Abstract
We identify in this study a 27-amino-acid motif which is conserved between the Drosophila melanogaster period protein (PER) and the three mammalian PERs. Characterization of PER lacking this motif (PERΔ) shows that it is important for phosphorylation of Drosophila PER by casein kinase Iɛ (CKIɛ; doubletime protein or DBT) and CKII. S2 cell assays indicate that the domain also contributes significantly to PER nuclear localization as well as to PER transcriptional repressor activity. These two phenomena appear linked, since PERΔ transcriptional repressor activity in S2 cells was restored when nuclear localization was facilitated. Two less direct assays of PERΔ activity in flies can be interpreted similarly. The separate assay of nuclear import and export suggests that the domain functions in part to facilitate PER phosphorylation within the cytoplasm, which in turn promotes nuclear entry. As there is evidence that the kinases also function within the nucleus to promote transcriptional repression, we suggest that there is a subsequent collaboration between phosphorylated PER and the kinases to repress CLK-CYC activity, probably through the phosphorylation of CLK. This is then followed by additional PER phosphorylation, which occurs within the nucleus and leads to PER degradation.
Many organisms contain circadian clocks, which keep temporal order and even anticipate daily environmental changes. These biological clocks are self-sustaining biochemical oscillators which underlie the daily cycling of many molecular, physiological, and behavioral processes. In several model systems, genetics has provided an entrée into circadian mechanisms by identifying putative clock proteins and then facilitating their study. About a dozen circadian genes have been identified in Drosophila melanogaster (18).
Drosophila period (per) was the first rhythm gene identified in any organism (29). per mRNA levels and transcription exhibit circadian fluctuations, and per mRNA levels peak earlier and the cycle is shorter in the short-period per allele pers (21, 22, 46). This is consistent with the short behavioral period and suggested a causal relationship between the per gene product (PERIOD [PER]) and the regulation of circadian rhythms (22). Moreover, the fact that PER is nuclear (34) and has a sequence relationship with a bona fide transcription factor (7) suggested that it acts directly to influence circadian transcription.
Indeed, PER appears to function as a transcription repressor. There is now a well-described molecular circuit consisting of two positive transcription factors, CLOCK (CLK) and CYCLE (CYC), and two CLK-CYC repressors, PER and TIMELESS (TIM). The CLK-CYC heterodimeric complex activates transcription of per and timeless (tim). This gives rise to PER and TIM, which repress CLK-CYC transcription activation and inhibit their own (per and tim) transcription (e.g., references 25 and 55). Although other loops exist, this negative feedback loop contributes to the cyclic transcription of per and other CLK-CYC direct target genes and more indirectly to the cycling of many other transcripts (e.g., reference 37). A similar feedback loop exists in mammals (4).
In addition to per transcriptional regulation, PER posttranscriptional regulation appears to be involved in the feedback loop, as well. Indeed, PER manifests dramatic changes in phosphorylation state as well as level throughout the day, as assayed by Western blotting of fly head extracts (12). Two kinases, a phosphatase and a ubiquitin ligase, are proposed to modify PER, and mutations that alter these activities significantly affect circadian rhythms (1, 17, 26, 28, 32, 41, 43). Mutations in the mammalian ortholog in one of these kinases, casein kinase Iɛ (CKIɛ) (doubletime product, DBT), also have dramatic effects on period in rodents (35). Moreover, two human sleep disorder families have mutations either in human kinase or in what is probably a human PER2 substrate region (50, 52). In addition, a comparison of PER levels with per mRNA levels in the fly system indicates that posttranslational regulation probably influences the timing of PER function as well as that of PER abundance fluctuations (10, 46, 48).
PER subcellular localization is also temporally regulated, as nuclear entry is gated by the circadian cycle. As this timing is affected by kinase mutants as well as PER mutants (1, 3, 8, 32, 33, 38), it appears that the circadian regulation of PER phosphorylation influences the timing of PER subcellular localization. This provides an attractive explanation for the role of PER phosphorylation in the timing of PER transcriptional repressor activity. There is, however, evidence that phosphorylation within the nucleus plays a more direct role in the repression of CLK-CYC activity (25, 55). Moreover, our previous study also suggested that the two PER kinases, CKII and DBT, affect PER transcriptional repression activity independently of nuclear localization (40).
To further understand the regulation of PER phosphorylation and its relationship to repression activity, we decided to study a region suggested from the characterization of transgenic flies containing two truncated PER fusion proteins (10, 47) (see below). Only the longer one was subject to progressive phosphorylation (10), suggesting that a region between the two endpoints is important for phosphorylation. This led to the identification of a PER 27-amino-acid (aa) motif which is conserved between Drosophila and all three mammalian PERs. The domain is important for PER phosphorylation, by CKII as well as by DBT, and for transcriptional repressor activity in S2 cells. As suggested by the previous characterization of PER kinases mentioned above, the data indicate that the domain also potentiates PER nuclear localization. Indeed, PERΔ (PER missing the 27-aa domain) regained S2 cell transcriptional repressor activity when nuclear localization was facilitated. Two less direct experiments with flies can be interpreted similarly. As there is evidence that the kinases also function within the nucleus to potentiate transcriptional repression, a parsimonious model posits that the domain functions to facilitate PER cytoplasmic phosphorylation and then to promote nuclear entry. Within the nucleus, phosphorylated PER then collaborates with kinases to repress CLK-CYC activity. This is followed by a second wave of PER phosphorylation, which occurs within the nucleus and leads to PER degradation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Plasmids and mutagenesis.
pActin (pAc) per V5 has been previously described (40); pAc dbt V5 was a kind gift from V. Suri. pAc perΔ V5 was generated using megaprimer-based mutagenesis method. Two pairs of primers were used. For the 5′ part, the forward primer is 5′ GGTGTCCCGGGCGGATCTCAAGCTGG 3′, and the reverse primer is 5′ ATCGTTTGCGCTTTTTTTCGAATTGACTGGCGGTATGGCGGCCGTTCC 3′. For the 3′ part, the forward primer is 5′ AATTCGAAAAAAAGCGCAAACGATACCCTTAAGATGCTGGAGTACAGC 3′, and the reverse primer is 5′ GGCAGGAGTGGTGACCGAGTGGAATGC 3′. The final PCR product was digested with XmaI/BstEII and ligated with the EcoRI/BstEII piece and the EcoRI/XmaI piece from pAc per V5. pAc perΔn V5, pAc perΔc V5, and pAc perAAA V5 were constructed in similar ways, using the same forward primer for the 5′ part and the same reverse primer for the 3′ part. The reverse primers for the 5′ parts of pAc perΔn V5, pAc perΔc V5, and pAc perAAA V5, respectively, are as follows: 5′ CTCGTCGTTGTGCTTTGGCGGTATGGCGGCCGTTCCGCCTTTGG 3′, 5′ CTCTTCTCACCCGTCCGTCGCTTATTGAGCAGGGATTCGGTCAGCGTG 3′, and 5′ GGCTTCCGCCAGCGCGACTGGCGGTATCGGGGCCGTTCC 3′. The forward primers for the 3′ parts of pAc perΔn V5, pAc perΔc V5, and pAc perAAA V5, respectively, are as follows: 5′ CGGCCGCCATACCGCCAAAGCACAACGACGAGATGGAGAAGTTC 3′, 5′ CCGAATCCCTGCTCAATAAGGGACGGACGGGTGAGAAGAGCAAGAAG 3′, and 5′ CCGCCAGTCGCGCTGGCGGAAGCCCTGCTCAATAAGCACAACGAC 3′. Nuclear localization signal (NLS) sequence (23) was appended onto the C terminus of pAc per V5. Two oligonucleotides, 5′ CGCGTCCAAAGAAAAAGCGTAAAGTCA 3′ and 5′ CCGGTGACTTTACGCTTTTTCTTTGGA 3′, were annealed, digested with MluI/AgeI, and ligated into MluI/AgeI-digested pAc per V5. The internal deletion, triple-point mutation, and NLS insertion were verified by sequencing. Plasmids used in the reporter assay (pAc Clk, 3 × 69 firefly-luciferase, and pCopia-renilla- luciferase) were described earlier (40).
