SUMMARY
Hematopoietic cells isolated from patients with Bcr-Abl-positive leukemia exhibit multiple abnormalities of cytoskeletal and integrin function. These abnormalities are thought to play a role in the pathogenesis of leukemia; however, the molecular events leading to these abnormalities are not fully understood. We show here that the Abi1 pathway is required for Bcr-Abl to stimulate actin cytoskeleton remodeling, integrin clustering, and cell adhesion. Expression of Bcr-Abl induces tyrosine phosphorylation of Abi1. This is accompanied by a subcellular translocation of Abi1/WAVE2 to a site adjacent to membrane, where an F-actin-enriched structure containing the adhesion molecules such as β1-integrin, paxillin, and vinculin is assembled. Bcr-Abl-induced membrane translocation of Abi1/WAVE2 requires direct interaction between Abi1 and Bcr-Abl, but is independent of phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Formation of the F-actin-rich complex correlates with an increased cell adhesion to fibronectin. More importantly, disruption of the interaction between Bcr-Abl and Abi1 by mutations either in Bcr-Abl or Abi1 not only abolished tyrosine phosphorylation of Abi1 and membrane translocation of Abi1/WAVE2, but also inhibited Bcr-Abl-stimulated actin cytoskeleton remodeling, integrin clustering, and cell adhesion to fibronectin. Together, these data define Abi1/WAVE2 as a downstream pathway that contributes to Bcr-Abl-induced abnormalities of cytoskeletal and integrin function.
Keywords: Abi1, Bcr-Abl, WAVE2, actin cytoskeleton, β1-integrin, cell adhesion
INTRODUCTION
Actin polymerization/depolymerization is a fundamental cellular process that controls cell shape, adhesion, and migration. This dynamic cellular process is spatiotemporally regulated in normal cells but its dysregulation is often associated with cellular transformation and tumorogenesis (Pollard and Borisy, 2003; Rao and Li, 2004). The Wiscott-Aldrich Syndrome Protein (WASp) family proteins, which consist of WASp, N-WASP, and WAVE/Scar 1, 2, and 3, are critical components in the signaling network that regulates actin polymerization (Bompard and Caron, 2004; Stradal et al., 2004). By interacting with actin and the Arp 2/3 complex, these proteins act as actin nucleation factors to promote actin polymerization. WASp family proteins are regulated by the small GTP binding proteins Rac and Cdc42 (Bompard and Caron, 2004). WASp and N-WASP, for example, contain a conserved Cdc42 binding domain. Association of GTP-bound Cdc42 to these proteins is a key step in their activation (Burns et al., 2004; Stradal et al., 2004). WAVE proteins, on the other hand, are regulated by Rac through a different mechanism. WAVE proteins do not contain a Rac binding site and therefore do not directly bind to Rac. Instead, these proteins form a complex with Hspc 300, Abl interactor (Abi) proteins, Nck-associated protein 1 (Nap1), and specifically Rac-associated (Sra) protein (Eden et al., 2002; Gautreau et al., 2004; Innocenti et al., 2004; Kunda et al., 2003; Steffen et al., 2004). Among these proteins Abi plays a central role in holding the complex together while Sra provides a binding site for active Rac (Gautreau et al., 2004; Innocenti et al., 2004; Steffen et al., 2004). Recent studies suggest that the complex formation and subsequent translocation are critical for WAVE activation (Innocenti et al., 2004; Leng et al., 2005). Still, how these cellular processes are regulated in cancer cells and whether the dysregulation of these cellular processes contributes to cellular transformation and tumorogenesis remain unclear.
Mammalian Abi proteins consist of three members, Abi1 (also known as e3b1), Abi2, and NESH (Biesova et al., 1997; Dai and Pendergast, 1995; Miyazaki et al., 2000; Shi et al., 1995; Wang et al., 1996; Ziemnicka-Kotula et al., 1998). Among these, Abi1 and Abi2 were first identified as the binding partners of c-Abl as well as oncogenic v-Abl and Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinases (Dai and Pendergast, 1995; Shi et al., 1995). Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinases are produced by a reciprocal t(9;22)(q34;q11) chromosomal translocation that fuses varying amounts of the bcr gene on chromosome 22 with sequences upstream of the second exon of the c-abl gene on chromosome 9. Depending on the amount of bcr sequences fused, three different Bcr-Abl fusion proteins with molecular masses of 185 kDa (p185Bcr-Abl), 210 kDa (p210Bcr-Abl), and 230 kDa (p230Bcr-Abl) may be produced (Melo and Deininger, 2004). Expression of Bcr-Abl is associated with greater than 95% of human chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) and a subset of acute lymphocytic leukemia cases (Melo and Deininger, 2004). Hematopoietic cells isolated from CML patients exhibit multiple abnormalities of cytoskeletal function, such as increased motility, altered adhesion, and decreased response to SDF-1α (Bazzoni et al., 1996; Gordon et al., 1987; Kramer et al., 1999; Salgia et al., 1997; Salgia et al., 1999; Verfaillie et al., 1992; Wertheim et al., 2003). These abnormalities may play a critical role in the progression of CML, as altered adhesion and increased motility may contribute to premature release of CML cells from bone marrow and accumulation of these cells in peripheral hematopoietic tissues such as blood and spleen. The abnormal cytoskeletal function observed in CML cells is caused by the Bcr-Abl oncoprotein, because expression of Bcr-Abl in hematopoietic cell lines is sufficient to induce these abnormalities (Kramer et al., 1999; McWhirter and Wang, 1997; Salgia et al., 1997; Wertheim et al., 2002; Wertheim et al., 2003). Several lines of evidence suggest that Bcr-Abl deregulates β1-integrin function, which may, at least in part, be responsible for altered adhesion and increased motility of CML cells (Bhatia et al., 1996; Salesse and Verfaillie, 2002; Skorski et al., 1998; Verfaillie et al., 1992). The β1-integrin is a subunit of integrin receptors found in hematopoietic cells that link the cytoskeleton to the extracellular matrix (Teixido et al., 1992; Verfaillie et al., 1992; Williams et al., 1991). Although the expression of Bcr-Abl in CML cells did not alter the protein levels of membrane β1-integrin (Bazzoni et al., 1996; Verfaillie et al., 1992; Wertheim et al., 2002), it induced abnormal interactions between β1-integrin and the actin cytoskeleton (Bhatia et al., 1999). Bhatia et al. proposed that abnormal integrin-cytoskeletal interaction restricts the mobility of integrin receptors and results in defective integrin function in CML progenitor cells (Bhatia et al., 1999). However, the precise mechanisms of Bcr-Abl-induced abnormal interaction of integrin and actin cytoskeleton remain largely unknown.
In previous studies we found that a mutant p185Bcr-Abl with the deletion of the Src homology 3 (SH3) domain and C-terminal proline-rich sequences (p185ΔSH3ΔC), failed to induce a CML-like disease in a bone marrow transplant (BMT) mouse model (Dai et al., 2001). One pathological difference that distinguishes p185ΔSH3ΔC BMT mice from wild type p185Bcr-Abl (p185wt) BMT mice is the lack of massive splenomegaly, a phenotype that is believed to result from the massive accumulation and retention of both mature and immature myeloid cells in the spleen. Notably, a proportion of p185ΔSH3ΔC BMT mice developed high peripheral white blood cell counts with normal spleen weight, suggesting that the p185ΔSH3ΔC was capable of stimulating cell proliferation and survival but failed to induce the accumulation and retention of myeloid cells in the spleen (Dai et al., 2001). These observations led us to hypothesize that p185ΔSH3ΔC may have a defect in stimulating abnormal cytoskeletal function. The SH3 domain and C-terminal proline-rich sequences are required for Bcr-Abl to bind to Abi1 and Abi2 (Dai et al., 2001; Dai and Pendergast, 1995; Shi et al., 1995). Given that Abi signaling plays a key role in regulating actin polymerization, we sought to test if this pathway is involved in Bcr-Abl-induced abnormalities of cytoskeletal function. Here we provide evidence that, through direct interaction with the SH3 domain and C-terminal proline-rich sequences of Bcr-Abl, Abi1 mediates Bcr-Abl-induced actin cytoskeleton remodeling and β1-integrin clustering. We also demonstrate that this pathway is required for Bcr-Abl to stimulate hematopoietic cell adhesion on fibronectin-coated surfaces.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell lines and reagents
Ba/F3 and 32D cells were grown in RPMI containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 15% WEHI3-conditioned medium as a source of IL-3. The Ba/F3 and 32D cell lines expressing wild type and the mutant forms of p185Bcr-Abl were generated by retroviral transduction, as described previously (Dai et al., 2001). Retroviral packaging cell line Bosc 23, kindly provided by Dr. W. S. Pear (University of Pennsylvania), was grown in DMEM containing 10% FBS. The preparation of rabbit polyclonal antibodies against Abi1 and Abi2 has been described previously (Courtney et al., 2000; Dai et al., 1998). The antibodies against WAVE2, p85 subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), and phosphotyrosine-containing proteins were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc. (Santa Cruz, CA). The monoclonal antibodies for Abl and β1-integrin (Ha2/5 and 9EG7) were obtained from BD Pharmingen (San Diego, CA). The other antibodies used were: monoclonal anti-β-actin (Sigma), FITC-conjugated monoclonal anti-β1-integrin (Chemicon International), anti-paxillin (BD Transduction Lab), and anti-vinculin (Sigma). The Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitor, imatinib mesylate (Gleevec), was kindly provided by Dr. J. DeGregori (University of Colorado Health Sciences Center). The protease inhibitor cocktail was purchased from Sigma.
Retroviral constructs
The full length cDNA encoding enhanced green fluorescence protein (GFP) was generated by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using pEGFP-C plasmid as template. The resultant cDNA fragment, which contains a 5′ Bam H1 site and 3′ Bgl II/Xho 1/Eco R1 sites, was digested by Bam H1/Eco R1 and subcloned into MSCV at Bgl II and Eco R1 sites. The resultant plasmid, MSCV-GFP, was used to construct the retroviral vectors expressing wild type and mutant forms of GFP-Abi1 and GFP-WAVE2 fusion proteins. Briefly, cDNAs encoding for Abi1 and WAVE2 were generated by PCR, respectively, and subcloned in-frame into MSCV-GFP at Bgl II/Eco R1 sites. The cDNAs encoding for Abi1PPLL were generated using QuikChange site-directed mutagenesis kit (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA) and subcloned into MSCV-GFP at Bgl II/Eco R1 sites, as specified by the manufacturer. The mutations were confirmed by sequencing analysis.
Fluorescence microscopy
Cultured Ba/F3 cell lines were starved for 4 hours in RPMI containing 0.5% BSA before fixation and staining. The starved cells were then fixed in 3.7% formaldehyde in PBS for 10 min, permeablized in 0.2% Triton X-100/PBS for 5 minutes, and stained with 50 μg/ml TRITC-conjugated phalloidin (Sigma, St. Louis, MO) in PBS. After washing extensively with PBS and a brief staining with DAPI (Sigma, St. Louis, MO) to visualize nuclei, 5-10 × 103 cells were loaded per slide by cytospin and mounted with Vectashield mounting medium (Vector, Burlingame, CA). Images were captured and analyzed using Zeiss two-photon laser scanning confocal microscope with LSM 5 Image software. For indirect immuno-fluorescence staining of Abi1 and Bcr-Abl, cells stained with TRITC-phalloidin as above were blocked with 2%BSA in PBS for 1 hour, and incubated with appropriate antibodies diluted in 1% BSA/PBS for 2 hours. After extensively washing with PBS, cells were incubated with Alexa-conjugated secondary antibodies (1:500; Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR) for 1 hour, washed again with PBS, and mounted on slides, as described above. The immuno-fluorescence staining for β1-intergrin was performed in both suspension cells and the cells adherent to fibronectin-coated surfaces as described above, except that for suspension cells, they were fixed in 3.7% formaldehyde in PBS for 10 min without permeablization.
