Abstract
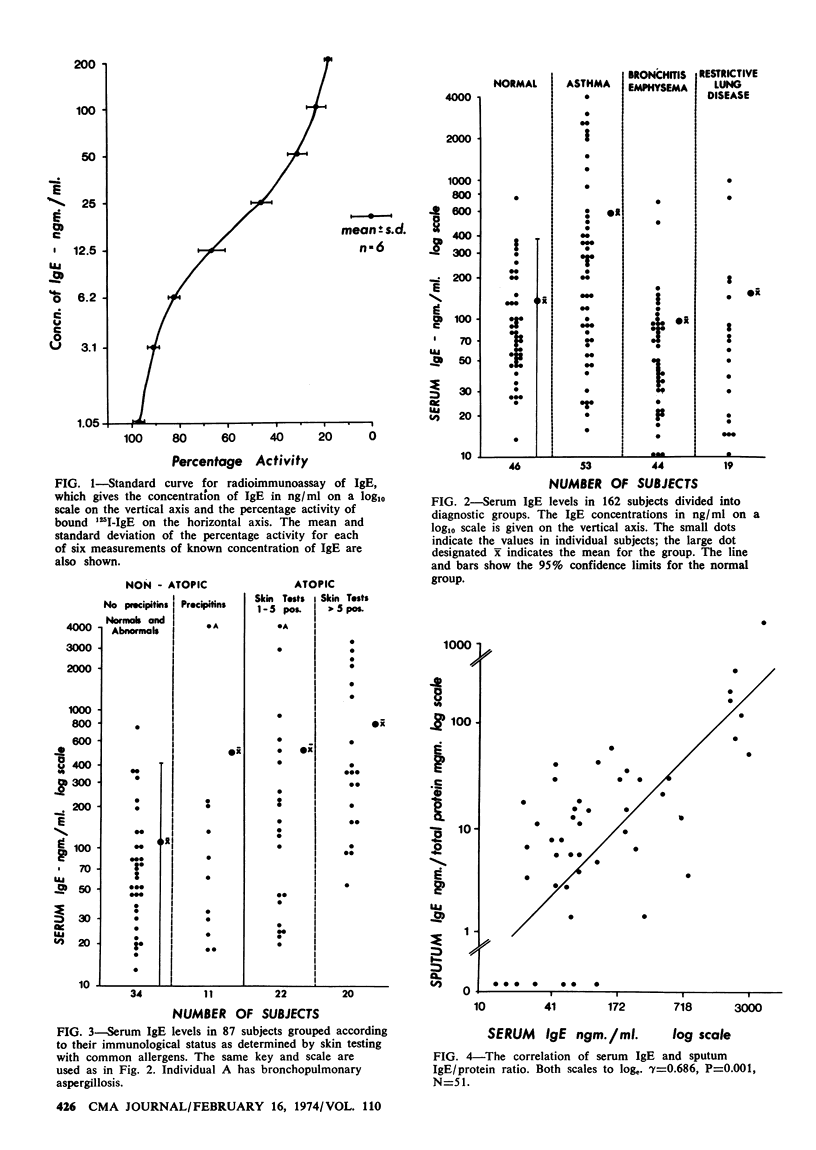
Using a solid-phase radioimmunoassay, serum IgE level was determined in 46 normal subjects, 53 patients with bronchial asthma, 44 patients with chronic bronchitis and / or emphysema, and 19 patients with restrictive lung disease. Sputum IgE was measured simultaneously in 51 of the subjects. The range of serum IgE concentration in the normal subjects was wide. It varied between 15 and 750 ng/ml with a mean of 135 ng. Asthmatic patients had significantly higher levels of serum IgE with a mean of 579 ng/ml, but only 30% fell outside the normal 95% confidence limits. Patients with chronic bronchitis, emphysema and restrictive lung diseases had normal IgE levels. There was a significant correlation between serum and sputum IgE levels.
Full text
PDF