesis of acute renal failure associated with traumatic and toxic injury; renal ischemia, nephrotoxic damage and the ischemic episode. J Clin Invest. 1951 Dec;30(121):1307–1439. doi: 10.1172/JCI102550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigdon R. H., Joyner A. L., Ricketts E. T. A Study of the Action of a Filtrable Staphylococcal Toxin on the Kidneys of Normal Rabbits. Am J Pathol. 1934 May;10(3):425–434.3. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLEGEL J. U., MOSES J. B. A method for visualization of kidney blood vessels applied to studies of the crush syndrome. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1950 Aug;74(4):832–837. doi: 10.3181/00379727-74-18061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS L., GOOD R. A. Studies on the generalized Shwartzman reaction: I. General observations concerning the phenomenon. J Exp Med. 1952 Dec;96(6):605–624. doi: 10.1084/jem.96.6.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