Biochemical assays
Subcellular fractionation experiment was performed as described (Wartmann et al, 1997) with modifications. Briefly, cells were disrupted by passing through 27G1/2 needle in hypotonic buffer (25 mM Hepes, pH 7.5, 2 mM EDTA, 2 mM NaVO4, 5 mM NaF, and 1% protease inhibitor cocktail), and centrifuged for 15 min at 600 × g to separate the nuclei and cytosol/membrane fractions. The supernatant was then centrifuged for 30 minutes at 100,000 g to yield the cytosol (S100) fraction and the membrane pellet (P100). For co-immunoprecipitation analysis, control Ba/F3 cells and the Ba/F3 cells expressing wild type and mutant forms of p185Bcr-Abl were lysed in lysis buffer (20 mM Hepes, pH7.2; 150 mM NaCl, 1% Triton X-100, and 10 % glycerol) and incubated with appropriate antibodies bound to Sepharose beads. The immunoprecipitates were separated on SDS-PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose, and immunoblotted with appropriate antibodies.
Cell adhesion assay
Ba/F3 cells and Ba/F3 cells expressing either p185wt alone or p185wt plus Abi1PPLL were suspended in RPMI+10%FBS with (Ba/F3) or without (Ba/F3 expressing p185wt or p185wt plus Abi1PPLL) 15% WEHI3-conditioned medium at a density of 1 × 105 cells/ml. The cells were plated in 6-well plates (2.5 ml/well) coated with fibronectin (BD Biosciences, Bedford, MA) and incubated at 37°C/5%CO2 for 16 hours. Nonadherent cells were removed and adherent cells were washed three times with 1 ml pre-warmed RPMI medium. The adherent cells then were trypsinized and collected. Both nonadherent and adherent cells were counted to determine the percentage of adherent cells. For treatment of p185wt-transformed cells with blocking antibody, either Ha2/5 anti-integrin antibody or control hamster IgM was added to cells (4 μg/2.5×105 cells) in fibronectin-coated 6-well plate. The cells were incubated at 37°C/5%CO2 for 16 hours and cell adhesion was determined as described above.
RESULTS
Differential regulation of Abi1 and Abi2 by Bcr-Abl in hematopoietic cells
We have previously shown that Abi proteins undergo ubiquitin-dependent degradation in hematopoietic cells transformed by Bcr-Abl (Dai et al., 1998). Although the antibody used in the previous studies was raised against Abi2 and was immunoreactive preferentially to Abi2, it cross-reacted, albeit weakly, with in vitro synthesized Abi1 (supplemental Fig. 1A). Without a specific antibody to Abi1, our earlier studies were unable to distinguish if the Bcr-Abl-induced degradation of Abi is specific for Abi2 or if it is common to both Abi1 and Abi2 (Dai et al., 1998). To address this question, we made use of an antibody raised against a peptide with sequences unique to Abi1 (Courtney et al., 2000), This antibody specifically recognizes Abi1 with no detectable cross-reactivity to Abi2 (supplemental Fig. 1A). Using this antibody, we examined the expression of Abi1 in murine pro-B cell line Ba/F3 and myeloid cell line 32D, as well as their derivatives transformed by p185wt. Abi1 was readily detected in control Ba/F3 and 32D cells transduced with an empty retroviral vector (Fig. 1A). There was no significant decrease in Abi1 protein level in Ba/F3 and 32D cells transformed by Bcr-Abl, as compared to the control cells (Fig. 1A). This is in contrast to our previous studies using Abi2 antibody, which detected immuno-reactive proteins only in control Ba/F3 and 32D cells but not in those transformed by p185wt (Dai, et al., 1998, also see supplemental Fig. 1B). Thus, the result suggests that Abi2, but not Abi1, is down-regulated by Bcr-Abl in hematopoietic cells.
Fig. 1.
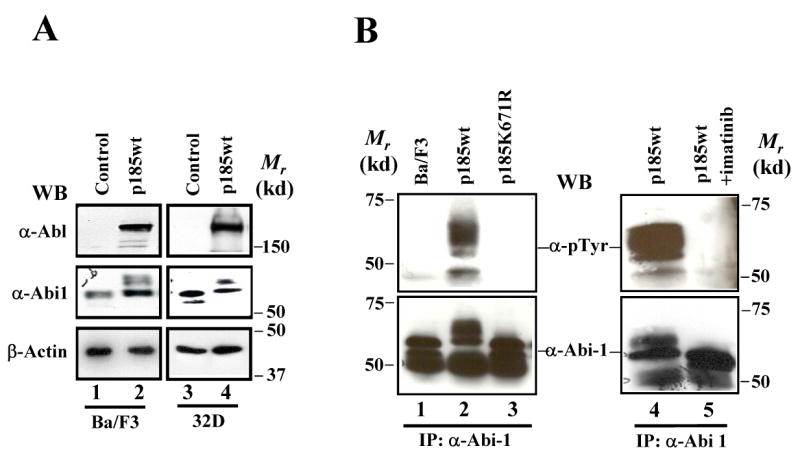
Abi1 is a downstream substrate of Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase. A. Ba/F3 and 32D cells were transduced with empty retroviral vector (control) or retroviral vector expressing p185Bcr-Abl (p185wt). Total lysates from 1×106 cells were analyzed by Western blot (WB) using indicated antibodies. B. Tyrosine phosphorylation of Abi1 in Bcr-Abl-transformed hematopoietic cells. Ba/F3 cells and the Ba/F3 expressing either p185wt or p185K671R were treated with or without 1 μM imatinib mesylate, as indicated. The lysates from 2×107 cells were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-Abi1 antibody, followed by Western blot analysis using anti-phosphotyrosine (α-pTyr) antibody (upper panel). The blots were then stripped and re-probed with anti-Abi1 antibody (lower panel). The relative molecular mass (Mr) is indicated and presented as kilodaltons (kd).
We noticed that the Bcr-Abl transformation induced additional bands with slower mobility on Western blots that were recognized by Abi1 antibody (Fig. 1A, middle panel, compare lanes 2 and 4 to lanes 1 and 3). The slower mobility species represent tyrosine-phosphorylated Abi1 as these proteins can be immunoprecipitated by Abi1 antibody and recognized either by Abi1 antibody or the antibody specific to phosphotyrosine proteins on Western blots (Fig. 1B, lanes 2 and 4). A kinase-deficient Bcr-Abl mutant (p185K671R) was unable to induce Abi1 tyrosine phosphorylation (Fig. 1B, lane 3), suggesting that the tyrosine kinase activity of Bcr-Abl is required for induction of Abi1 tyrosine phosphorylation. In support of this notion, the tyrosine phosphorylation of Abi1 was completely inhibited by imatinib mesylate, a compound that specifically blocks Bcr-Abl kinase activity (Fig. 1B, lane 5). Collectively, these results demonstrated that Abi1 and Abi2 are regulated differently by Bcr-Abl and that Abi1 is a downstream substrate of Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase in hematopoietic cells.
Bcr-Abl stimulates membrane translocation of Abi1 and WAVE2
To determine if Bcr-Abl signaling affects the interaction between Abi1 and WAVE, we examined complex formation between WAVE and Abi1 in Ba/F3 cells transformed by p185wt and compared it to that in control Ba/F3 cells transduced with an empty retroviral vector. Expression of WAVE2 in control Ba/F3 cells and the Ba/F3 cells transformed by p185wt was readily detected by Western blot analysis (Fig. 2A). WAVE2 was co-immunoprecipitated by Abi1 antibody in control Ba/F3 cells as well as in Ba/F3 cells transformed by p185wt (Fig. 2B, left panel), suggesting that these proteins form a complex in vivo and that the complex formation was not affected by Bcr-Abl transformation. Consistent with this notion, the reciprocal immunoprecipitation with WAVE2 antibody demonstrated that both tyrosine-phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated forms of Abi1 were capable of binding to WAVE2 (Fig. 2B, lane 5). Based on these results, we conclude that it is unlikely that the signaling from Bcr-Abl to Abi1 plays a major role in regulation of Abi1/WAVE2 complex formation in Ba/F3 cells.
Fig. 2.
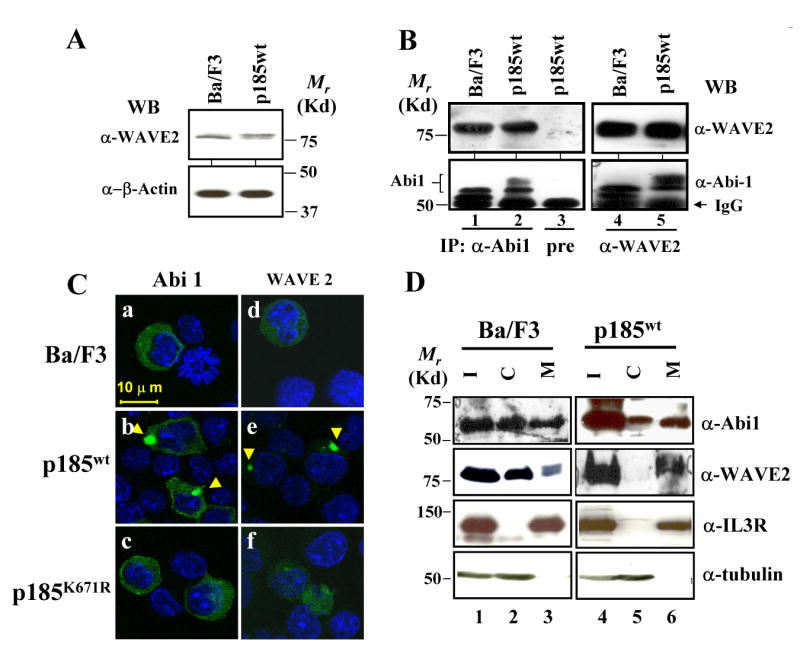
Complex formation and membrane translocation of Abi1/WAVE2 in Ba/F3 cells transformed by p185wt. A. Expression of WAVE2 in Ba/F3 and p185wt-transformed Ba/F3 cells. Total lysates from 2×105 cells were analyzed by Western blot using indicated antibodies. B. Complex formation of Abi1 and WAVE2. The lysates from Ba/F3 cells transduced with either an empty retroviral vector (control) or the retroviral vector expressing p185wt were immunoprecipitated with anti-Abi1 antibody, anti-WAVE2 antibody, or pre-immune rabbit serum (pre), as indicated. The immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blot using indicated antibodies. C. Bcr-Abl-induced membrane translocation of Abi1/WAVE2. Retroviral vectors expressing GFP-Abi1 (panels a-c) and GFP-WAVE2 (panels d-f) were introduced into Ba/F3 cells or Ba/F3 cells expressing wild type and the mutant form of p185Bcr-Abl, as indicated. The subcellular localization of GFP-Abi1 and GFP-WAVE2 was analyzed by two-photon confocal microscopy. Nuclei were stained by DAPI (blue). Arrowheads indicate the membrane localization of Abi1 and WAVE2. Bar: 10 μm. D. Subcellular distributions of Abi1 and WAVE2 in Ba/F3 and the Ba/F3 transformed by p185wt. The Ba/F3 cells and the Ba/F3 cells transformed by p185wt were lysed and fractionated to separate the cytosol (C) and plasma membrane (M). The equal amounts of total lysate (I, input), cytosol, and membrane fractions were separated on SDS-PAGE and analyzed by Western blot using antibodies specific to Abi1 and WAVE2, as indicated. To monitor the quality of the fractionation, the blot was also probed with the antibodies to the β subunit of IL-3 receptor and α-tubulin, the proteins known to be in membrane and cytosol, respectively.
