Fig. 4.
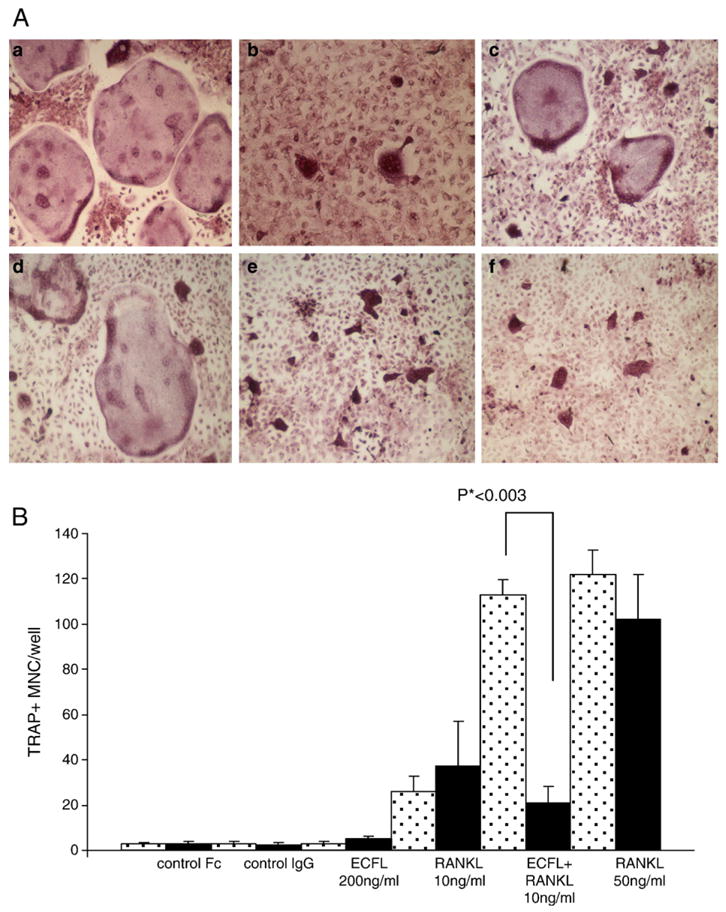
Anti-ICAM-1 inhibits ECF-L-induced OCL formation. (A) TRACP staining was performed and the number of TRACP+ multinucleated cells in each well was counted. MDBM cells were treated with RANKL 50 ng/ml (a), RANKL 10 ng/ml (b) and RANKL 10 ng/ml+ECF-L-Fc 200 ng/ml (c) and in the presence of the blocking anti-ICAM 1 antibody RANKL 50 ng/ml, (d) RANKL 10 ng/ml (e) and RANKL 10 ng/ml+ECF-Fc 200 ng/ml (f). (B) Anti-ICAM-1 inhibits ECF-L-induced OCL formation. Anti-ICAM-1 antibody was added to mouse bone marrow cultures stimulated with 200 ng/ml of ECF-L-Fc. Control cultures were treated with a control Fc protein (200 ng/ml) and control IgG protein. Anti-ICAM-1 antibody did not inhibit TRACP+ multinucleated cells induced by 50 ng/ml RANKL, but inhibited TRACP+ MNC formation induced by 10 ng/ml RANKL and 200 ng/ml of ECF-L-Fc. Results represent the mean±SD. A similar pattern of results was seen in three independent experiments. Stippled bars represent cultures treated with control IgG and solid bars are cultures treated with anti-ICAM-1 antibody.
