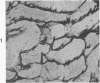
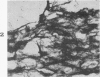
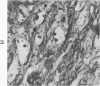
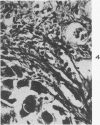
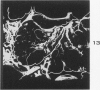
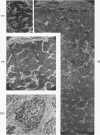
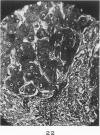
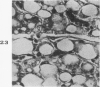
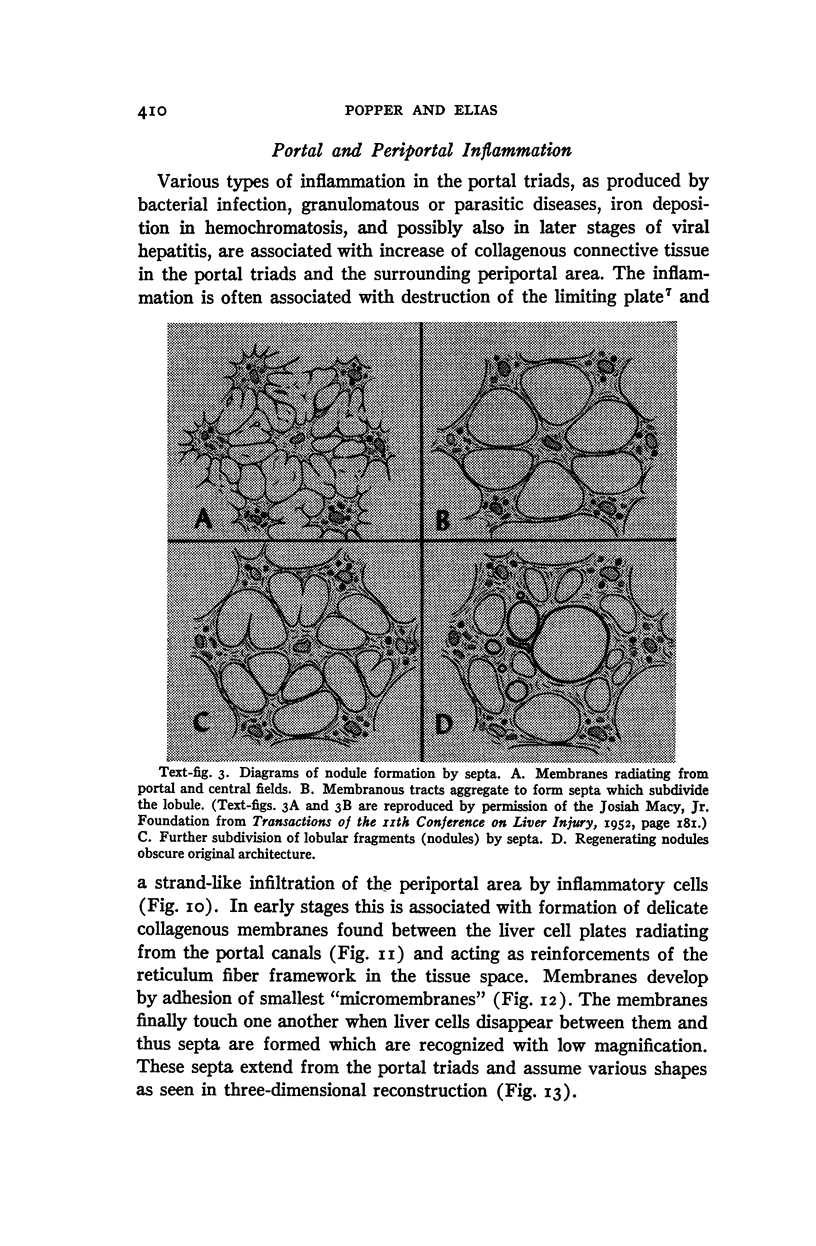
Full text
PDF





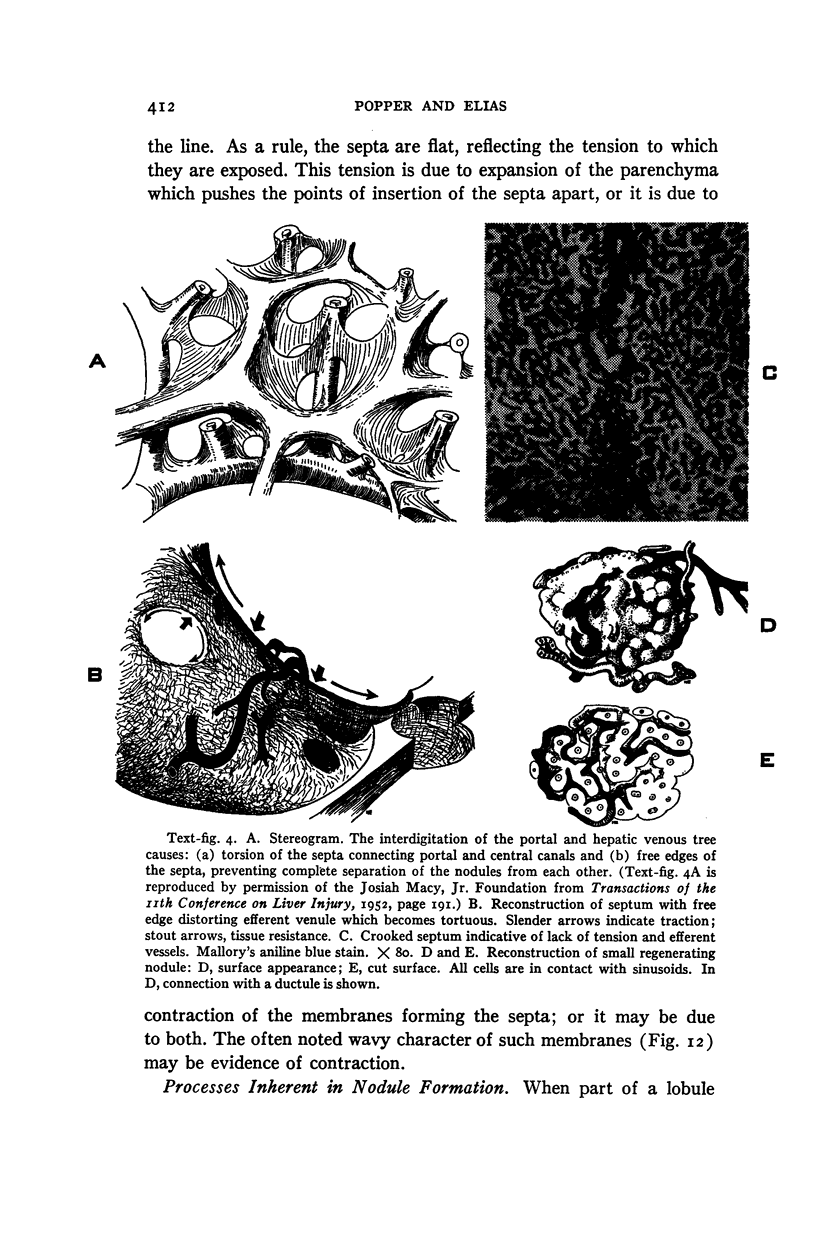







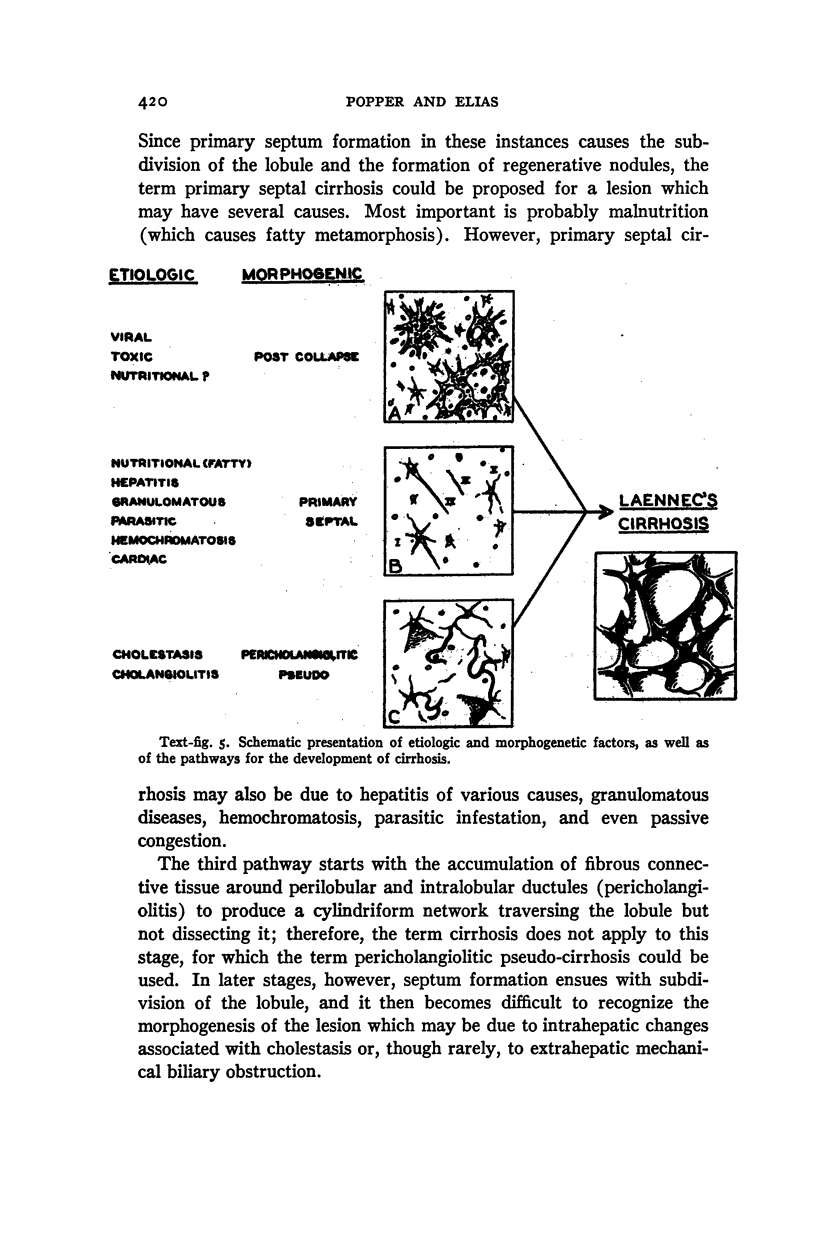











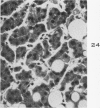
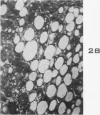
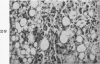
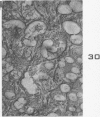
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AHRENS E. H., Jr, PAYNE M. A., KUNKEL H. G., EISENMENGER W. J., BLONDHEIM S. H. Primary biliary cirrhosis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1950 Dec;29(4):299–364. doi: 10.1097/00005792-195012000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAGGENSTOSS A. H., STAUFFER M. H. Posthepatitic and alcoholic cirrhosis: clinicopathologic study of 43 cases of each. Gastroenterology. 1952 Oct;22(2):157–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENZ E. J., BAGGENSTOSS A. H., WOLLAEGER E. E. Atrophy of the left lobe of the liver. AMA Arch Pathol. 1952 Apr;53(4):315–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUCHER N. L. R., SCOTT J. F., AUB J. C. Regeneration of the liver in parabiotic rats. Cancer Res. 1951 Jun;11(6):457–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor C. L. Fatty infiltration of the liver and the development of cirrhosis in diabetes and chronic alcoholism. Am J Pathol. 