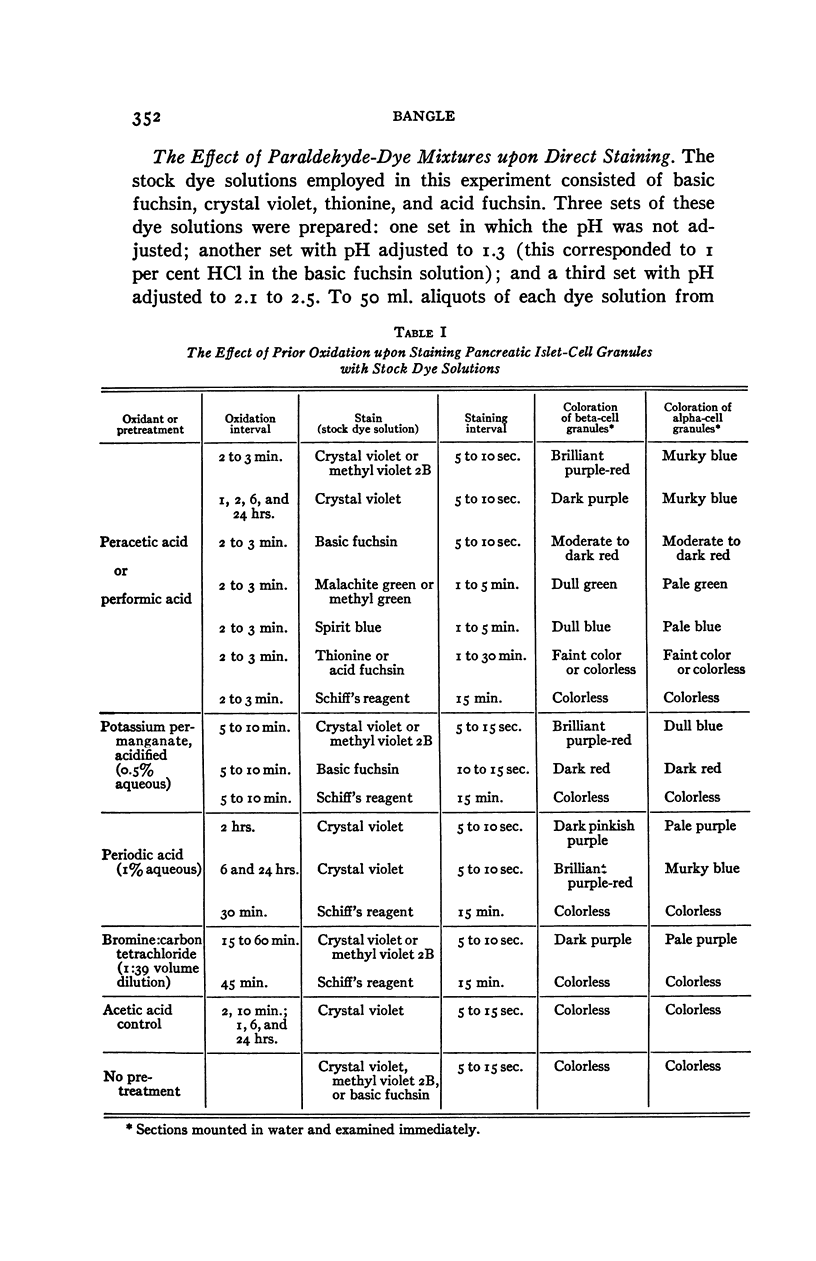
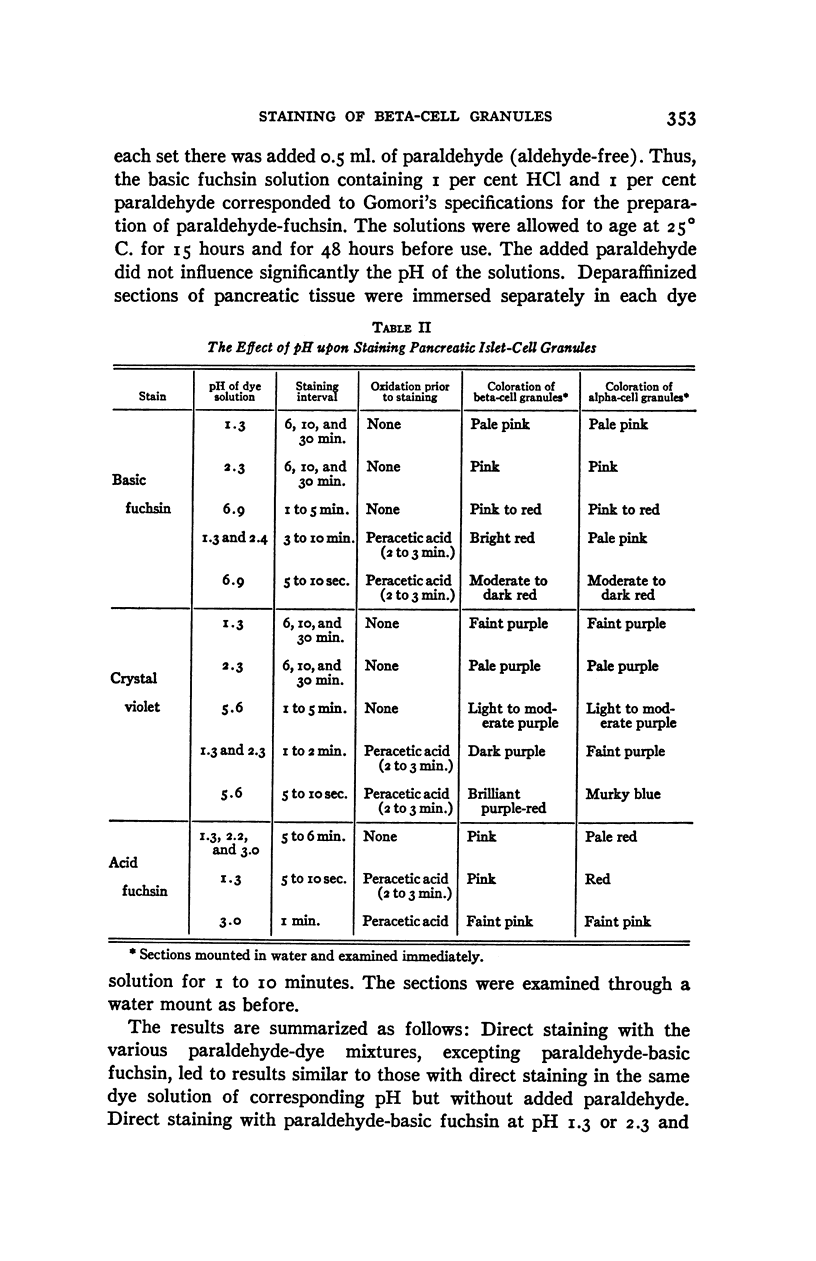
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BANGLE R., Jr Gomori's paraldehydefuchsin stain. I. Physico-chemical and staining properties of the dye. J Histochem Cytochem. 1954 Jul;2(4):291–299. doi: 10.1177/2.4.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BELL E. T. The incidence and significance of degranulation of the beta cells in the islets of Langerhans in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1953 Mar-Apr;2(2):125–129. doi: 10.2337/diab.2.2.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOMORI G. Aldehyde-fuchsin: a new stain for elastic tissue. Am J Clin Pathol. 1950 Jul;20(7):665–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOTT H. R., CLAYTON B. P. A comparison of the staining affinities of aldehyde fuchsin and the Schiff reagent. J Histochem Cytochem. 1953 Sep;1(5):336–352. doi: 10.1177/1.5.336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOTT H. R. Rapid staining of beta cell granules in pancreatic islets. Stain Technol. 1952 Sep;27(5):267–268. doi: 10.3109/10520295209105089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F. Fractionation of oxidized insulin. Biochem J. 1949;44(1):126–128. doi: 10.1042/bj0440126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