Cell culture techniques.
S2 cells were maintained in insect cell culture media (HyClone) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Invitrogen) and penicillin-streptomycin (Invitrogen) at 25°C in an incubator as described previously (39). Luciferase activity was measured using a dual luciferase reporter assay kit (Promega) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Transfection was done using Cellfectin (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer's recommendations. Double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) was synthesized using a MEGAScript high-yield transcription kit (Ambion) following the manufacturer's instructions. dsRNA was applied to S2 cells 2 days prior to transfection. Leptomycin was added to S2 cells 4 to 6 h prior to the harvest. For immunocytochemistry, transfected S2 cells were fixed, blocked, and incubated with mouse anti-V5 antibody (Invitrogen) followed by fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated anti-mouse antibody (Jackson Research Laboratory). A detailed description of cell culture techniques was previously provided (40).
Western blotting.
Extraction buffer (20 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 100 mM KCl, 5% glycerol, 20 mM β-glycerophosphate, 100 μM Na3VO4, 10 mM EDTA, 0.5% Triton X-100, 1 mM dithiothreitol) supplemented with Complete protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche) was used to lyse S2 cells. For fly head samples, flies were entrained at least 3 days in a 12-h-light/12-h-dark incubator and collected on dry ice at the indicated times. Fly heads were separated, collected, and homogenized with the extraction buffer. For both S2 cell and fly head samples, the lysate was run, transferred, and probed with primary and secondary antibodies according to standard techniques. Mouse anti-V5 antibody (Invitrogen) and horseradish peroxidase-conjugated anti-mouse antibody (Amersham) were used.
Fly stocks, behavioral assay, and fly head Western blotting.
elavc155GAL4, pdfGAL4, UAS-per24, and EP (X) 1576 have been previously described (24, 42, 54). Transgenic flies containing UAS-perΔ were generated using a standard protocol. perΔ from pAc perΔ was cloned into EcoRI/XhoI-digested pUAST. Locomotor activity measurement and analysis have been previously described (19, 31). Essentially, flies were entrained for at least 3 days in 12-h-light/12-h-dark conditions before being released into constant darkness. Data from at least 5 days in constant darkness were collected and computed. Fly head Western blotting was done according to the method of Zeng et al. (56).
RESULTS
Identification of a conserved region required for progressive phosphorylation and degradation of PER.
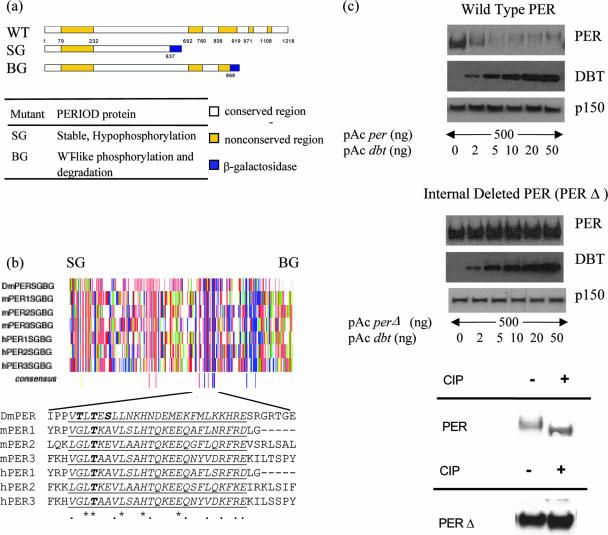
Two transgenic lines, containing different truncated PER fusion proteins, suggested that a region of approximately 230 aa might be involved in PER phosphorylation and degradation (10, 47). In transgenic per-sg flies, PER-SG (aa 1 to 637 followed by beta-galactosidase) showed defective phosphorylation and was highly stable, i.e., exhibited no observable circadian oscillation in PER phosphorylation or PER levels. In contrast, PER-BG (aa 1 to 868 followed by beta-galactosidase) exhibited phosphorylation and degradation patterns similar to those of wild-type PER. This difference pointed to PER amino acid region 638 to 868 as relevant to progressive phosphorylation and degradation (Fig. 1a) (also suggested in reference 11). Since progressive PER phosphorylation appears well conserved from Drosophila to mammals (12, 30), we searched for and found sequence homology between Drosophila and mammalian PERs within this region: there is a conserved stretch of 27 aa within roughly the same portion of each of these proteins (Fig. 1b).
FIG. 1.
Identification of a conserved region in Drosophila PER protein necessary for the progressive phosphorylation. (a) Comparative size of wild-type (WT) and two truncated forms (SG and BG) of PER protein. Numbers represent amino acid positions. (Bottom) Table summarizes behavior of PER-SG and PER-BG in wild-type flies (concluded from references 10 and 47). Conserved and nonconserved regions are as defined by Colot et al. (6). (b) Amino acid sequence alignment of Drosophila and mammalian PER proteins reveals a short highly conserved sequence from aa 637 to 868 in Drosophila PER which is present in PER-BG but not in PER-SG. Each vertical line represents a single amino acid; color represents its chemical property (acidic [D and E] in red, hydrophobic [A, G, I, L and V] in gray, amido [N and Q] in violet, aromatic [F, W and Y] in orange, basic [R, H and K] in blue, hydroxyl [S and T] in pink, proline in green, and sulfur containing [C and M] in yellow; single-letter codes for amino acids are in brackets). SG and BG signify the last amino acids in PER-SG and PER-BG, respectively. The alignment was performed using CLUSTALW in McVector software. Asterisks indicate identical amino acids, and dots indicate similar amino acids. Underlined is a putative conserved sequence. (c) Deletion of the conserved sequence renders Drosophila PER resistant to DBT-induced progressive phosphorylation and degradation (top and middle) and hypophosphorylated (bottom). Western blot of wild-type PER (top) and of PERΔ (from which the conserved sequence is removed) (middle) from S2 cells overexpressing PER and increasing amounts of DBT. PER and DBT were detected using mouse anti-V5 antibody. p150 protein is used as a loading control. CIP, calf intestine phosphatase.
We then assayed the contribution of this motif to PER phosphorylation and degradation in the Drosophila S2 cell system. Consistent with previously published results (28), increasing amounts of transfected DBT led to dose-dependent PER hyperphosphorylation and degradation (Fig. 1c, top). We generated a 31-aa internal deletion of PER and subjected this mutant (pAc perΔ, encoding PERΔ) to the same assay. Intriguingly, PERΔ is highly stable, and DBT cotransfection showed no apparent effect on PERΔ mobility and stability (Fig. 1c, middle). Indeed, PER migrates noticeably slower than PERΔ (Fig. 2c), and phosphatase treatment increased PER mobility (Fig. 1c, bottom). PERΔ undergoes only a slight shift in mobility after phosphatase treatment (Fig. 1c, bottom), consistent with hypophosphorylation. These observations support the notion that the conserved motif contributes to PER progressive phosphorylation and degradation.
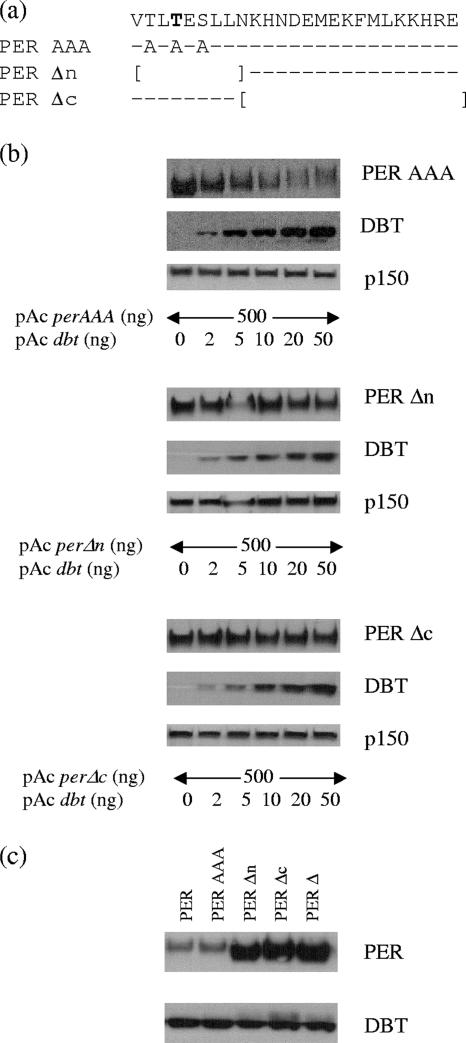
FIG. 2.