1938 May;14(3):347–364.9. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELIAS H. A re-examination of the structure of the mammalian liver; the hepatic lobule and its relation to the vascular and biliary systems. Am J Anat. 1949 Nov;85(3):379-456, 15 pl. doi: 10.1002/aja.1000850303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELIAS H., PETTY D. Gross anatomy of the blood vessels and ducts within the human liver. Am J Anat. 1952 Jan;90(1):59–111. doi: 10.1002/aja.1000900104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELIAS H., SOKOL A. Dependence of the lobular architecture of the liver on the porto-hepatic blood pressure gradient. Anat Rec. 1953 Jan;115(1):71–85. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091150107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELIAS H. The liver cord concept after 100 years. Science. 1949 Nov 4;110(2862):470-2, illust. doi: 10.1126/science.110.2862.470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLEGG R. E., EIDINGER D., LEBLOND C. P. Some carbohydrate components of reticular fibers. Science. 1953 Nov 20;118(3073):614–616. doi: 10.1126/science.118.3073.614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GYORGY P. Experimental hepatic injury. Am J Dig Dis. 1952 Dec;19(12):392–396. doi: 10.1007/BF02881130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARTROFT W. S. Accumulation of fat in liver cells and in lipodiastaemata preceding experimental dietary cirrhosis. Anat Rec. 1950 Jan;106(1):61–87. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091060107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARTROFT W. S., RIDOUT J. H. Pathogenesis of the cirrhosis produced by choline deficiency; escape of lipid from fatty hepatic cysts into the biliary and vascular systems. Am J Pathol. 1951 Nov-Dec;27(6):951–989. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELTY R. H., BAGGENSTOSS A. H., BUTT H. R. The relation of the regenerated liver nodule to the vascular bed in cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1950 Jun;15(2):285–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucké B., Mallory T. The Fulminant Form of Epidemic Hepatitis. Am J Pathol. 1946 Sep;22(5):867–945. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSCHCOWITZ E. The morphology and pathogenesis of cardiac fibrosis of the liver. Ann Intern Med. 1952 Apr;36(4):933–955. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-36-4-933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacMAHON H. E., THANNHAUSER S. J. Congenital dysplasia of the interlobular bile ducts with extensive skin xanthomata; congenital acholangic biliary cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1952 Aug;21(4):488–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPPER H., DE LA HUERGA J., KOCHWESER D. Hepatic injury due to conditioned sulfo amino acid deficiency. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1954 May 10;57(6):936–947. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1954.tb36473.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPPER H., ELIAS H., PETTY D. E. Vascular pattern of the cirrhotic liver. Am J Clin Pathol. 1952 Aug;22(8):717–729. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/22.8.717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPPER H. Liver disease-morphologic considerations. Am J Med. 1954 Jan;16(1):98–117. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(54)90326-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPPER H., SZANTO P. B., ELIAS H. Transition of fatty liver into cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1955 Feb;28(2):183-92; discussion, 208-15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANDALL J. T., FRASER R. D. B., JACKSON S., MARTIN A. V. W., NORTH A. C. T. Aspects of collagen structure. Nature. 1952 Jun 21;169(4312):1029–1033. doi: 10.1038/1691029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHERLOCK S. The liver in heart failure; relation of anatomical, functional, and circulatory changes. Br Heart J. 1951 Jul;13(3):273–293. doi: 10.1136/hrt.13.3.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UNGAR H. Transformation of the hepatic vasculature of rats following protracted experimental poisoning with carbon tetrachloride; its possible relation to the formation of urate calculi in the urinary tract. Am J Pathol. 1951 Sep-Oct;27(5):871–883. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLACH H. F., POPPER H. Central necrosis of the liver. AMA Arch Pathol. 1950 Jan;49(1):33-42, illust. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]