Next, we tested if Bcr-Abl signaling plays a role in regulating subcellular localization of Abi1 and WAVE2. To this end, retroviruses expressing either a GFP-tagged Abi1 or WAVE2 were generated and introduced into Ba/F3 cells as well as the Ba/F3 cells expressing p185wt or p185K671R. The subcellular distribution of GFP-Abi1 and GFP-WAVE2 were then examined by two-photon confocal microscopy. Both GFP-Abi1 and GFP-WAVE2 exhibited a diffuse cytoplasmic distribution in control Ba/F3 cells (Fig. 2C, panels a and d). By contrast, a polarized cytoplasmic localization of GFP-Abi1 and GFP-WAVE2 was observed in Ba/F3 cells transformed by p185wt (Fig. 2C, panels b and e). In particular, Abi1 and WAVE2 were found concentrated in a spot adjacent to the membrane. This distribution pattern of Abi1 is not an artifact caused by overexpression or by GFP fusion, as the same pattern was observed for endogenous Abi1 in p185wt-transformed cells by indirect immuno-fluorescence staining (see Fig. 3). The fact that a kinase deficient p185K671R was unable to induce such a pattern (Fig. 2C, panels c and f) further supports that the polarized cytoplasmic localization of GFP-Abi1 and WAVE2 was indeed induced by Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase.
Fig. 3.
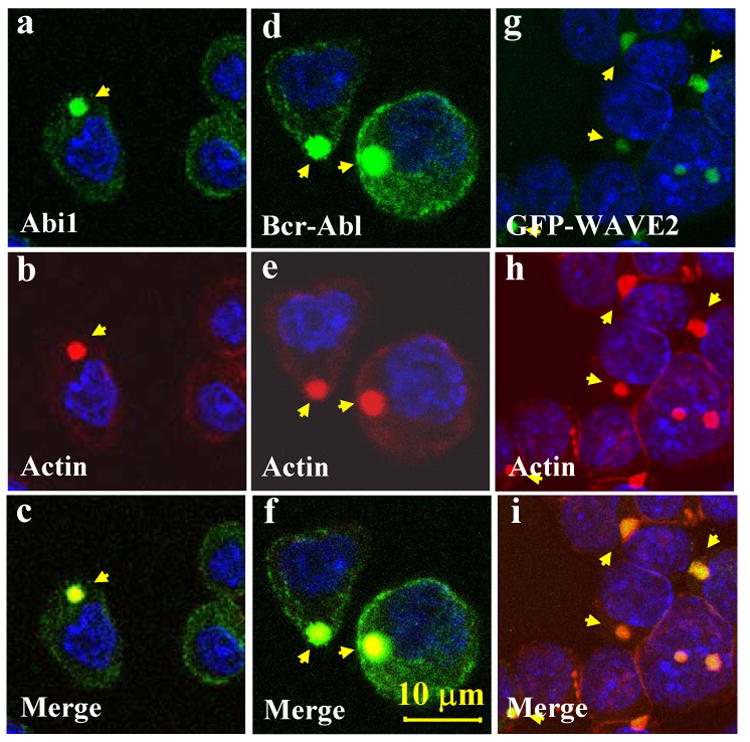
Co-localization of Abi1, Bcr-Abl and WAVE2 with an abnormal F-actin-rich structure. Ba/F3 cells expressing p185wt were probed with anti-Abi1 (a-c) and anti-Abl (d-f) antibodies, respectively. This was followed by staining with FITC-conjugated secondary antibody. Cells were then counterstained with TRITC-conjugated phalloidin and DAPI to visualize F-actin and nuclei, respectively. In panels g-i, the Ba/F3 cells expressing p185wt were transduced with retrovirus expressing GFP-WAVE2 and counterstained by TRITC-conjugated phalloidin and DAPI. Subcellular distribution of Abi1 (a, green), Bcr-Abl (d, green), GFP-WAVE2 (g, green), and F-actin structures (b, e, h, red) were visualized by two-photon confocal microscopy, as indicated by arrows. The co-localization of these proteins with abnormal F-actin structure is shown by merged images (c, f, i). Bar: 10 μm.
To determine if Abi1 and WAVE2 were associated with plasma membrane in Bcr-Abl transformed cells, a subcellular fractionation experiment was performed. As shown in Fig. 2D, Abi1 and WAVE2 were found in both cytosol and membrane fractions in parental Ba/F3 cells. However, we observed an increase in membrane-associated Abi1 and WAVE2 in cells transformed by p185wt Bcr-Abl (Fig. 2D, compare lane 6 to lane 5). This finding is consistent with the observation that, upon Bcr-Abl transformation, most Abi1 and WAVE2 were relocated to a site adjacent to the membrane (Fig. 2C). Together, our results indicate that Bcr-Abl transformation induces a translocation of Abi1/WAVE2 to plasma membrane.
Abi1, Bcr-Abl, and WAVE2 co-localize with an F-actin-enriched structure in Bcr-Abl-transformed hematopoietic cells
Given that the Abi1/WAVE2 pathway plays a central role in regulating actin polymerization (Stradal et al., 2004), we asked if the membrane translocation of Abi1/WAVE2 is associated with Bcr-Abl-induced abnormal actin cytoskeleton remodeling. Consistent with previous reports (McWhirter and Wang, 1997; Salgia et al., 1997; Skourides et al., 1999), expression of p185wt in Ba/F3 cells induced a profound actin cytoskeleton remodeling. A spot intensively stained by TRITC-conjugated phalloidin, indicative of an aggregate of filamentous actin (F-actin), was observed in p185wt-transformed cells (supplemental Fig. 2A, panel b). A similar structure was also observed in hematopoietic cells isolated from Bcr-Abl-positive leukemia patients (Bhatia et al., 1999, Li and Dai, unpublished data). It is notable that the F-actin-enriched structure induced by p185wt appeared similar to the pattern of p185wt-induced Abi1 and WAVE2 distribution in both size and localization (compare the supplemental Fig. 2, panel b to Fig. 2C, panels b and e). The indirect immuno-fluorescence staining of p185wt-transformed cells with anti-Abi1 or anti-Abl antibodies followed by counterstaining with TRITC-conjugated phalloidin revealed that Abi1 (Fig. 3, panels a-c) and Bcr-Abl (Fig. 3, panels d-f) co-localize with this F-actin-enriched structure. To determine if WAVE2 also co-localizes with this abnormal structure, the p185wt-transformed Ba/F3 cells were transduced with the retrovirus expressing GFP-WAVE2 and cells were counterstained by TRITC-conjugated phalloidin. The GFP-WAVE2 and F-actin were visualized by two-photon confocal microscopy. As shown in Fig. 3, WAVE2 (panels g-i) also co-localizes with the F-actin-enriched structure.
β1-integrin, paxillin, and vinculin are clustered and associated with F-actin-enriched structures in Bcr-Abl-transformed cells
Actin cytoskeleton organization plays a key role in regulation of integrin distribution and function (Schwartz et al., 1995). To determine if the abnormal F-actin-enriched structures induced by p185wt affects membrane distribution of integrin, we stained control Ba/F3 cells and the Ba/F3 cells expressing either p185wt or p185K671R with FITC-conjugated antibody specific for β1-integrin, a common subunit of integrin receptors found in hematopoietic cells (Teixido et al., 1992; Verfaillie et al., 1992). As shown in Fig. 4A (left panel), the control Ba/F3 cells displayed even membrane distribution of β1-integrin. In contrast, β1-integrin in Ba/F3 cells transformed by p185wt was clustered (Fig. 4A, middle panel). The β1-integrin clustering was Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase dependent, as the kinase-deficient p185K671R failed to induce such clustering (Fig. 4A, right panel). To determine if the clustered β1-integrin is associated with abnormal actin-enriched structure, cells were counterstained with TRITC-conjugated phalloidin following the immuno-fluorescence staining with anti-β1-integrin antibody. As shown in Fig. 4B (panels a-c), the clustered β1-integrin was found to co-localize with the abnormal actin-enriched structures. Furthermore, paxillin (Fig. 4B, panels d-f) and vinculin (Fig. 4B, panels g-i), the adhesion proteins known to link integrin to the cytoskeleton (Burridge et al., 1988), were also found in association with the F-actin-enriched structures in p185wt-expressing cells. The association of the F-actin-enriched structures with adhesion proteins and β1-integrin appeared to be specific, as α-tubulin, a cytoplasmic protein, was not found to co-localize with this abnormal structural complex (Fig. 4B, panels j-l). Together, these results suggest that p185wt-induced F-actin-enriched structures interacted with β1-integrin, possibly through adhesion-associated molecules such as paxillin and vinculin.
Fig. 4.
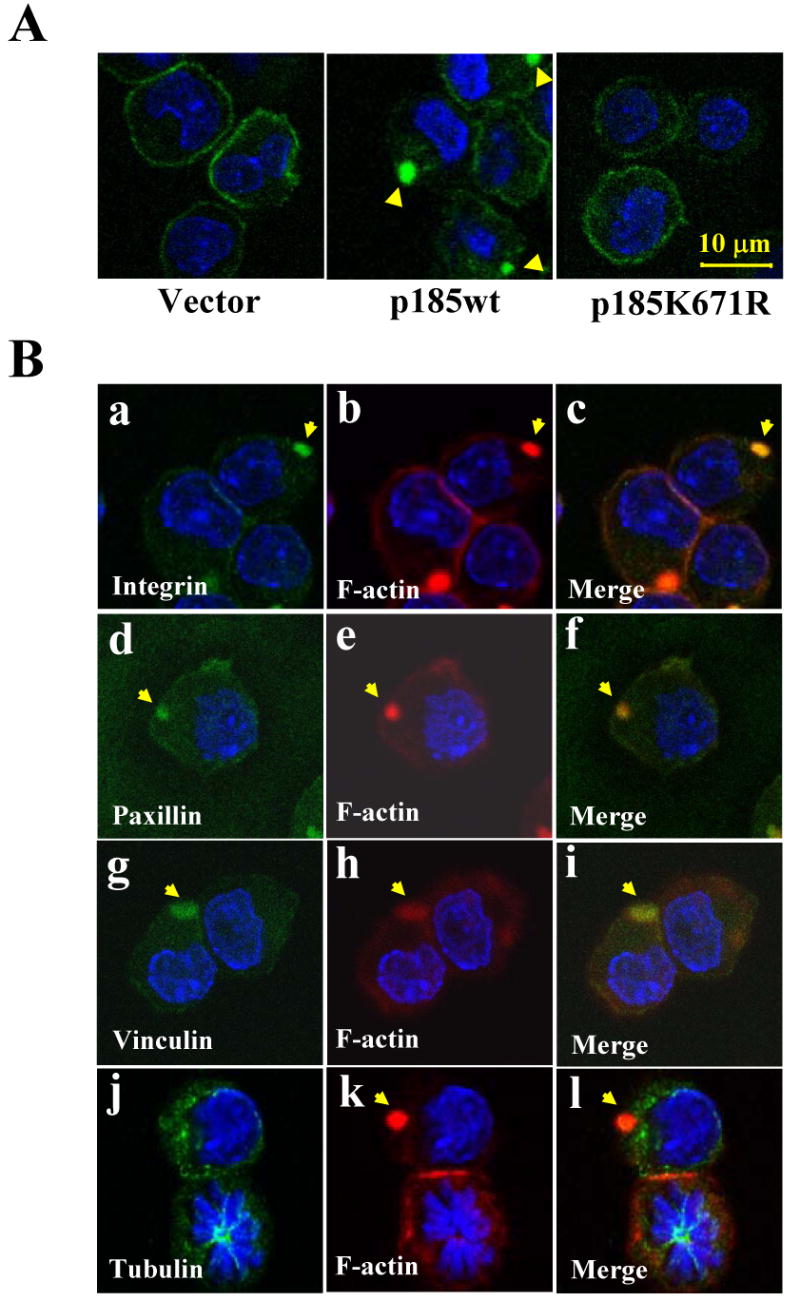
The expression of p185Bcr-Abl induced integrin clustering. A. β1-integrin clustering in p185wt-transformed Ba/F3 cells. The Ba/F3 cells transduced with indicated retroviruses were starved, fixed, and stained with FITC-conjugated monoclonal antibody against β1-integrin. Cells were then stained with DAPI to visualize nuclei. Images were captured by two-photon confocal microscopy and the β1-integrin clustering is indicated by arrowhead. Bar: 10 μm. B. Co-localization of β1-integrin, paxillin, and vinculin with abnormal actin-enriched structure. The Ba/F3 cells expressing p185wt were starved, fixed, permeablized, and probed with FITC-conjugated antibodies against β1-integrin, paxillin, tubulin, and vinculin (green), as indicated. The cells were then counterstained with TRITC-conjugated phalloidin (red) and DAPI (blue) to visualize F-actin and nuclei, respectively. Images were captured by two-photon confocal microscopy and the co-localization of integrin, paxillin, and vinculin with abnormal actin-enriched structure is shown in merged images, as indicated by arrows. Bar: 10 μm.