This conserved region likely functions as a protein-protein interaction domain rather than as a required initial phosphorylation site. (a) A representation of three additional mutants of otherwise wild-type PER protein, with PER-AAA having all possible phosphorylation sites mutated and replaced by alanine and PERΔn and PERΔc having smaller internal deletions (indicated by brackets). The conserved sequence is on the top line, dashes indicate no change in amino acids, and boldface indicates the conserved threonine found in Drosophila and mammalian PER proteins. (b) Western blot analysis of these three mutants from S2 cells overexpressing PER and increasing amounts of DBT. (c) Comparison of electrophoretic mobilities of wild-type PER and various mutants.
Mutagenesis analysis of PERΔ.
The domain contains several hydrophilic amino acids, including three serine/threonine residues, suggesting that it could serve as a phosphorylation substrate region (Fig. 1b); one threonine is present in both Drosophila and mammalian PER. To test whether the phosphorylation defect is due to the loss of an initial phosphorylation event at one of these residues, we generated a mutation of the conserved threonine residue and a triple mutation of all serine and threonine residues (replacing them with alanine) (Fig. 2a) and tested them for DBT-induced phosphorylation and degradation in S2 cells.
Both point mutants (PER TAS [data not shown] and PER AAA [Fig. 2b]) appear somewhat more stable than wild-type PER for DBT-induced phosphorylation and degradation, yet the patterns are more similar to that of PER than to that of PERΔ (Fig. 2b and 1c). Indeed, their mobilities suggest that they are hyperphosphorylated compared to PERΔ (Fig. 2c), and phosphatase treatment gave rise to a similar conclusion (data not shown). The data indicate that these residues are dispensable for PER progressive phosphorylation, suggesting that the motif rather serves as a protein-interacting domain.
We also generated two smaller internal deletion mutants: one deleted the 9 N-terminal amino acids (pAc perΔn, which includes the three serine/threonine residues), and the other deleted the 18 C-terminal amino acids (pAc perΔc, which leaves all serine/threonine residues intact) (Fig. 2a). We tested them by cotransfection with increasing amounts of pAc dbt. Both appear resistant to DBT-induced phosphorylation and degradation; they are hypophosphorylated and highly stable, similar to PERΔ (Fig. 2b). The hypophosphorylation of PERΔc indicates that the serine/threonine residues are insufficient for proper phosphorylation. Taken together with the observed hyperphosphorylation of the conserved threonine point mutation and the triple point mutation, the motif likely functions primarily as a protein-interacting domain or a structural motif necessary for DBT-induced/dependent progressive phosphorylation and degradation. The results are similar to those of Kim and colleagues (25a).
We have previously proposed that PER phosphorylation by CKII as well as DBT is important for its potent repression activity (40). However, the use of CKII and DBT RNA interference (RNAi) in this previous study precludes defining a cause-and-effect relationship between PER phosphorylation and transcriptional repression activity. We therefore sought to examine the repression activity of hypophosphorylated PERΔ in S2 cells.
The conserved region is important for PER transcription repression activity.
To this end, we compared PER and PERΔ in the widely used S2 cell circadian transcription assay. The transcriptional activation potential of CLK-CYC is assayed with a luciferase reporter gene fused to an artificial circadian response sequence (20), which is shown here in the presence of increasing amounts of per plasmid DNA. Repression activities of different PERs are estimated by the relative decrease in normalized luciferase activity as a function of PER dose; relative PER levels were assayed in parallel by Western blotting.
As previously described, PER represses CLK-CYC activity in a dose-dependent manner: the normalized luciferase activity decreases in parallel with the increase in pAc per and PER (Fig. 3a, left). In contrast, PERΔ manifests much weaker repressor activity despite much more protein (Fig. 3a, right). The other mutants behave as predicted from the phosphorylation assays: the serine/threonine point mutants function relatively normally, and the two smaller internal deletion mutants, PERΔn and PERΔc, are only weakly active in the repression activity assay despite much more protein than wild-type PER (data not shown). The data suggest that the conserved region is important for PER function, likely through effects on phosphorylation.
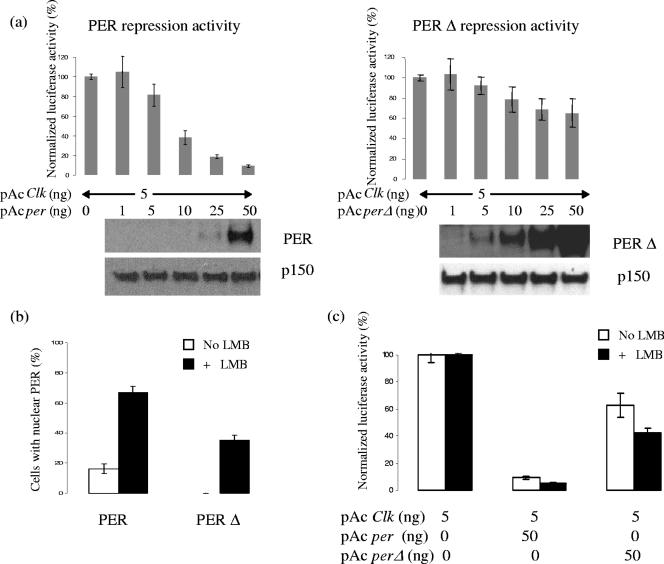
FIG. 3.
Removal of the conserved sequence weakens transcriptional repression activity of PER protein. This defect could be from reduction in nuclear localization as well as independent of the change in subcellular localization; these possibilities are not mutually exclusive. (a) Repression activity of PER and PERΔ from S2 cell reporter assay, with increasing amounts of PER. The graph represents normalized luciferase activity, which is inversely related to the repression activity. (Bottom) Western blots of PER and p150 (as a loading control) are shown. (b) Percentages of S2 cells with distinct nuclear PER staining, without or with nuclear export inhibitor LMB, which suggests that PERΔ is defective at both the nuclear entry and export levels. (c) Repression activity of PERΔ is moderately stronger with the application of LMB, though still weaker than that of wild-type PER, which implies that the reduction of the repression activity could be either dependent on or independent of nuclear localization.
Nuclear localization and repression activity of PERΔ.
As mutants of the PER kinases DBT and CKII have alterations in the timing of PER nuclear localization (1, 3, 9, 32), we considered that the alterations in repression activity of the mutant PERs could be linked to subcellular localization changes. Indeed, PERΔ showed a marked reduction in S2 cell nuclear localization to undetectable levels (Fig. 3b). To distinguish between an effect on nuclear entry and an effect on nuclear retention, we added leptomycin B (LMB) (14, 15), an inhibitor of CRM1-dependent nuclear export. This approach has been previously used to successfully inhibit PER export from S2 cell nuclei (40). Remarkably, nuclear PERΔ increased dramatically to about 35% (Fig. 3b), indicating that some protein can access nuclei but is exported more efficiently than wild-type PER. This is consistent with our previous RNAi experiments, which also suggested that hypophosphorylated PER is retained less well and/or exported more efficiently than wild-type PER (40). However, 35% is still much less than the ∼70% characteristic of wild-type PER in LMB (Fig. 3b), indicating that nuclear import is also defective in PERΔ.
PERΔ repression activity also increased with LMB, but it was still considerably lower than that of wild-type PER, without as well as with LMB (Fig. 3c). This is despite a nuclear accumulation of PERΔ with LMB greater than that of wild-type PER in the absence of LMB (35% versus 15%), suggesting that there is a decrease in PERΔ transcriptional repressor activity independent of the nuclear import defect.
perΔ cannot rescue the arrhythmicity phenotype of per0.
To address the question of whether the conserved motif is required for PER biological activity in vivo (in flies), eight independent transgenic lines containing UAS-perΔ were generated. The panneuronal driver elavc155GAL4 was used to drive the expression of perΔ, as it has been shown to successfully rescue the per0 arrhythmic phenotype (54). Indeed, elavc155GAL4 per0; UAS-per24 restored the rhythmicity of per0 successfully (81% rhythmic), whereas all eight elavc155GAL4 per0; UAS-perΔ lines were uniformly unable to rescue per0 arrhythmicity (Table 1; representative actograms are also shown in Fig. 4a). We confirmed that PERΔ is expressed by PER Western blotting from flies collected at two time points, zeitgeber time (ZT) 12 and ZT 24 (Fig. 4c). Consistent with the results from S2 cells, PERΔ displayed no significant mobility change between time points, whereas wild-type PER migrated noticeably slower at ZT 24, reflecting its hyperphosphorylated state (Fig. 2c). PERΔ levels differ among these lines (Fig. 4c), indicating that the uniform failure to rescue per0 arrhythmicity was not due to a failure to express sufficient PER (see below).
TABLE 1.
Summary of locomotor activity rhythms of rescued per0 mutant flies with wild-type per or perΔ
| Genotypea | No. (%) of flies tested
|
τ (h) (SD)b | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Rhythmic | Arrhythmic | ||
| elavGAL4 per0; UAS-per24/CyO; +/+ | 64 | 52 (81.25) | 12 (18.75) | 24.41 (0.55) |
| elavGAL4 per0; CyO/+; +/UAS-perΔ1A1n | 7 | 0 (0.00) | 7 (100.00) | NA (NA) |
| elavGAL4 per0; CyO/UAS-perΔ1A1r; +/+ | 45 | 0 (0.00) | 45 (100.00) | NA (NA) |
| elavGAL4 per0; CyO/UAS-perΔ2C2; +/+ | 9 | 0 (0.00) | 9 (100.00) | NA (NA) |
| elavGAL4 per0; CyO/UAS-perΔ2C3; +/+ | 8 | 0 (0.00) | 8 (100.00) | NA (NA) |
| elavGAL4 per0; CyO/UAS-perΔ2C4; +/+ | 31 | 0 (0.00) | 31 (100.00) | NA (NA) |
| elavGAL4 per0; CyO/+; +/UAS-perΔ2X1 | 65 | 0 (0.00) | 65 (100.00) | NA (NA) |
| elavGAL4 per0; CyO/+; +/UAS-perΔ2Y1 | 60 | 0 (0.00) | 60 (100.00) | NA (NA) |
| elavGAL4 per0; CyO/+; +/UAS-perΔ3O1 | 14 | 0 (0.00) | 14 (100.00) | NA (NA) |
elavc115GAL4 was used in all experiments.
τ, free-run period, an average from rhythmic flies. NA, not applicable.
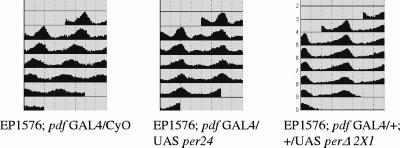
FIG. 4.
PERΔ is not fully functional yet maintains partial biological activity. (a) Expression of the wild-type per gene rescues the arrhythmic behavior of the per0 mutant, while that of perΔ does not. Expression of the per gene is under the UAS regulatory sequence, which is driven by a panneuronal driver, elavc155-GAL4 (54). Each panel represents grouped locomotor activity of individual genotypes in constant darkness. Three independent lines of UAS-perΔ are shown here (1A1r, 2Y1, and 2X1); a complete summary is in Table 1. (b) In wild-type-equivalent background (elavc155-GAL4; UAS-per24), the expression of PERΔ could interfere with the behavioral period. Each panel represents grouped locomotor activity of individual genotypes in constant darkness. Three independent lines of UAS-perΔ are shown here (1A1r, 2Y1, and 2X1); a complete summary is in Table 2. (c) Western blot analysis of PER from fly head extract collected at two time points (ZT 12 and ZT 24). Flies were entrained in 12 h light/12 h dark for at least 3 days prior to the collection. Rabbit anti-PER antibody was used for the detection.
perΔ has partial biological activity.
Because PERΔ retains some S2 cell repression activity, we used a less demanding behavioral assay and examined whether PERΔ expression might interfere with wild-type PER activity. Different UAS-perΔ inserts were added to the elavc155GAL4 per0; UAS-per24 genotype, and flies were tested for locomotor activity rhythms (a summary of all lines tested is present in Table 2, and representative actograms are shown in Fig. 4b).
TABLE 2.
Summary of locomotor activity rhythms of wild-type flies with additional per or perΔ expressiona
| Genotype | No. (%) of flies tested
|
τ (h) (SD) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Rhythmic | Arrhythmic | ||
| elavGAL4 per0; UAS-per24/UAS-per24; +/+ | 29 | 17 (58.62) | 12 (41.38) | 25.42 (1.18) |
| elavGAL4 per0; UAS-per24/+; +/UAS-perΔ1A1n | 8 | 7 (87.50) | 1 (12.50) | 24.00 (0.72) |
| elavGAL4 per0; UAS-per24/UAS-perΔ1A1r; +/+ | 42 | 38 (90.48) | 4 (9.52) | 24.29 (0.53) |
| elavGAL4 per0; UAS-per24/UAS-perΔ2C2; +/+ | 18 | 18 (100.00) | 0 (0.00) | 25.37 (0.52) |
| elavGAL4 per0; UAS-per24/UAS-perΔ2C3; +/+ | 6 | 0 (0.00) | 6 (100.00) | NA (NA) |
| elavGAL4 per0; UAS-per24/UAS-perΔ2C4; +/+ | 19 | 16 (84.21) | 3 (15.79) | 26.11 (0.66) |
| elavGAL4 per0; UAS-per24/+; +/UAS-perΔ2X1 | 62 | 2 (3.23) | 60 (96.77) | 27.15 (0.92) |
| elavGAL4 per0; UAS-per24/+; +/UAS-perΔ2Y1 | 57 | 50 (87.72) | 7 (12.28) | 25.40 (0.69) |
| elavGAL4 per0; UAS-per24/+; +/UAS-perΔ3O1 | 15 | 0 (0.00) | 15 (100.00) | NA (NA) |
Please consult Table 1 for explanation of genotypes and abbreviations.
Three classes of behavioral phenotypes were observed from elavc155GAL4 per0; UAS-per24-UAS-perΔ: (i) wild-type period (two lines), (ii) long period (three lines) (t ∼ 25.3 to 26.1 h); and (iii) arrhythmic (three lines) (Fig. 4b and Table 2). Notably, in vivo PER levels correlate well with the phenotypes (Fig. 4c), i.e., line 1A1r has no altered behavioral phenotype and the lowest PER levels, whereas line 2X1 was arrhythmic with the highest PER levels. The latter line recalls previous results showing that ectopic overexpression of wild-type per leads to behavioral arrhythmicity (54). Moreover, the observation that moderate perΔ expression causes period lengthening is similar to the long period of double-insert flies (elavc155GAL4 per0; UAS-per24-UAS-per24), which is about 25.4 h (Table 2) (54). The results are intriguing, because they suggest that PERΔ possesses some biological activities similar to those of wild-type PER, at least in an otherwise wild-type background.
We also recalled previous results that PER-SG (the beta-galactosidase fusion protein that lacks this conserved domain and is apparently hypophosphorylated) resides exclusively in the cytoplasm in a tim01 background but relocates to the nucleus in tim+ (51). Since PERΔ exhibits a dramatic reduction in nuclear localization (Fig. 3b) and weaker repression activity seems to be partially due to a change in subcellular localization (Fig. 3c), we considered that PERΔ activity in an otherwise wild-type fly (Fig. 4b and Table 2) could be due to an improvement of PERΔ nuclear localization relative to S2 cells. We decided to test this hypothesis by assaying the effect of PERΔ in a strain that may have even better PER nuclear localization due to overexpression of the putative TIM kinase SGG (shaggy; glycogen synthase kinase 3) (36). SGG overexpression in tim-expressing neurons causes period shortening, due apparently to accelerated PER and TIM nuclear entry (36). SGG overexpression in circadian pacemaker neurons only (PDF [pigment-dispersing factor] cells) shortens the period to about 21 h (49), also presumably due to advanced nuclear entry.