PI3K pathway is not required for Bcr-Abl-induced Abi1 translocation and F-actin remodeling
Innocenti et al. reported recently that Abi1 interacts with p85 subunit of PI3K to form a multimolecular complex localized in membrane ruffle (Innocenti et al., 2003). The formation of this multimolecular complex is critical for activation of Rac and Rac-dependent actin remodeling (Innocenti et al., 2003). To test if PI3K pathway is also involved in Bcr-Abl-induced Abi1 translocation and F-actin remodeling, three approaches were explored. First, immunoprecipitation followed by Western blotting was performed to determine if Abi1 forms a complex with p85 subunit of PI3K. As shown in Fig. 5A (left panel, lanes 3 and 4), under the condition in which WAVE2 was co-immunoprecipitated by Abi1 antibody, we were unable to detect p85 in anti-Abi1 immunoprecipitates from Ba/F3 and p185wt-transformed cells. Similarly, the anti-p85 antibodies failed to co-immunoprecipitate Abi1 from Ba/F3 cells and p185wt-transformed cells (Fig. 5A, right panel). Second, because the phosphorylation of tyrosine 407 in Abi1 is required for its interaction with p85 as well as for growth factor-stimulated actin remodeling (Innocenti et al., 2003), we asked if the mutation of this tyrosine affects the Bcr-Abl-induced Abi1 translocation and F-actin remodeling. A substitution of tyrosine 407 with phenylalanine in Abi1 (Abi1Y407F) did not reduce the overall tyrosine phosphorylation of Abi1Y407F in p185wt-transformed cells, as compared to wild type Abi1 (Fig. 5B, compare lane 3 to lane2 in left panel). The mutant Abi1 displayed a similar pattern of subcellular distribution as that of wild type Abi1 when expressed as a GFP-fusion protein in p185wt-transformed Ba/F3 cells (Fig. 5B and supplemental Fig. 2B). Further, the expression of Abi1Y407F had no effects on p185wt-induced F-actin remodeling (supplemental Fig. 2B, panel h). Together, these results suggest that the tyrosine 407 of Abi1 is not a major phosphorylation site required for Bcr-Abl-induced Abi1 translocation and F-actin remodeling. Last, we made use of a specific PI3K inhibitor, LY294002, to test if the pharmacological inhibition of PI3K has any effect on Bcr-Abl-induced Abi1 membrane translocation and F-actin remodeling. The p185wt-transformed Ba/F3 cells were transduced with retrovirus expressing GFP-Abi1 and treated with either LY294002 or Bcr-Abl inhibitor imatinib. In contrast to imatinib, which effectively inhibited the Bcr-Abl-induced Abi1 translocation (Fig. 5C, middle panel), LY294002 had no effects on the membrane translocation of GFP-Abi1 (Fig. 5C, right panel). Similarly, the formation of F-actin-enriched structures in p185wt-transformed Ba/F3 cells was inhibited by imatinib (supplemental Fig. 2A, panel c), but not LY294002 (supplemental Fig. 2A, panel d). Collectively, the results from these studies support that Bcr-Abl induces Abi1 translocation and F-actin remodeling independently of PI3K pathway.
Fig. 5.
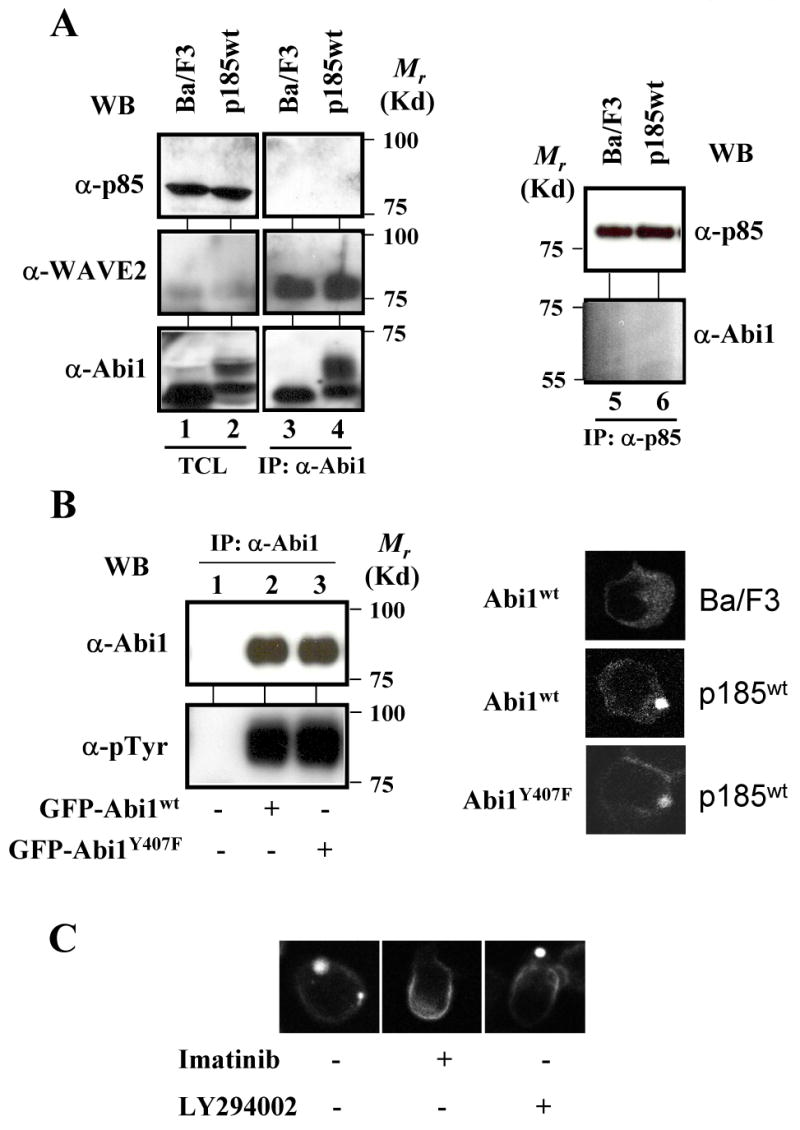
The PI3K pathway is not required for Bcr-Abl-induced membrane translocation of Abi1. A. Abi1 does not form complex with p85 subunit of PI3K in Ba/F3 cells and the Ba/F3 cells transformed by p185wt. The lysates from 2×107 Ba/F3 cells and the Ba/F3 cells transformed by p185wt were immunoprecipitated by anti-Abi1 (lanes 3 and 4, left panel) and anti-p85 (lanes 5 and 6, right panel) antibodies, respectively. The immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blotting using the indicated antibodies. A portion of total cell lysates (TCL) equivalent to 2×105 cells (p85 and WAVE2), or 1×106 cells (Abi1) was also analyzed by Western blotting to show the expression level of Abi1, p85, and WAVE2 (lanes 1 and 2, left panel). B. The mutation at tyrosine 407 does not affect the Bcr-Abl-induced membrane translocation of Abi1Y407F. Left panel: lysates from p185wt-transformed Ba/F3 cells (lane 1) and the p185wt-transformed Ba/F3 cells expressing either GFP-Abi1 (lane 2) or GFP-Abi1Y407F (lane 3) were immunoprecipitated by anti-Abi1 antibody and analyzed by Western blotting using the antibodies indicated. Right panel: Ba/F3 cells and Ba/F3 cells transformed by p185wt, as indicated, were transduced with retroviruses expressing either GFP-Abi1 or GFP-Abi1Y407F. The subcellular distribution of GFP-fusion proteins was visualized by 2-photon confocal microscopy. C. LY294002 failed to inhibit Bcr-Abl-induced membrane translocation of GFP-Abi1. The p185wt-transformed Ba/F3 cells were transduced with the retrovirus expressing GFP-Abi1. The cells were then left untreated or treated with either 10 μM imatinib or 50 μM LY294002, as indicated, for 8 hours. The cells were fixed and counterstained with TRITC-conjugated phalloidin and DAPI to visualize the F-actin and nuclei, respectively. Images were captured by two-photon confocal microscopy. A color picture is presented in supplemental Fig. 2B.
Abi1 pathway is required for Bcr-Abl-induced actin cytoskeleton remodeling and integrin clustering
To determine if the Abi1 pathway is required for Bcr-Abl-induced abnormal actin remodeling and integrin clustering, we made use of p185ΔSH3ΔC, a mutant Bcr-Abl with the deletion of the SH3 domain and C-terminal proline-rich sequences (supplemental Fig. 3A). In previous studies we and others have shown that the SH3 domain and C-terminal proline-rich sequences are required for Bcr-Abl to bind to Abi1 and Abi2 (Dai et al., 2001; Shi et al., 1995). Deletion of these sequences did not affect tyrosine kinase activity of p185ΔSH3ΔC (Dai et al., 2001), but completely abolished its ability to bind to Abi1 and to induce Abi1 tyrosine phosphorylation (supplemental Fig. 3B). Deletion of these sequences also caused the inability of p185ΔSH3ΔC to induce membrane translocation of Abi1 (Fig. 6, panel b) and WAVE2 (Fig. 6, panel d) in Ba/F3 cells. Together, these results indicate that p185ΔSH3ΔC is defective in signaling to the Abi1 pathway. Correlated with this defect, p185ΔSH3ΔC failed to induce abnormal F-actin rich structures (Fig. 6, panel h) and β1-integrin clustering (Fig. 6, panel f) when expressed in Ba/F3 cells. These results are consistent with a role of Abi1 pathway in Bcr-Abl-induced abnormal actin remodeling and integrin clustering.
Fig. 6.