As a control, we first examined cooverexpression of wild-type per (UAS-per24) in the EP (X) 1576 (containing UAS-sgg)-pdfGAL4 background. Rather unexpectedly, UAS-per expression in the PDF neurons restores normal periods to this transgenic line (Table 3 and Fig. 5). We then tested the effect of PERΔ in the same background. Surprisingly, UAS-perΔ has an effect very similar to that of UAS-per24 (Table 3 and a representative actogram in Fig. 5); that is, the locomotor activity period of pdfGAL4-UAS-sgg-UAS-perΔ becomes normal. Since pdfGAL4-UAS-per24 as well as pdfGAL4-UAS-perΔ showed no significant period lengthening without SGG overexpression (data not shown), this effect is not a simple additive period effect. The results substantiate the notion that PERΔ has biological activity in flies and suggest that the inability of PERΔ to rescue per0 is linked to inefficient nuclear localization. They predict that more direct improvements in PERΔ nuclear localization might further increase PERΔ repressor activity in the S2 cell assay.
TABLE 3.
Summary of locomotor activity rhythms of pdfGAL4-UAS-sgg flies with additional per or perΔ expressiona
| Genotype | No. (%) of flies tested
|
τ (h) (SD) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Rhythmic | Arrhythmic | ||
| EP (X) 1576; pdf-GAL4/CyO; +/+ | 20 | 20 (100.00) | 0 (0.00) | 20.99 (0.53) |
| EP (X) 1576; pdf-GAL4/UAS-per24; +/+ | 34 | 34 (100.00) | 0 (0.00) | 24.07 (0.34) |
| EP (X) 1576; pdf-GAL4/UAS-perΔ 1A1r; +/+ | 23 | 23 (100.00) | 0 (0.00) | 23.37 (0.40) |
| EP (X) 1576; pdf-GAL4/UAS-perΔ 2C2; +/+ | 33 | 33 (100.00) | 0 (0.00) | 24.55 (0.42) |
| EP (X) 1576; pdf-GAL4/UAS-perΔ 2C4; +/+ | 32 | 31 (96.88) | 1 (3.13) | 24.34 (0.47) |
| EP (X) 1576; pdf-GAL4/+; +/UAS-perΔ 2Y1 | 31 | 31 (100.00) | 0 (0.00) | 24.52 (0.42) |
| EP (X) 1576; pdf-GAL4/+; +/UAS-perΔ 2X1 | 25 | 24 (96.00) | 1 (4.00) | 24.88 (0.36) |
Please consult Table 1 for explanation of genotypes and abbreviations.
FIG. 5.
Physiological activities of wild-type per and perΔ are very similar in flies with accelerated nuclear translocation of PER. Representation of grouped locomotor activity in constant darkness of pdf-GAL4-UAS-sgg [from EP (X) 1576], exhibiting shortening of the period (a); pdf-GAL4-UAS-sgg-UAS-per24, exhibiting normal period (b); and pdf-GAL4-UAS-sgg-UAS-perΔ, having normal period (c). Three independent lines of UAS-perΔ are shown here. A complete summary of UAS-perΔ lines tested is in Table 3.
Rescue of PERΔ nuclear import restores its suppression activity.
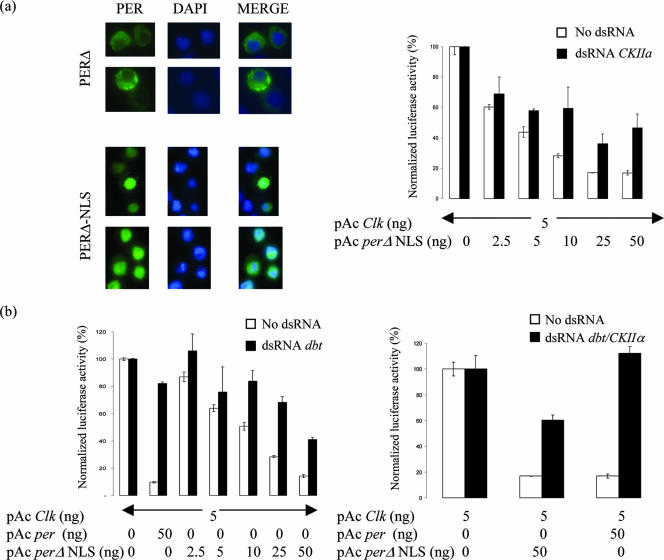
To test this prediction, we added an NLS (23) to PERΔ and created PERΔ-NLS. As expected, PERΔ-NLS localized exclusively to the nucleus in S2 cells (Fig. 6a). Surprisingly, PERΔ-NLS is also much more potent than PERΔ in suppressing CLK-CYC transcription activation (Fig. 6b). This was intriguing, because we previously proposed that PER phosphorylation by DBT and CKII is critical for PER suppression activity (40).
FIG. 6.
Enhancement of nuclear entry by addition of NLS rescues the transcriptional repression activity defect of PERΔ. This much-improved repression activity of PERΔ-NLS remains sensitive to down-regulation of DBT and CKII similar to wild-type PER, albeit to lesser extent, suggesting that these kinases could be involved in both nuclear localization and repression activity potentiation of PER. (a) Immunocytochemistry of PERΔ (top) and PERΔ-NLS (bottom). (Left) Staining of PER using anti-V5 antibody; (middle) nuclear staining using DAPI (4′,6′-diamidino-2-phenylindole); (right) merged image showing subcellular localization of PERΔ and PERΔ-NLS. (b) PERΔ-NLS regains active repression activity (bottom left and top right; unfilled bars); reduction of DBT and of CKIIα activity by RNAi reduces the repression activity (bottom left and top right, respectively; filled bars). The graph depicts normalized luciferase activity from S2 cell repression activity assay using increasing amounts of PERΔ-NLS; wild-type PER was used as a control (second column). (Bottom right) RNAi of both kinases shows stronger effect but to an extent noticeably less than that for wild-type PER.
To further examine PERΔ-NLS suppression activity and especially its dependence on DBT and CKII, we examined the effect of dsRNA against DBT, CKIIα, or both. Interestingly and consistent with our previous observations (40), knock-down of both kinases significantly reduces suppression activity of PERΔ-NLS (Fig. 6b). It is notable, however, that all dsRNA effects are smaller for PERΔ-NLS than for PER. Taken together, the results indicate that these kinases contribute to PER transcriptional repressor activity independently of their effects on PER nuclear localization.
DISCUSSION
We identify in this paper a 27-aa motif of Drosophila PER which is conserved in mammalian PERs. It contributes to normal Drosophila PER phosphorylation by CKII and DBT as well as to PER transcriptional repressor activity. Molecular characterization of PERΔ in S2 cells suggests that the domain also contributes significantly to PER nuclear localization. Indeed, PERΔ regained S2 cell transcriptional repressor activity when nuclear localization was facilitated, and two less direct experiments with flies can be interpreted similarly. There is also evidence that the two kinases function to potentiate transcriptional repression independently of their effects on PER nuclear localization. The data indicate that the domain functions to facilitate phosphorylation, which contributes to PER nuclear localization, transcriptional repressor activity, and PER degradation.
We initially hypothesized that the domain might serve as an early phosphorylation site which must be phosphorylated for subsequent phosphorylation events to occur. However, mutagenesis of all possible phosphorylation sites does not prevent progressive phosphorylation, and a small subdeletion containing all potential phosphorylation sites gives rise to hypophosphorylated PERs like PERΔ. We note that Kim and colleagues independently identified and deleted a somewhat larger region of ∼50 aa which includes our ∼30 aa. They also mutagenized potential phosphorylation sites and obtained nearly identical effects on PER phosphorylation and transcriptional repressor activity in S2 cells (25a).
We then considered that the domain serves as a protein-protein interaction module and recruits protein(s) required for PER phosphorylation. One intriguing candidate is a direct interaction with DBT itself. Indeed, while this work was in progress, Eide and colleagues suggested that the comparable region in mammalian PER functions as a DBT-interacting domain (13). Moreover, Kim and colleagues report that a somewhat larger deletion significantly compromises the interaction between PER and DBT, in flies as well as in S2 cells (25a; we also observe a reduced interaction between DBT and PERΔ in S2 cell extracts [data not shown]), supporting the notion that this domain interacts with DBT.
On the other hand, there are indications that this domain is not the sole region of PER mediating a DBT interaction. First, Kloss and colleagues have previously shown that the domain is dispensable for physical interaction of PER and DBT, i.e., a PER fragment missing the conserved motif can bind DBT in vitro (26) as well as in vivo (27). Second, Cyran and colleagues demonstrated that a PER molecule missing this domain responds biologically to a DBT mutation in a manner similar to that of wild-type PER (9). Third, PERΔ is essentially insensitive to DBT-induced phosphorylation and degradation in S2 cells (Fig. 1), despite only a modest reduction in DBT coimmunoprecipitation (reference 25a and data not shown.). This suggests that there is an additional problem in the nature of the DBT-PER interaction. Fourth, PERΔ (and in particular PERΔ-NLS) is a partially active repressor and is DBT sensitive, suggesting that PERΔ still interacts with DBT. Fifth, our S2 cell repression assays show little distinction between the effects of RNAi against CKII and DBT, suggesting that the defect is unlikely to be completely DBT specific (although we note that this could reflect the absence of a DBT-specific binding domain and a kinase order of DBT first and CKII second). Finally, the N-terminal portion of the Drosophila domain lies outside of the mammalian domain identified by Eide and colleagues. More importantly, deletion of this region of mammalian PER did not affect the mPER-CKIɛ interaction (13), whereas deletion of this region in Drosophila PER (PERΔn) confers resistance to PER phosphorylation. Based on all of these considerations, we prefer the notion that the 27-aa Drosophila domain has a more indirect and/or a wider effect on kinase binding or on the conformation of the complex of kinase(s) and substrate. We speculate that it could be part of a more complex DBT binding surface and/or that it interacts with another protein which is involved in enabling phosphorylation by both DBT and CKII (Fig. 7).
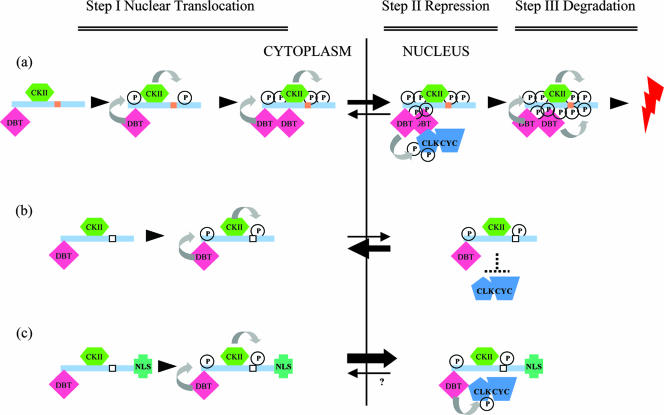
FIG. 7.
Model. (a) We propose that the conserved domain (brown rectangle) is involved in progressive phosphorylation. In the first step (step I), newly synthesized PER is phosphorylated by DBT and CKII; however, this progressive phosphorylation is dependent on the conserved domain (see the text for more detail). This domain could enhance phosphorylation either by interacting with kinases itself or by helping to recruit other kinases to PER (DBT and CKII included). In any case, proper phosphorylation leads to PER nuclear translocation. In the second step within the nucleus (step II), PER represses CLK-CYC transcriptional activation in association with DBT, as recently suggested (25, 55), and perhaps with CKII. In the third step (step III), phosphorylation by DBT and CKII promotes PER degradation. (b) Removal of the conserved domain (empty rectangle) weakens the kinase-PER interactions, disables progressive phosphorylation, inhibits PER nuclear localization, and results in a large reduction in repression activity. (c) Addition of an NLS increases PERΔ repression activity, suggesting that PERΔ is an active repressor and that the reduction in PERΔ repression activity is primarily due to a defect in nuclear localization. Curved arrows indicate progressive phosphorylation, whereas forward and reverse black arrows indicate nuclear entry and export, respectively. Although the rate of nuclear export of PERΔ-NLS is uncertain, it is apparently negligible relative to that of nuclear entry.
In addition to the loss of progressive phosphorylation, PERΔ is notably less nuclear than PER in S2 cells (Fig. 3b). We have proposed previously that nuclear localization of PER is a consequence of PER nucleus-cytoplasm shuttling (40), which has also been observed for mammalian PERs (53). In addition, TIM nuclear localization has been recently shown to result from dynamic nuclear import and export (2). Three observations with flies lead us to propose that hypophosphorylated PER favors a cytoplasmic location, whereas hyperphosphorylated PER more favors the nucleus. First, PER becomes progressively phosphorylated throughout the night (12). Second, PER appears exclusively cytoplasmic at the beginning of the night and then becomes more and more nuclear towards the end of the night, a phenomenon observed for photoreceptor cells as well as for the brain (44, 51). Third, the precise timing of TIM-PER nuclear entry in S2 cells is difficult to imagine without some temporal phosphorylation events. These observations also fit with the fact that wild-type PER, which is more phosphorylated than PERΔ, is also more nuclear.
Our analysis further suggests that the reduction in PERΔ nuclear localization in S2 cells is caused by decreased nuclear import as well as increased nuclear export. About 60 to 70% of wild-type PER is nuclear with LMB, whereas about 15% is nuclear without drug. This suggests that about 60 to 70% of PER shuttles, of which about 20 to 25% is retained in nuclei at steady state (i.e., 15% of 60 to 70%). In case of PERΔ, only about 30% is nuclear with LMB, indicating that the fraction of PER capable of entering the nucleus drops from 60 to 70% to about 30%. In addition, the fraction of nuclear PERΔ approaches zero without LMB, suggesting that the efficiency of PERΔ nuclear export is close to 100%. This contrasts with a value of about 75 to 80% for wild-type PER. We therefore conclude that decreased nuclear import as well as increased nuclear export causes the reduction in nuclear PERΔ. The increased nuclear export could reflect a failure of PERΔ to interact with nuclear components as previously proposed (40).
Two putative PER kinases, CKII and DBT, influence PER nuclear localization. CKII likely plays a direct role, as CKII hypomorphic mutants and PER mutations in CKII phosphorylation sites affect the timing of PER nuclear entry during a normal circadian cycle in flies (1, 32, 33). In contrast, the role of DBT in PER nuclear entry is controversial (3, 9): for example, a hypomorphic DBT mutant (dbtS) also exhibits delayed PER nuclear localization (3), whereas a DBT mutant with severely reduced activity may enable PER nuclear localization (9). This suggests that differing PER phosphorylation sites could have opposite effects on PER nuclear localization (16). Because our results suggest that PERΔ is still partially phosphorylated by CKII and DBT, it is difficult to attribute the change in nuclear localization to a specific kinase. Nonetheless, it is likely that the failure to undergo normal phosphorylation contributes to the almost exclusive cytoplasmic localization of PERΔ.
Is this why PERΔ has so little transcriptional repressor activity? The simplest interpretation of the dramatic activity recovery of PERΔ-NLS is that subcellular localization makes a substantial contribution to activity in the S2 cell system (Fig. 7c). We note in this context that nuclear localization of PERΔ-NLS is much greater than that of wild-type PER, even in the presence of LMB (Fig. 3b). This suggests that PER nuclear entry is intrinsically inefficient in S2 cells, reflecting perhaps the absence of TIM. TIM is known to promote PER nuclear entry in flies (51), and temporal gating of nuclear entry appears to be a property of the TIM-PER complex in S2 cells (38). Unfortunately, the addition of TIM does not substantially improve PER nuclear localization in our steady-state S2 cell assays (data not shown).