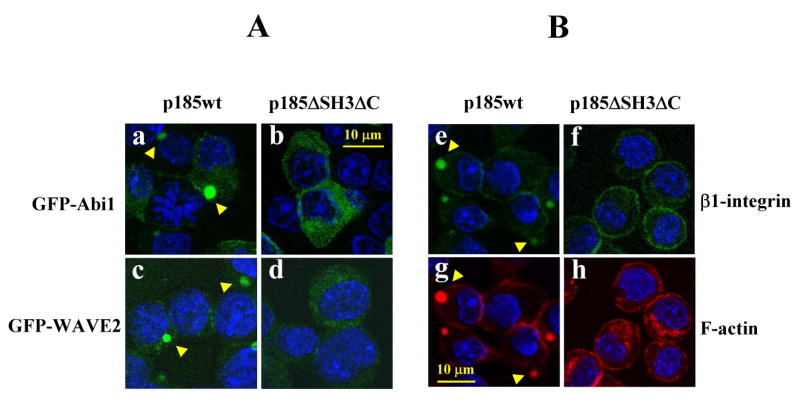
The p185ΔSH3ΔC failed to induce the membrane translocation of Abi1/WAVE2, integrin clustering, and abnormal actin remodeling. A. Ba/F3 cells expressing either p185wt (a and c) or p185ΔSH3Δc (b and d) were transduced with the retroviral vectors expressing either GFP-Abi1 (a and b) or GFP-WAVE2 (c and d). The cells were fixed and GFP-fusion proteins were visualized by 2-photon confocal microscopy. B. Ba/F3 cells transduced with either p185wt (e and g) or p185ΔSH3ΔC (f and h) were fixed and incubated with FITC-conjugated monoclonal antibody specific for β1-integrin (e and f). The cells were also stained with TRITC-conjugated phalloidin to visualize F-actin (g and h). The nuclei of the cells shown in C and D were stained by DAPI (blue) and the arrowheads indicate the subcellular localization of GFP-Abi1 (a), WAVE2 (c), clustering β1-integrin (e), as well as abnormal actin-enriched structures (g) in p185wt-transformed cells. Bar: 10 μm.
In addition to Abi1, the SH3 domain and C-terminal proline-rich sequences of Bcr-Abl also interact with other signaling molecules. It is therefore possible that the failure of p185ΔSH3ΔC to induce actin-enriched structures is due to its inability of activating these pathways, rather than Abi1 pathway. To directly test the role of the Abi1 pathway in Bcr-Abl-induced abnormal actin remodeling, we generated Abi1PPLL, a mutant Abi1 in which the proline residues 180 and 434 in the PXXP motif and the SH3 domain, respectively, are replaced by leucine (Fig. 7A). Previous studies suggest that proline 180 is likely to be involved in the interaction with Abl SH3 domain (Dai and Pendergast, 1995; Ren et al., 1994), whereas proline 434 is highly conserved among a diverse set of SH3 domains and is thought to be critical for binding to Abl C-terminal PXXP motif (Dai and Pendergast, 1995; Musacchio et al., 1992; Ren et al., 1994; Van Etten et al., 1995). The mutations of these proline residues resulted in the inability of Abi1PPLL to bind to Bcr-Abl (Fig. 7B) and to be tyrosine-phosphorylated when expressed in p185wt-transformed cells (Fig. 7C). The mutant protein, however, retains the ability to interact with WAVE2 (supplemental Fig. 4A) and Hem1 (supplemental Fig. 4B), a member of Nap1 family proteins specifically expressed in hematopoietic cells (Weiner et al., 2006). We therefore predicted that this mutant Abi1, when overexpressed in p185wt-transformed cells, may serve as a dominant negative molecule to interfere with the signal transduction from Bcr-Abl to endogenous Abi1. To test this, retroviruses expressing GFP-tagged wild type Abi1 and Abi1PPLL were generated and introduced into Ba/F3 cells expressing p185wt. The cells were then stained with TRITC-conjugated phalloidin and subjected to two-photon confocal microscopy analysis. As shown in Fig. 7D, while the wild type Abi1 was found to co-localize with the F-actin-enriched structure, Abi1PPLL displayed a diffuse cytoplasmic distribution in Ba/F3 cells transformed by p185wt. Moreover, no F-actin-enriched structure was observed in p185wt-transformed Ba/F3 cells that express GFP-Abi1PPLL (Fig. 7D, compare panel c to f), indicating that the expression of Abi1PPLL inhibited Bcr-Abl-induced actin cytoskeleton remodeling. This finding, together with the finding that p185ΔSH3ΔC failed to induce the F-actin-enriched structure (Fig. 6), strongly supports a role for Abi1 in Bcr-Abl-induced actin cytoskeleton reorganization.
Fig. 7.
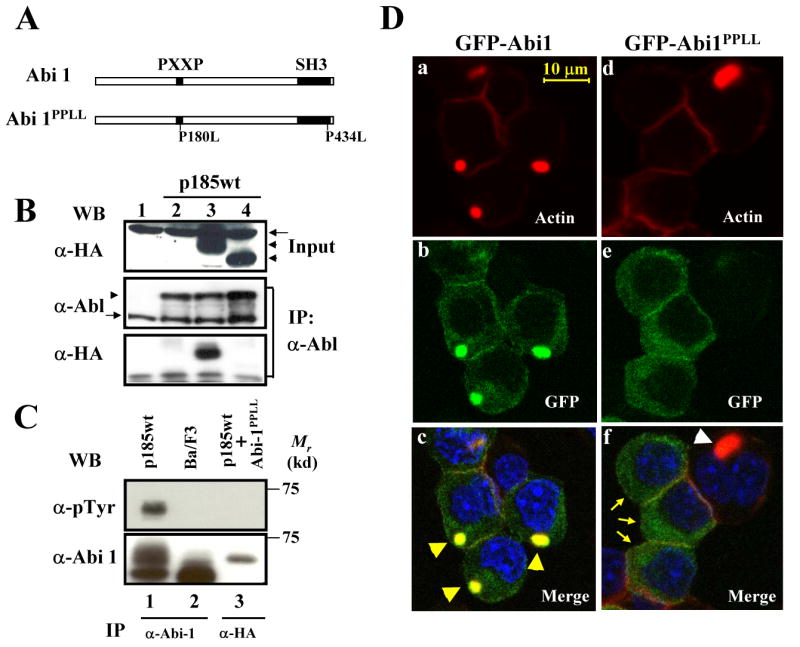
Expression of Abi1PPLL inhibited Bcr-Abl-induced abnormal actin cytoskeleton remodeling. A. Schematic diagram of Abi1 and Abi1PPLL. B. Abi1PPLL is defective in binding to Bcr-Abl. Ba/F3 cells (lane 1) and the Ba/F3 cells expressing p185wt alone (lane 2), p185wt plus HA-tagged Abi1 (lane 3), and p185wt plus HA-tagged Abi1PPLL (lane 4) were lysed and immunoprecipitated with anti-Abl antibody. The immunoprecipitates (middle and lower panels) and 1/50 of total cell lysates used for IP (Input, upper panel) were analyzed by Western blot using indicated antibodies. The HA-tagged Abi1 and Abi1PPLL are indicated by arrowheads, whereas a non-specific band cross-reacted with anti-HA antibody is indicated by arrow (upper panel). The anti-Abl antibody recognized both Bcr-Abl and endogenous c-Abl, as indicated by arrowhead and arrow, respectively (middle panel). C. Abi1PPLL failed to be tyrosine-phosphorylated by Bcr-Abl. Ba/F3 cells (lane 2) and Ba/F3 cells expressing p185wt alone (lane 1) or p185wt plus HA-tagged Abi1PPLL (lane 3), were lysed and immunoprecipitated with indicated antibodies. The immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blot using indicated antibodies. D. Inhibition of Bcr-Abl-induced abnormal actin remodeling by Abi1PPLL. Ba/F3 cells transformed by p185wt were transduced with retroviruses expressing either GFP-Abi1 (a-c) or GFP-Abi1PPLL (d-f). Cells were fixed and stained with TRITC-conjugated phalloidin and DAPI to visualize F-actin (red) and nuclei (blue), respectively. Subcellular localization of GFP-fusion proteins (b, e, green) and F-actin structure (a, d, red) were analyzed by two-photon confocal microscopy. The merged images were also shown (c, f). The arrowheads in panel c indicate abnormal actin-enriched structures that co-localize with GFP-Abi1, whereas arrows in panel f indicate the p185wt-transformed cells that express GFP-Abi1PPLL. An open arrowhead in panel f indicates abnormal actin-enriched structure in a cell that did not express Abi1PPLL. Bar: 10 μm.
Blockade of the Abi1 pathway or β1-integrin function impairs Bcr-Abl-stimulated hematopoietic cell adhesion on fibronectin-coated surfaces
Actin cytoskeleton structure and integrin function are pivotal for control of cell adhesion (Hynes, 2002; Martin et al., 2002; Schwartz and Ginsberg, 2002). The finding that the Abi1 pathway is required for Bcr-Abl to induce abnormal actin remodeling and integrin clustering raises the question as to whether this pathway is responsible for abnormal adhesion of Bcr-Abl-positive leukemic cells to fibronectin, a phenotype thought to play a role in the pathogenesis of CML (Bazzoni et al., 1996; Gordon et al., 1987; Hemmeryckx et al., 2001; Salesse and Verfaillie, 2002; Wertheim et al., 2003). To address this question, we examined the adhesion of p185wt-transformed Ba/F3 cells to fibronectin-coated surfaces and compared it to those of control Ba/F3 cells as well as the Ba/F3 cells expressing p185ΔSH3ΔC, the mutant Bcr-Abl defective in signaling to Abi1. Consistent with the previous reports (Bazzoni et al, 1996, Wertheim et al, 2003), expression of p185wt in Ba/F3 cells increased cell adhesion to fibronectin-coated surfaces threefold compared to parental cells (Fig. 8A). However, the ability of Bcr-Abl to stimulate Ba/F3 cell adhesion was greatly reduced by deletion of the SH3 and C-terminal proline-rich sequences (Fig. 8A, left panel), suggesting that the Abi1 pathway is required for Bcr-Abl to stimulate cell adhesion to fibronectin. This is further supported by study of Abi1PPLL, a mutant Abi1 defective in binding to Bcr-Abl (Fig. 7B). We have shown that expression of Abi1PPLL inhibited Bcr-Abl-induced actin cytoskeleton remodeling (Fig. 7C). Correlating with its inhibitory effect on actin cytoskeleton remodeling, expression of Abi1PPLL in p185wt-transformed Ba/F3 cells resulted in a remarkable decrease of cell adhesion to fibronectin, as compared to parental p185wt-transformed cells (Fig. 8A, right panel).
Fig. 8.