Nonetheless, PERΔ-NLS is still sensitive to DBT and CKII RNAi, consistent with our previous suggestion that DBT and CKII influence PER-mediated repression activity independently of nuclear localization (40). This also fits well with the recent proposal that PER brings DBT to the CLK-CYC complex, which leads to CLK phosphorylation and suppression of transcriptional activation potential (25, 55). The most parsimonious interpretation of our data is therefore that phosphorylation of cytoplasmic PER potentiates nuclear entry, after which DBT and CKII collaborate with phospho-PER to inhibit CLK-CYC activity (Fig. 7a, step I). One possibility is that an interaction between the PER complex and CLK-CYC redirects the kinases to phosphorylate CLK-CYC (Fig. 7b, step II). Current evidence in the literature suggests a subsequent role of DBT (and likely CKII) in promoting PER degradation (26, 41), so we postulate that phosphorylation of nuclear PER by DBT and CKII continues after CLK phosphorylation and CLK-CYC transcriptional inhibition (Fig. 7a, step III).
In light of the S2 cell results, it is not surprising that PER from elavc155GAL4 per0; UAS-perΔ is hypophosphorylated and cannot rescue per0 behavioral arrhythmicity. How then does UAS-perΔ lengthen circadian period in a wild-type background indistinguishably from UAS-per? A previous report indicates that a truncated PER-beta-galactosidase fusion gene (PER-SG), which also lacks this conserved domain, manifests apparently normal nuclear localization in a wild-type background but only cytoplasmic localization in a tim0 background (51). Together with our observation that facilitation of PERΔ nuclear entry circumvents the repression activity defect in S2 cells, we suggest that the PERΔ period lengthening reflects transcriptional repression activity due to enhanced nuclear localization in flies relative to S2 cells. Moreover, Kim and colleagues have observed nuclear localization of their PERΔ construct in flies (25a). PER-SG, in contrast, does not interfere with behavioral period in an otherwise wild-type background (47), probably because the SG fusion protein lacks a PER CLK-CYC-interacting domain (5). All of these considerations suggest that PERΔ biological activity in flies reflects the ability to repress CLK-CYC activity. This interpretation applies equally well to the similar effects of UAS-per and UAS-perΔ on the period of pdfGAL4 UAS-sgg flies (Table 3).
This then begs the question of why elavc155GAL4 per0; UAS-perΔ does not rescue per0 behavioral arrhythmicity. One possibility is that PERΔ transcriptional repression activity is quantitatively or qualitatively deficient in flies: it is sufficient for period lengthening in an otherwise wild-type background, i.e., to complement PER, but inadequate in a per0 background. A second is that the deficit in PERΔ phosphorylation causes aberrant timing when PERΔ is the sole source of PER, i.e., in a per0 background. This problem could be with the kinetics of PER accumulation and nuclear localization and/or with PER degradation, both of which probably require a proper relationship between PER and kinases. We favor this second possibility, as it also explains why additional doses of per shorten period whereas additional PER, i.e., UAS-per, lengthens period in a wild-type background (45, 54): the former possibility would reflect accelerated accumulation and nuclear entry (phosphorylation), whereas the latter is similar to what we observe here, namely, improperly timed, enhanced repression. This should be testable by a comparison of the repression activities of UAS-per and UAS-perΔ in vivo.
Acknowledgments
We thank Issac Edery for communication of unpublished results and Vipin Suri for pAc dbt. Many thanks to members of the Rosbash laboratory, particularly Jerome Menet, Sebastian Kaderner, Jose Agosto, Emi Nagoshi, Rachna Kaushik, and Rebecca Schoer, for fruitful discussions and comments, and to Heather Felton for administrative assistance. Special thanks for Ying Peng, Yi Gao, and Hanson Du for technical help. Antibody for p150 was a kind gift from Michael Welte. LMB was a generous gift from Minoru Yoshida. M.R. is an HHMI investigator.
The work was supported by awards to M.R. from the NIH (grant NS44232) and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Footnotes
Published ahead of print on 23 April 2007.
REFERENCES
- 1.Akten, B., E. Jauch, G. K. Genova, E. Y. Kim, I. Edery, T. Raabe, and F. R. Jackson. 2003. A role for CK2 in the Drosophila circadian oscillator. Nat. Neurosci. 6:251-257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ashmore, L. J., S. Sathyanarayanan, D. W. Silvestre, M. M. Emerson, P. Schotland, and A. Sehgal. 2003. Novel insights into the regulation of the timeless protein. J. Neurosci. 23:7810-7819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bao, S., J. Rihel, E. Bjes, J. Y. Fan, and J. L. Price. 2001. The Drosophila double-timeS mutation delays the nuclear accumulation of period protein and affects the feedback regulation of period mRNA. J. Neurosci. 21:7117-7126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bell-Pedersen, D., V. M. Cassone, D. J. Earnest, S. S. Golden, P. E. Hardin, T. L. Thomas, and M. J. Zoran. 2005. Circadian rhythms from multiple oscillators: lessons from diverse organisms. Nat. Rev. Genet. 6:544-556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chang, D. C., and S. M. Reppert. 2003. A novel C-terminal domain of Drosophila PERIOD inhibits dCLOCK:CYCLE-mediated transcription. Curr. Biol. 13:758-762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Colot, H. V., J. C. Hall, and M. Rosbash. 1988. Interspecific comparison of the period gene of Drosophila reveals large blocks of non-conserved coding DNA. EMBO J. 7:3929-3937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Crews, S. T., J. B. Thomas, and C. S. Goodman. 1988. The Drosophila single-minded gene encodes a nuclear protein with sequence similarity to the per gene product. Cell 52:143-152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Curtin, K. D., Z. J. Huang, and M. Rosbash. 1995. Temporally regulated nuclear entry of the Drosophila period protein contributes to the circadian clock. Neuron 14:365-372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cyran, S. A., G. Yiannoulos, A. M. Buchsbaum, L. Saez, M. W. Young, and J. Blau. 2005. The double-time protein kinase regulates the subcellular localization of the Drosophila clock protein period. J. Neurosci. 25:5430-5437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dembinska, M. E., R. Stanewsky, J. C. Hall, and M. Rosbash. 1997. Circadian cycling of a PERIOD-beta-galactosidase fusion protein in Drosophila: evidence for cyclical degradation. J. Biol. Rhythms 12:157-172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Edery, I. 1999. Role of posttranscriptional regulation in circadian clocks: lessons from Drosophila. Chronobiol. Int. 16:377-414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Edery, I., L. J. Zwiebel, M. E. Dembinska, and M. Rosbash. 1994. Temporal phosphorylation of the Drosophila period protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91:2260-2264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Eide, E. J., M. F. Woolf, H. Kang, P. Woolf, W. Hurst, F. Camacho, E. L. Vielhaber, A. Giovanni, and D. M. Virshup. 2005. Control of mammalian circadian rhythm by CKIɛ-regulated proteasome-mediated PER2 degradation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 25:2795-2807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Fornerod, M., M. Ohno, M. Yoshida, and I. W. Mattaj. 1997. CRM1 is an export receptor for leucine-rich nuclear export signals. Cell 90:1051-1060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fukuda, M., S. Asano, T. Nakamura, M. Adachi, M. Yoshida, M. Yanagida, and E. Nishida. 1997. CRM1 is responsible for intracellular transport mediated by the nuclear export signal. Nature 390:308-311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gallego, M., E. J. Eide, M. F. Woolf, D. M. Virshup, and D. B. Forger. 2006. An opposite role for tau in circadian rhythms revealed by mathematical modeling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103:10618-10623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Grima, B., A. Lamouroux, E. Chelot, C. Papin, B. Limbourg-Bouchon, and F. Rouyer. 2002. The F-box protein slimb controls the levels of clock proteins period and timeless. Nature 420:178-182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hall, J. 2003. Genetics and molecular biology of rhythms in Drosophila and other insects. Adv. Genet. 48:1-280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hamblen, M., W. A. Zehring, C. P. Kyriacou, P. Reddy, Q. Yu, D. A. Wheeler, L. J. Zwiebel, R. J. Konopka, M. Rosbash, and J. C. Hall. 1986. Germ-line transformation involving DNA from the period locus in Drosophila melanogaster: overlapping genomic fragments that restore circadian and ultradian rhythmicity to per0 and per- mutants. J. Neurogenet. 3:249-291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hao, H., D. L. Allen, and P. E. Hardin. 1997. A circadian enhancer mediates PER-dependent mRNA cycling in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol. Cell. Biol. 17:3687-3693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hardin, P. E., J. C. Hall, and M. Rosbash. 1992. Circadian oscillations in period gene mRNA levels are transcriptionally regulated. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:11711-11715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hardin, P. E., J. C. Hall, and M. Rosbash. 1990. Feedback of the Drosophila period gene product on circadian cycling of its messenger RNA levels. Nature 343:536-540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kalderon, D., W. D. Richardson, A. F. Markham, and A. E. Smith. 1984. Sequence requirements for nuclear location of simian virus 40 large-T antigen. Nature 311:33-38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kaneko, M., J. Park, Y. Cheng, P. Hardin, and J. Hall. 2000. Disruption of synaptic transmission or clock-gene-product oscillations in circadian pacemaker cells of Drosophila cause abnormal behavioral rhythms. J. Neurobiol. 43:207-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kim, E. Y., and I. Edery. 2006. Balance between DBT/CKIepsilon kinase and protein phosphatase activities regulate phosphorylation and stability of Drosophila CLOCK protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103:6178-6183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25a.Kim, E. Y., H. W. Ko, W. Yu, P. E. Hardin, and I. Edery. 2007. A DOUBLETIME kinase binding domain on the Drosophila PERIOD protein is essential for its hyperphosphorylation, transcriptional repression, and circadian clock function. Mol. Cell. Biol. 27:5014-5028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kloss, B., J. L. Price, L. Saez, J. Blau, A. Rothenfluh, C. S. Wesley, and M. W. Young. 1998. The Drosophila clock gene double-time encodes a protein closely related to human casein kinase Iepsilon. Cell 94:97-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kloss, B., A. Rothenfluh, M. W. Young, and L. Saez. 2001. Phosphorylation of period is influenced by cycling physical associations of double-time, period, and timeless in the Drosophila clock. Neuron 30:699-706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ko, H. W., J. Jiang, and I. Edery. 2002. Role for Slimb in the degradation of Drosophila Period protein phosphorylated by Doubletime. Nature 420:673-678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Konopka, R. J., and S. Benzer. 1971. Clock mutants of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 68:2112-2116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lee, C., J. P. Etchegaray, F. R. Cagampang, A. S. Loudon, and S. M. Reppert. 2001. Posttranslational mechanisms regulate the mammalian circadian clock. Cell 107:855-867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Levine, J. D., P. Funes, H. B. Dowse, and J. C. Hall. 2002. Signal analysis of behavioral and molecular cycles. BMC Neurosci. 3:1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lin, J. M., V. L. Kilman, K. Keegan, B. Paddock, M. Emery-Le, M. Rosbash, and R. Allada. 2002. A role for casein kinase 2alpha in the Drosophila circadian clock. Nature 420:816-820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lin, J. M., A. Schroeder, and R. Allada. 2005. In vivo circadian function of casein kinase 2 phosphorylation sites in Drosophila PERIOD. J. Neurosci. 25:11175-11183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Liu, X., L. J. Zwiebel, D. Hinton, S. Benzer, J. C. Hall, and M. Rosbash. 1992. The period gene encodes a predominantly nuclear protein in adult Drosophila. J. Neurosci. 12:2735-2744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lowrey, P. L., K. Shimomura, M. P. Antoch, S. Yamazaki, P. D. Zemenides, M. R. Ralph, M. Menaker, and J. S. Takahashi. 2000. Positional syntenic cloning and functional characterization of the mammalian circadian mutation tau. Science 288:483-492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Martinek, S., S. Inonog, A. S. Manoukian, and M. W. Young. 2001. A role for the segment polarity gene shaggy/GSK-3 in the Drosophila circadian clock. Cell 105:769-779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.McDonald, M. J., and M. Rosbash. 2001. Microarray analysis and organization of circadian gene expression in Drosophila. Cell 107:567-578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Meyer, P., L. Saez, and M. W. Young. 2006. PER-TIM interactions in living Drosophila cells: an interval timer for the circadian clock. Science 311:226-229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Nawathean, P., J. S. Menet, and M. Rosbash. 2005. Assaying the Drosophila negative feedback loop with RNA interference in s2 cells. Methods Enzymol. 393:610-622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Nawathean, P., and M. Rosbash. 2004. The doubletime and CKII kinases collaborate to potentiate Drosophila PER transcriptional repressor activity. Mol. Cell 13:213-223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Price, J. L., J. Blau, A. Rothenfluh, M. Abodeely, B. Kloss, and M. W. Young. 1998. double-time is a novel Drosophila clock gene that regulates PERIOD protein accumulation. Cell 94:83-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Renn, S. C., J. H. Park, M. Rosbash, J. C. Hall, and P. H. Taghert. 1999. A pdf neuropeptide gene mutation and ablation of PDF neurons each cause severe abnormalities of behavioral circadian rhythms in Drosophila. Cell 99:791-802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Sathyanarayanan, S., X. Zheng, R. Xiao, and A. Sehgal. 2004. Posttranslational regulation of Drosophila PERIOD protein by protein phosphatase 2A. Cell 116:603-615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Shafer, O. T., M. Rosbash, and J. W. Truman. 2002. Sequential nuclear accumulation of the clock proteins period and timeless in the pacemaker neurons of Drosophila melanogaster. J. Neurosci. 22:5946-5954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Smith, R. F., and R. J. Konopka. 1982. Effects of dosage alterations at the per locus on the period of the circadian clock of Drosophila. Mol. Gen. Genet. 189:30-36. [Google Scholar]
- 46.So, W. V., and M. Rosbash. 1997. Post-transcriptional regulation contributes to Drosophila clock gene mRNA cycling. EMBO J. 16:7146-7155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Stanewsky, R., B. Frisch, C. Brandes, M. J. Hamblen-Coyle, M. Rosbash, and J. C. Hall. 1997. Temporal and spatial expression patterns of transgenes containing increasing amounts of the Drosophila clock gene period and lacZ reporter: mapping elements of the PER protein involved in circadian cycling. J. Neurosci. 17:676-696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Stanewsky, R., C. F. Jamison, J. D. Plautz, S. A. Kay, and J. C. Hall. 1997. Multiple circadian-regulated elements contribute to cycling period gene expression in Drosophila. EMBO J. 16:5006-5018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Stoleru, D., Y. Peng., P. Nawathean, and M. Rosbash. 2005. A resetting signal between Drosophila pacemakers synchronizes morning and evening activity. Nature 438:238-242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Toh, K. L., C. R. Jones, Y. He, E. J. Eide, W. A. Hinz, D. M. Virshup, L. J. Ptacek, and Y. H. Fu. 2001. An hPer2 phosphorylation site mutation in familial advanced sleep-phase syndrome. Science 291:1040-1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Vosshall, L. B., J. L. Price, A. Sehgal, L. Saez, and M. W. Young. 1994. Block in nuclear localization of period protein by a second clock mutation, timeless. Science 263:1606-1609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Xu, Y., Q. S. Padiath, R. E. Shapiro, C. R. Jones, S. C. Wu, N. Saigoh, K. Saigoh, L. J. Ptacek, and Y. H. Fu. 2005. Functional consequences of a CKIdelta mutation causing familial advanced sleep phase syndrome. Nature 434:640-644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Yagita, K., F. Tamanini, M. Yasuda, J. H. Hoeijmakers, G. T. van der Horst, and H. Okamura. 2002. Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling and mCRY-dependent inhibition of ubiquitylation of the mPER2 clock protein. EMBO J. 21:1301-1314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Yang, Z., and A. Sehgal. 2001. Role of molecular oscillations in generating behavioral rhythms in Drosophila. Neuron 29:453-467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Yu, W., H. Zheng, J. H. Houl, B. Dauwalder, and P. E. Hardin. 2006. PER-dependent rhythms in CLK phosphorylation and E-box binding regulate circadian transcription. Genes Dev. 20:723-733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Zeng, H., Z. Qian, M. P. Myers, and M. Rosbash. 1996. A light-entrainment mechanism for the Drosophila circadian clock. Nature 380:129-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]