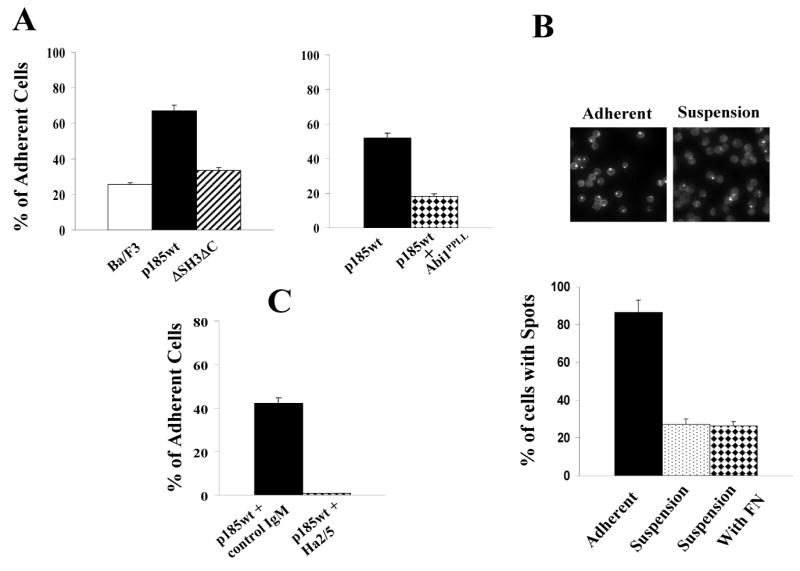
Blockade of Abi1 pathway or β1-integrin function impaired the ability of Bcr-Abl to stimulate cell adhesion to fibronectin. A. Abi1 pathway is required for Bcr-Abl-stimulated cell adhesion to fibronectin-coated surfaces. Left panel: Ba/F3 cells and the Ba/F3 cells expressing either p185wt or p185ΔSH3ΔC were grown in fibroncetin-coated 6-well plate (2.5×105/well) for 16 hours. The total cells and the cells that were adherent to fibronectin-coated surfaces were counted and the percentage of adherent cells calculated. The vertical axis shows the percentage of the adherent cells and is expressed as the average +/− S.D. of duplicate wells. Data are representative of two independent experiments. Right panel: The Ba/F3 cells expressing p185wt alone or p185wt plus Abi1PPLL were grown in fibroncetin-coated plate (2.5×105/well) for 16 hours. The total cells and the cells that were adherent to fibronectin-coated surfaces were counted and the percentage of adherent cells calculated. The data represent the average +/− S.D of triplicate wells. B. The F-actin-rich structures are enriched in adherent p185wt-transformed Ba/F3 cells. The p185wt-transformed Ba/F3 cells were grown in fibronectin-coated plates with or without fibronectin supplemented in medium (5 μg/ml) for 16 hours. Adherent and non-adherent cells were harvested separately and stained by TRITC-conjugated phalloidin and DAPI to visualize F-actin and nuclei, respectively, by flurescence microscopy (upper panel). The percentage of the cells containing the F-actin-rich structures (spots) from three randomly selected fields in adherent cells as well as non-adherent cells was statistically calculated and expressed as the average +/− S.D. (lower panel). The data is a representative of three independent experiments. C. Bcr-Abl-stimulated cell adhesion to fibronectin is β1-integrin dependent. The p185wt-transformed Ba/F3 cells were treated with either Ha2/5 or a control hamster IgM (4 μg/2.5×105 cells) and plated in fibroncetin-coated plate (2.5×105 cells/well) for 16 hours. The total cells and the cells that were adherent to fibronectin-coated surfaces were counted and the percentage of adherent cells calculated. The data represents the average +/− S.D of triplicate wells and is the representative of two independent experiments.
It is unlikely that the increased cell adhesion to fibronectin in p185wt-transformed cells is caused by an elevation of integrin expression, as no significant increase in β1-integrin protein level was observed among BaF3 cells and the Ba/F3 derivatives expressing the wild type and mutant forms of Bcr-Abl (supplemental Fig. 5). However, the increased adhesion of p185wt-transformed cells to fibronectin-coated surfaces correlated with the induction of the F-actin-enriched structures. This is demonstrated by analysis of the F-actin-enriched structures in p185wt-transformed Ba/F3 cells grown in fibronectin-coated plates. The cells adhered to fibronectin-coated surfaces and those remained in suspension were collected separately and analyzed for F-actin-enriched structures by fluorescence microscopy. As shown in Fig. 8B, greater than 86% of adherent cells displayed abnormal F-actin-enriched structures. In contrast, only 27% of suspension cells were found to have such structures. The enrichment of the F-actin-rich structures in adherent cells is not due to the stimulation by surface-bound fibronectin, as the addition of fibronectin into culture medium did not increase the formation of the F-actin-enriched structures in suspension cells (Fig. 8B). Rather, it is more likely that Bcr-Abl-induced F-actin-enriched structures facilitate cells to adhere to fibronectin-coated surfaces, possibly by promoting integrin clustering. In support of this notion, β1-integrin was found clustered and co-localized with F-actin-enriched structures in adherent Ba/F3 cells transformed by p185wt, but not p185ΔSH3ΔC (supplemental Fig. 6). Furthermore, Bcr-Abl-stimulated cell adhesion to fibronectin is β1-integrin dependent and is abrogated completely by the treatment with Ha2/5 (Fig. 8C), a specific β1-integrin antibody capable of blocking β1-integrin-mediated cell adhesion.
DISCUSSION
Previous work has shown that deletion of the SH3 domain and C-terminal proline-rich sequences of p185Bcr-Abl impaired its ability to induce leukemogenesis (Dai et al., 2001). The mechanism involved, however, was not clear. In this study, we demonstrate that the SH3 domain and C-terminal proline-rich sequences are required for Bcr-Abl to induce the tyrosine phosphorylation of Abi1 and membrane translocation of Abi1/WAVE2. Deletion of these sequences not only abolished the tyrosine phosphorylaion of Abi1 and membrane translocation of Abi1/WAVE2, but also abrogated the ability of Bcr-Abl to induce actin cytoskeleton remodeling and β1-integrin clustering. Mutant Bcr-Abl with the deletion of these sequences is also deficient in stimulating hematopoietic cell adhesion to fibronectin. Furthermore, expression of a mutant Abi1 defective in binding to the SH3 domain and C-terminal proline-rich sequences of Bcr-Abl inhibited abnormal actin cytoskeleton remodeling and Bcr-Abl-stimulated cell adhesion. Together, these findings place Abi1 signaling as an immediate downstream pathway that links p185Bcr-Abl to abnormal cytoskeletal function. These results may provide a mechanistic explanation of why p185ΔSH3ΔC failed to induce CML-like disease in BMT mice (Dai et al., 2001).
Integrin receptors link the force-generating actin cytoskeleton to extracellular matrix and, therefore, play a central role in control of cell adhesion and motility. The integrin function is regulated by not only extracellular matrix, but also actin cytoskeleton and other membrane or intracellular signaling molecules (Hynes, 2002; Martin et al., 2002; Schwartz and Ginsberg, 2002). In Bcr-Abl-positive leukemic cells, integrin function is abnormal and this abnormality is believed to be caused by abnormal integrin-cytoskeletal interaction (Bhatia et al., 1999). The pathways that link Bcr-Abl to abnormal integrin-cytoskeletal interaction, however, remain to be defined. We found that β1-integrin was clustered and was associated with an F-actin-enriched structure in p185wt-transformed Ba/F3 cells. The constitutive clustering of β1-integrin was independent of extracellular stimulation since it was found in the resting p185wt-transformed cells grown in suspension. The interaction of β1-integrin with the abnormal actin-enriched structure, which was induced by p185Bcr-Abl through the Abi1 pathway, is likely a causative event for β1-integrin clustering. This is supported by the finding that the blockade of the signaling from Bcr-Abl to Abi1 abrogated not only abnormal actin cytoskeleton remodeling but also integrin clustering. Thus, our studies show, for the first time, that Abi1 pathway is required for Bcr-Abl to induce abnormal integrin-cytoskeletal interaction. Notably, the F-actin-enriched structures observed in p185wt-transformed cell lines are also present in hematopoietic cells isolated from CML patient (Bhatia et al., 1999, Li and Dai, unpublished data), suggesting that a similar mechanism may also be utilized by CML cells to deregulate integrin function and cell adhesion.
In addition to abnormal cell adhesion, Abi1 pathway may also contribute to other cellular processes critical for leukemic cell homing, such as cell migration and invasion. This is supported by our previous observation that deletion of the SH3 domain and C-terminal proline-rich sequences in Bcr-Abl not only abrogated its signaling to Abi1, but also inhibited its ability to induce spontaneous migration of Ba/F3 cells on fibronectin-coated surfaces (Dai et al., 2001). Consistent with this observation, expression of Abi1PPLL in p185wt-transformed cells not only inhibited Bcr-Abl-induced abnormal actin remodeling and cell adhesion, but also impaired the spontaneous cell migration on fibronectin-coated surfaces (supplemental Fig. 7). Further, ablation of Abi1 in p185wt-transformed Ba/F3 cells by short hairpin RNA not only inhibited Bcr-Abl-stimulated actin cytoskeleton remodeling and cell adhesion, but also impaired Bcr-Abl-induced spontaneous cell migration and leukemogenesis (Yu and Dai, unpublished data). Taken together, these results provide the strong evidence that Abi1 pathway plays an important role in Bcr-Abl-induced leukemogenesis.
In a recent report, Leng et al. demonstrated that, when stimulated, c-Abl tyrosine kinase induced the tyrosine phosphorylation of Abi1 and promoted Abi1/WAVE2 membrane translocation (Leng et al., 2005). In this study, we show that p185Bcr-Abl, a constitutively active tyrosine kinase, stimulated Abi1 tyrosine phosphorylation and membrane translocation of Abi1/WAVE2 complex. These studies highlight membrane translocation of Abi1/WAVE2 as a critical regulatory step for WAVE activation and actin cytoskeleton reorganization. Using a melanoma cell line B16F1, Leng et al. also reported that WAVE2 was phosphorylated on tyrosine 150 and that the complex assembly of Abi1 and WAVE2 was enhanced when c-Abl was activated by PDGF stimulation (Leng et al., 2005). In studies described here, we did not observe an increase in Abi1/WAVE2 complex assembly in p185wt-transformed Ba/F3 cells (Fig. 2B). In fact, we found that even in resting Ba/F3 cells, most of Abi1 and WAVE2 present as a complex and can be easily co-immunoprecipitated with each other (Li and Dai, unpublished data). This observation is in line with those described by Gautreau et al (Gautreau et al., 2004) and Innocenti et al (Innocenti et al., 2004), who demonstrated that Abi, Nap, Sra and WAVE 2 were only present as a complex in Hela cells and that stimulation of cells with EGF did not affect the complex formation. Although the discrepancy between our observations and those reported by Leng et al. may be explained by differences in experimental systems, our data and those of Leng et al. raise the possibility that c-Abl and Bcr-Abl may regulate complex formation of Abi1/WAVE2 differently.
The mechanism by which Bcr-Abl induces membrane translocation of Abi1 in hematopoietic cells differs from those utilized by fibroblast and adherent tumor cells such as Hela cells and melanoma cells B16F1, in which Abi1 was found to localize to the membrane ruffle and the tip of lamellipodia (Stradal et al. 2001, Innocenti et al., 2004, and Leng et al 2005). The PI3K pathway, for example, is required for PDGF-stimulated membrane translocation of Abi1 in fibroblast (Innocenti et al., 2003), but is dispensable for Bcr-Abl-induced Abi1 translocation in hematopoietic cells. Abi1PPLL, a mutant Abi1 deficient in binding to Bcr-Abl, failed to translocate to membrane in p185wt-transformed Ba/F3 cells. However, this mutant Abi1 displayed the same membrane-associated distribution as the wild type Abi1 in adherent human kidney-derived 293 cells (Sun and Dai, unpublished data). Although the tyrosine phosphorylation of Abi1 appears to be critical for its membrane translocation in both fibroblast (Innocenti et al., 2003, Leng et al., 2005) and Bcr-Abl-transformed hematopoietic cells, the mechanism involved differs too. The phosphorylation of tyrosine 407 has been shown to be critical for membrane translocation of Abi1 in fibroblast, as it provides an anchorage site for PI3K (Innocenti et al., 2003). This tyrosine, however, is not required for Bcr-Abl-induced Abi1 translocation in hematopoietic cells (Fig. 5). It is possible that Bcr-Abl may induce the phosphorylation of other tyrosine residue(s) in Abi1, which may provide an anchorage site for proteins yet to be identified or, alternatively, which may modify the actin polymerization promoting activity of Abi1/WAVE2 complex. Further investigation is necessary to map these tyrosine residue(s) and to define the role of tyrosine phosphorylation of Abi1 in the regulation of membrane translocation.
Supplementary Material
Supplemental Fig. 1 Specificity of anti-Abi1 antibody and down-regulation of Abi2 in murine hematopoietic cell lines transformed by p185wt. A. Myc-tagged Abi1 and Abi2 were produced in vitro by coupled transcription/translation and subjected to Western blot analysis using indicated antibodies. B. Ba/F3 and 32D cells were transduced with empty retroviral vector (control) or retroviral vector expressing p185wt. Total lysates from 1×106 cells were analyzed by Western blot using anti-Abi2 antibody.
Supplemental Fig. 2 PI3K pathway is not required for Bcr-Abl-induced abnormal F-actin remodeling. A. Imatinib, but not LY294002, inhibited Bcr-Abl-induced abnormal actin cytoskeleton remodeling. Ba/F3 cells (a) and the Ba/F3 transformed by p185wt (b) were treated without (a and b) or with either 1 μM imatinib (c) or 50 μM LY294002 (d). The cells were fixed, permeablized, and stained with TRITC-conjugated phalloidin and DAPI to visualize F-actin and nuclei, respectively. Images were captured by fluorescence microscope. Arrowheads indicate the abnormal F-actin-enriched structures. B. Tyrosine 407 is not required for Bcr-Abl-induced membrane translocation of Abi1 and actin remodeling. Ba/F3 cells and the Ba/F3 cells transformed by p185wt were transduced with retroviruses expressing either GFP-Abi1 or GFP-Abi1Y407F, as indicated. Cells were fixed, permeablized, and stained by TRITC-conjugated phalloidin and DAPI. Images were captured by 2-photon confocal microscope. Bar: 10 μm.
Supplemental Fig. 3 Deletion of the SH3 domain and C-terminal proline-rich sequences in Bcr-Abl abrogates its signal transduction to Abi1. A. Schematic representation of p185wt and p185ΔSH3ΔC. B. The p185ΔSH3ΔC is deficient in binding to Abi1 and inducing Abi1 phosphorylation. The lysates from Ba/F3 cells transduced with empty retroviral vector (C) or the retroviral vectors expressing either p185wt (WT) or p185ΔSH3ΔC (Mu) were immunoprecipitated with anti-Abi1 antibody. The immunoprecipitates (middle and lower panels) and 1/50 of total cell lysates used for IP (TCL, upper panel) were subjected to Western blot analysis using antibodies specific for Abl, Abi1, and phosphotyrosine (pTyr), as indicated. The anti-Abl antibody recognizes both Bcr-Abl and endogenous c-Abl.
Supplemental Fig. 4 Abi1PPLL retains the ability to interact with WAVE2 and Hem1. A. The p185wt-transformed Ba/F3 cells were transduced with retroviruses expressing either HA-tagged Abi1 or Abi1PPLL. The parental cells (lane 1) as well as the cells that express HA-Abi1 (lane 2) or HA-Abi1PPLL (lane 3) were lysed and immunoprecipitated with an antibody specific for HA-tag. The immunoprecipitates were subjected to Western blot (WB) analysis using indicated antibodies. B. The parental p185wt-transformed Ba/F3 cells (lane 1) and the p185wt-transformed cells expressing myc-tagged Hem1 (lanes 2 and 3) were transduced with retroviruses expressing either HA-tagged Abi1 (lane 2) or Abi1PPLL (lane 3). The cell lysates were immunoprecipitated by anti-HA antibody and the immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blot using indicated antibodies.
Supplemental Fig. 5 The β1-integrin protein level is not elevated among Ba/F3 cells and the Ba/F3 cells expressing the wild type and mutant forms of Bcr-Abl and Abi1. A. Lysates from Ba/F3 cells and the Ba/F3 cells expressing p185wt, p185ΔSH3ΔC, and p185wt plus Abi1PPLL, as indicated, were subjected to Western blot analysis using anti-β1-integrin antibody. The Western blot analysis using anti-β-actin antibody was also included to show equal loading. B. Analysis of surface β1-integrin level by flow cytometry. Parental Ba/F3 cells and Ba/F3 cells expressing p185wt, p185ΔSH3ΔC, or p185wt plus Abi1PPLL, as indicated, were fixed and probed with anti-β1-integrin antibody, or normal rabbit IgG as control. Cells then were stained by Alexa-conjugated secondary antibody and subjected to flow cytometry analysis. MFI: median fluorescence intensities.
Supplemental Fig. 6 β1-integrin is clustered and co-localized with abnormal F-actin-enriched structures in p185wt-transformed Ba/F3 cells adherent to fibronectin-coated surfaces. The Ba/F3 cells and Ba/F3 cells expressing either p185wt or p185ΔSH3ΔC, as indicated, were plated on glass coverslips coated with fibronectin and grown for 16 hours. Adherent cells were fixed, permeablized, and probed with rat monoclonal anti-β1-integrin antibody. Cells were then stained with FITC-conjugated mouse anti-rat IgG for β1-integrin (green), TRITC-conjugated phalloidin for F-actin (red), and DAPI for nuclei (blue), as indicated. The images were captured by Nikon TE-2000 fluorescence microscope. β1-integrin clustering is indicated by arrowhead and the co-localization of integrin with abnormal actin-enriched structure is shown in merged images.
Supplemental Fig. 7 Expression of Abi1PPLL inhibited Bcr-Abl-induced spontaneous cell migration on fibronectin-coated surfaces. Ba/F3 cells and the Ba/F3 cells expressing p185wt were transduced with retrovirus expressing GFP-Abi1PPLL. Spontaneous cell migration on fibronectin-coated surfaces was determined by Transwell migration assay. The vertical axis shows the percentage of migrated cells and is expressed as the average +/− S.D of triplicate wells. *, P< 0.05 vs. p185wt-expressing cells (n=3). Data are representative of three independent experiments.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. A. M. Pendergast for the reagents generated in her lab, Drs. J. DeGregori, A. Kraft, X. Meng, K. Pfenninger, and R. Scheinman for stimulating discussion and critical review of the manuscript, and Steven Fadul for assistance and access to confocal microscopes. This work was supported by National Institute of Health Grant R01 CA94921 (to Z.D.). C.J.H. is supported by National Institutes of Health Grant R01 HL61382.
Abbreviations
- Abi
Abl interactor
- BMT
bone marrow transplant
- CML
chronic myelogenous leukemia
- GFP
green fluorescence protein
- PI3K
phosphoinositide 3-kinase
- SH3
Src homology 3
- WASp
Wiscott-Aldrich Syndrome Protein
References
- Bazzoni G, Carlesso N, Griffin JD, Hemler ME. Bcr/Abl expression stimulates integrin function in hematopoietic cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1996;98:521–8. doi: 10.1172/JCI118820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia R, McCarthy JB, Verfaillie CM. Interferon-alpha restores normal beta 1 integrin-mediated inhibition of hematopoietic progenitor proliferation by the marrow microenvironment in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood. 1996;87:3883–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia R, Munthe HA, Verfaillie CM. Role of abnormal integrin-cytoskeletal interactions in impaired beta1 integrin function in chronic myelogenous leukemia hematopoietic progenitors. Exp Hematol. 1999;27:1384–96. doi: 10.1016/s0301-472x(99)00084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biesova Z, Piccoli C, Wong WT. Isolation and characterization of e3B1, an eps8 binding protein that regulates cell growth. Oncogene. 1997;14:233–41. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1200822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bompard G, Caron E. Regulation of WASP/WAVE proteins: making a long story short. J Cell Biol. 2004;166:957–62. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200403127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns S, Cory GO, Vainchenker W, Thrasher AJ. Mechanisms of WASp-mediated hematologic and immunologic disease. Blood. 2004;104:3454–62. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-04-1678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K, Fath K, Kelly T, Nuckolls G, Turner C. Focal adhesions: transmembrane junctions between the extracellular matrix and the cytoskeleton. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:487–525. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.002415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney KD, Grove M, Vandongen H, Vandongen A, LaMantia AS, Pendergast AM. Localization and phosphorylation of Abl-interactor proteins, Abi-1 and Abi-2, in the developing nervous system. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2000;16:244–57. doi: 10.1006/mcne.2000.0865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dai Z, Kerzic P, Schroeder WG, McNiece IK. Deletion of the Src homology 3 domain and C-terminal proline-rich sequences in Bcr-Abl prevents Abl interactor 2 degradation and spontaneous cell migration and impairs leukemogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:28954–60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M101170200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dai Z, Pendergast AM. Abi-2, a novel SH3-containing protein interacts with the c-Abl tyrosine kinase and modulates c-Abl transforming activity. Genes Dev. 1995;9:2569–82. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.21.2569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dai Z, Quackenbush RC, Courtney KD, Grove M, Cortez D, Reuther GW, Pendergast AM. Oncogenic Abl and Src tyrosine kinases elicit the ubiquitin-dependent degradation of target proteins through a Ras-independent pathway. Genes Dev. 1998;12:1415–24. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.10.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eden S, Rohatgi R, Podtelejnikov AV, Mann M, Kirschner MW. Mechanism of regulation of WAVE1-induced actin nucleation by Rac1 and Nck. Nature. 2002;418:790–3. doi: 10.1038/nature00859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautreau A, Ho HY, Li J, Steen H, Gygi SP, Kirschner MW. Purification and architecture of the ubiquitous Wave complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:4379–83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400628101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon MY, Dowding CR, Riley GP, Goldman JM, Greaves MF. Altered adhesive interactions with marrow stroma of haematopoietic progenitor cells in chronic myeloid leukaemia. Nature. 1987;328:342–4. doi: 10.1038/328342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmeryckx B, van Wijk A, Reichert A, Kaartinen V, de Jong R, Pattengale PK, Gonzalez-Gomez I, Groffen J, Heisterkamp N. Crkl enhances leukemogenesis in BCR/ABL P190 transgenic mice. Cancer Res. 2001;61:1398–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes RO. Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell. 2002;110:673–87. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00971-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innocenti M, Frittoli E, Ponzanelli I, Falck JR, Brachmann SM, Di Fiore PP, Scita G. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase activates Rac by entering in a complex with Eps8, Abi1, and Sos-1. J Cell Biol. 2003;160:17–23. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200206079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innocenti M, Zucconi A, Disanza A, Frittoli E, Areces LB, Steffen A, Stradal TE, Di Fiore PP, Carlier MF, Scita G. Abi1 is essential for the formation and activation of a WAVE2 signalling complex. Nat Cell Biol. 2004;6:319–27. doi: 10.1038/ncb1105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer A, Horner S, Willer A, Fruehauf S, Hochhaus A, Hallek M, Hehlmann R. Adhesion to fibronectin stimulates proliferation of wild-type and bcr/abl-transfected murine hematopoietic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96:2087–92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.5.2087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunda P, Craig G, Dominguez V, Baum B. Abi, Sra1, and Kette control the stability and localization of SCAR/WAVE to regulate the formation of actin-based protrusions. Curr Biol. 2003;13:1867–75. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2003.10.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leng Y, Zhang J, Badour K, Arpaia E, Freeman S, Cheung P, Siu M, Siminovitch K. Abelson-interactor-1 promotes WAVE2 membrane translocation and Abelson-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation required for WAVE2 activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:1098–103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0409120102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin KH, Slack JK, Boerner SA, Martin CC, Parsons JT. Integrin connections map: to infinity and beyond. Science. 2002;296:1652–3. doi: 10.1126/science.296.5573.1652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McWhirter JR, Wang JY. Effect of Bcr sequences on the cellular function of the Bcr-Abl oncoprotein. Oncogene. 1997;15:1625–34. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melo JV, Deininger MW. Biology of chronic myelogenous leukemia--signaling pathways of initiation and transformation. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2004;18:545–68. vii–viii. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2004.03.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki K, Matsuda S, Ichigotani Y, Takenouchi Y, Hayashi K, Fukuda Y, Nimura Y, Hamaguchi M. Isolation and characterization of a novel human gene (NESH) which encodes a putative signaling molecule similar to e3B1 protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1493:237–41. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4781(00)00158-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musacchio A, Noble M, Pauptit R, Wierenga R, Saraste M. Crystal structure of a Src-homology 3 (SH3) domain. Nature. 1992;359:851–5. doi: 10.1038/359851a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard TD, Borisy GG. Cellular motility driven by assembly and disassembly of actin filaments. Cell. 2003;112:453–65. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00120-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao J, Li N. Microfilament actin remodeling as a potential target for cancer drug development. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2004;4:345–54. doi: 10.2174/1568009043332998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren R, Ye ZS, Baltimore D. Abl protein-tyrosine kinase selects the Crk adapter as a substrate using SH3-binding sites. Genes Dev. 1994;8:783–95. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.7.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salesse S, Verfaillie CM. Mechanisms underlying abnormal trafficking and expansion of malignant progenitors in CML: BCR/ABL-induced defects in integrin function in CML. Oncogene. 2002;21:8605–11. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salgia R, Li JL, Ewaniuk DS, Pear W, Pisick E, Burky SA, Ernst T, Sattler M, Chen LB, Griffin JD. BCR/ABL induces multiple abnormalities of cytoskeletal function. J Clin Invest. 1997;100:46–57. doi: 10.1172/JCI119520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salgia R, Quackenbush E, Lin J, Souchkova N, Sattler M, Ewaniuk DS, Klucher KM, Daley GQ, Kraeft SK, Sackstein R, et al. The BCR/ABL oncogene alters the chemotactic response to stromal-derived factor-1alpha. Blood. 1999;94:4233–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz MA, Ginsberg MH. Networks and crosstalk: integrin signalling spreads. Nat Cell Biol. 2002;4:E65–8. doi: 10.1038/ncb0402-e65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz MA, Schaller MD, Ginsberg MH. Integrins: emerging paradigms of signal transduction. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1995;11:549–99. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.11.110195.003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y, Alin K, Goff SP. Abl-interactor-1, a novel SH3 protein binding to the carboxy-terminal portion of the Abl protein, suppresses v-abl transforming activity. Genes Dev. 1995;9:2583–97. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.21.2583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skorski T, Nieborowska-Skorska M, Wlodarski P, Wasik M, Trotta R, Kanakaraj P, Salomoni P, Antonyak M, Martinez R, Majewski M, et al. The SH3 domain contributes to BCR/ABL-dependent leukemogenesis in vivo: role in adhesion, invasion, and homing. Blood. 1998;91:406–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skourides PA, Perera SA, Ren R. Polarized distribution of Bcr-Abl in migrating myeloid cells and co-localization of Bcr-Abl and its target proteins. Oncogene. 1999;18:1165–76. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen A, Rottner K, Ehinger J, Innocenti M, Scita G, Wehland J, Stradal TE. Sra-1 and Nap1 link Rac to actin assembly driving lamellipodia formation. Embo J. 2004;23:749–59. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stradal TE, Rottner K, Disanza A, Confalonieri S, Innocenti M, Scita G. Regulation of actin dynamics by WASP and WAVE family proteins. Trends Cell Biol. 2004;14:303–11. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2004.04.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teixido J, Hemler ME, Greenberger JS, Anklesaria P. Role of beta 1 and beta 2 integrins in the adhesion of human CD34hi stem cells to bone marrow stroma. J Clin Invest. 1992;90:358–67. doi: 10.1172/JCI115870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Etten RA, Debnath J, Zhou H, Casasnovas JM. Introduction of a loss-of-function point mutation from the SH3 region of the Caenorhabditis elegans sem-5 gene activates the transforming ability of c-abl in vivo and abolishes binding of proline-rich ligands in vitro. Oncogene. 1995;10:1977–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verfaillie CM, McCarthy JB, McGlave PB. Mechanisms underlying abnormal trafficking of malignant progenitors in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Decreased adhesion to stroma and fibronectin but increased adhesion to the basement membrane components laminin and collagen type IV. J Clin Invest. 1992;90:1232–41. doi: 10.1172/JCI115985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B, Mysliwiec T, Krainc D, Jensen RA, Sonoda G, Testa JR, Golemis EA, Kruh GD. Identification of ArgBP1, an Arg protein tyrosine kinase binding protein that is the human homologue of a CNS-specific Xenopus gene. Oncogene. 1996;12:1921–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wartmann M, Hofer P, Turowski P, Saltiel AR, Hynes NE. Negative modulation of membrane localization of the Raf-1 protein kinase by hyperphosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:3915–23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.7.3915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner OD, Rentel MC, Ott A, Brown GE, Jedrychowski M, Yaffe MB, Gygi SP, Cantley LC, Bourne HR, Kirschner MW. Hem-1 complexes are essential for Rac activation, actin polymerization, and myosin regulation during neutrophil chemotaxis. PLoS Biol. 2006;4:e38. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertheim JA, Forsythe K, Druker BJ, Hammer D, Boettiger D, Pear WS. BCR-ABL-induced adhesion defects are tyrosine kinase-independent. Blood. 2002;99:4122–30. doi: 10.1182/blood.v99.11.4122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertheim JA, Perera SA, Hammer DA, Ren R, Boettiger D, Pear WS. Localization of BCR-ABL to F-actin regulates cell adhesion but does not attenuate CML development. Blood. 2003;102:2220–8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-01-0062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams DA, Rios M, Stephens C, Patel VP. Fibronectin and VLA-4 in haematopoietic stem cell-microenvironment interactions. Nature. 1991;352:438–41. doi: 10.1038/352438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziemnicka-Kotula D, Xu J, Gu H, Potempska A, Kim KS, Jenkins EC, Trenkner E, Kotula L. Identification of a candidate human spectrin Src homology 3 domain-binding protein suggests a general mechanism of association of tyrosine kinases with the spectrin-based membrane skeleton. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:13681–92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.22.13681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplemental Fig. 1 Specificity of anti-Abi1 antibody and down-regulation of Abi2 in murine hematopoietic cell lines transformed by p185wt. A. Myc-tagged Abi1 and Abi2 were produced in vitro by coupled transcription/translation and subjected to Western blot analysis using indicated antibodies. B. Ba/F3 and 32D cells were transduced with empty retroviral vector (control) or retroviral vector expressing p185wt. Total lysates from 1×106 cells were analyzed by Western blot using anti-Abi2 antibody.
Supplemental Fig. 2 PI3K pathway is not required for Bcr-Abl-induced abnormal F-actin remodeling. A. Imatinib, but not LY294002, inhibited Bcr-Abl-induced abnormal actin cytoskeleton remodeling. Ba/F3 cells (a) and the Ba/F3 transformed by p185wt (b) were treated without (a and b) or with either 1 μM imatinib (c) or 50 μM LY294002 (d). The cells were fixed, permeablized, and stained with TRITC-conjugated phalloidin and DAPI to visualize F-actin and nuclei, respectively. Images were captured by fluorescence microscope. Arrowheads indicate the abnormal F-actin-enriched structures. B. Tyrosine 407 is not required for Bcr-Abl-induced membrane translocation of Abi1 and actin remodeling. Ba/F3 cells and the Ba/F3 cells transformed by p185wt were transduced with retroviruses expressing either GFP-Abi1 or GFP-Abi1Y407F, as indicated. Cells were fixed, permeablized, and stained by TRITC-conjugated phalloidin and DAPI. Images were captured by 2-photon confocal microscope. Bar: 10 μm.
Supplemental Fig. 3 Deletion of the SH3 domain and C-terminal proline-rich sequences in Bcr-Abl abrogates its signal transduction to Abi1. A. Schematic representation of p185wt and p185ΔSH3ΔC. B. The p185ΔSH3ΔC is deficient in binding to Abi1 and inducing Abi1 phosphorylation. The lysates from Ba/F3 cells transduced with empty retroviral vector (C) or the retroviral vectors expressing either p185wt (WT) or p185ΔSH3ΔC (Mu) were immunoprecipitated with anti-Abi1 antibody. The immunoprecipitates (middle and lower panels) and 1/50 of total cell lysates used for IP (TCL, upper panel) were subjected to Western blot analysis using antibodies specific for Abl, Abi1, and phosphotyrosine (pTyr), as indicated. The anti-Abl antibody recognizes both Bcr-Abl and endogenous c-Abl.
Supplemental Fig. 4 Abi1PPLL retains the ability to interact with WAVE2 and Hem1. A. The p185wt-transformed Ba/F3 cells were transduced with retroviruses expressing either HA-tagged Abi1 or Abi1PPLL. The parental cells (lane 1) as well as the cells that express HA-Abi1 (lane 2) or HA-Abi1PPLL (lane 3) were lysed and immunoprecipitated with an antibody specific for HA-tag. The immunoprecipitates were subjected to Western blot (WB) analysis using indicated antibodies. B. The parental p185wt-transformed Ba/F3 cells (lane 1) and the p185wt-transformed cells expressing myc-tagged Hem1 (lanes 2 and 3) were transduced with retroviruses expressing either HA-tagged Abi1 (lane 2) or Abi1PPLL (lane 3). The cell lysates were immunoprecipitated by anti-HA antibody and the immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blot using indicated antibodies.
Supplemental Fig. 5 The β1-integrin protein level is not elevated among Ba/F3 cells and the Ba/F3 cells expressing the wild type and mutant forms of Bcr-Abl and Abi1. A. Lysates from Ba/F3 cells and the Ba/F3 cells expressing p185wt, p185ΔSH3ΔC, and p185wt plus Abi1PPLL, as indicated, were subjected to Western blot analysis using anti-β1-integrin antibody. The Western blot analysis using anti-β-actin antibody was also included to show equal loading. B. Analysis of surface β1-integrin level by flow cytometry. Parental Ba/F3 cells and Ba/F3 cells expressing p185wt, p185ΔSH3ΔC, or p185wt plus Abi1PPLL, as indicated, were fixed and probed with anti-β1-integrin antibody, or normal rabbit IgG as control. Cells then were stained by Alexa-conjugated secondary antibody and subjected to flow cytometry analysis. MFI: median fluorescence intensities.
Supplemental Fig. 6 β1-integrin is clustered and co-localized with abnormal F-actin-enriched structures in p185wt-transformed Ba/F3 cells adherent to fibronectin-coated surfaces. The Ba/F3 cells and Ba/F3 cells expressing either p185wt or p185ΔSH3ΔC, as indicated, were plated on glass coverslips coated with fibronectin and grown for 16 hours. Adherent cells were fixed, permeablized, and probed with rat monoclonal anti-β1-integrin antibody. Cells were then stained with FITC-conjugated mouse anti-rat IgG for β1-integrin (green), TRITC-conjugated phalloidin for F-actin (red), and DAPI for nuclei (blue), as indicated. The images were captured by Nikon TE-2000 fluorescence microscope. β1-integrin clustering is indicated by arrowhead and the co-localization of integrin with abnormal actin-enriched structure is shown in merged images.
Supplemental Fig. 7 Expression of Abi1PPLL inhibited Bcr-Abl-induced spontaneous cell migration on fibronectin-coated surfaces. Ba/F3 cells and the Ba/F3 cells expressing p185wt were transduced with retrovirus expressing GFP-Abi1PPLL. Spontaneous cell migration on fibronectin-coated surfaces was determined by Transwell migration assay. The vertical axis shows the percentage of migrated cells and is expressed as the average +/− S.D of triplicate wells. *, P< 0.05 vs. p185wt-expressing cells (n=3). Data are representative of three independent experiments.


