Abstract
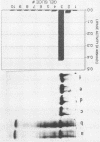
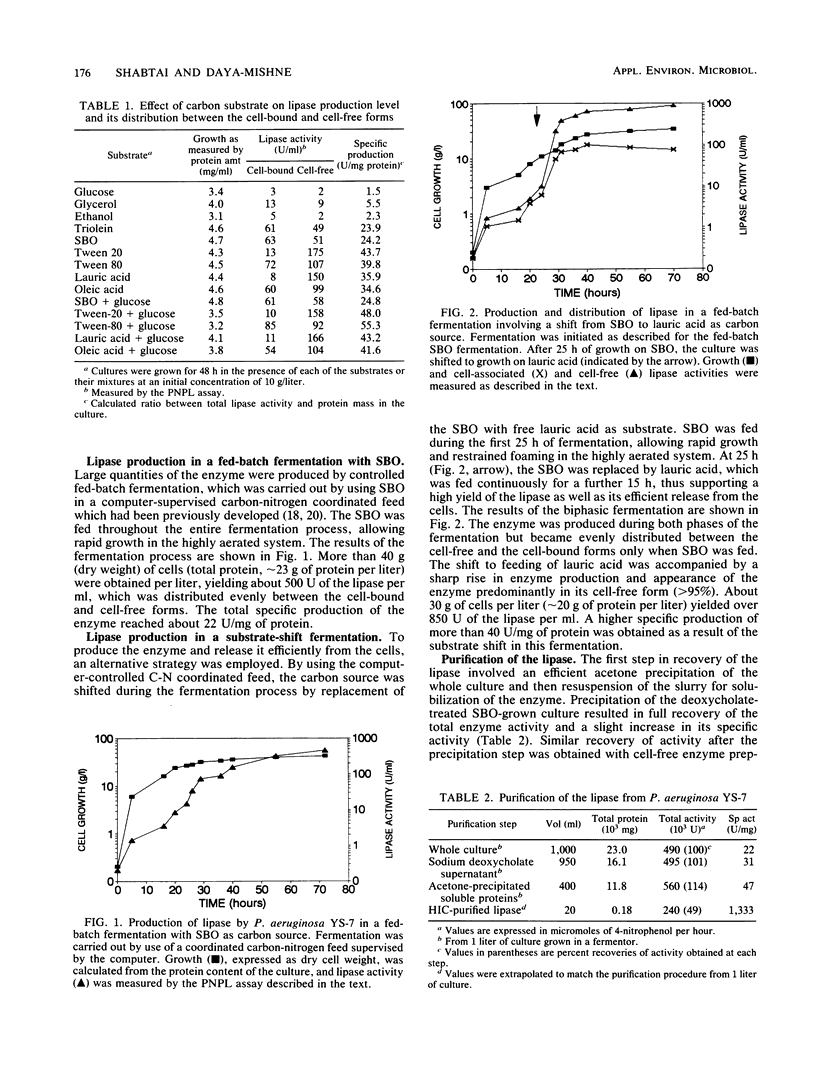
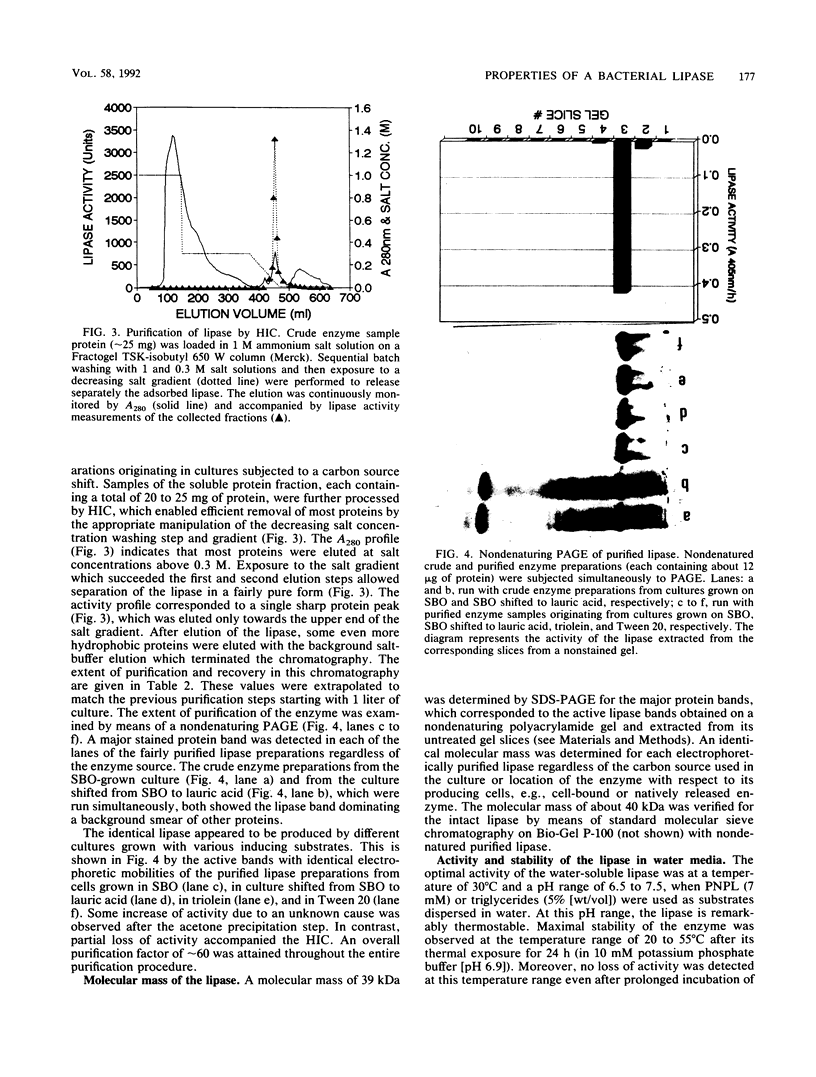
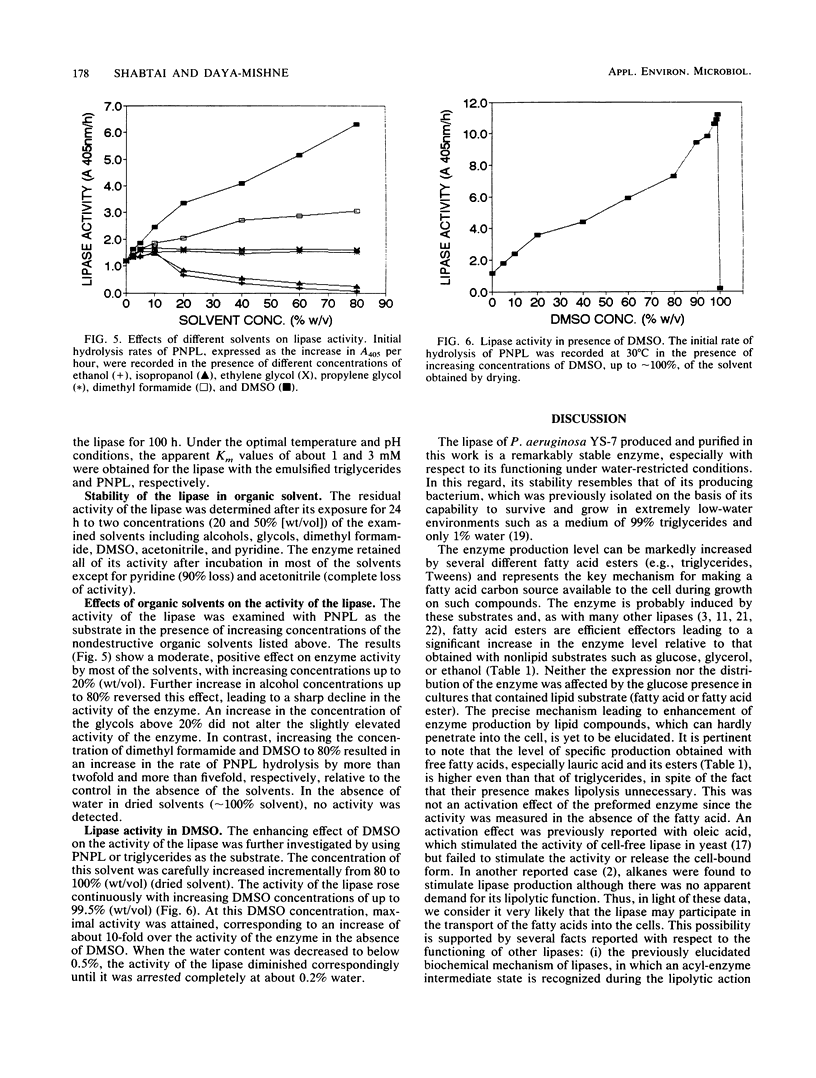
An extracellular lipase from the low-water-tolerant bacterium P. aeruginosa YS-7 was produced, purified, and characterized with respect to its functional properties in aqueous solutions and organic solvents. The enzyme was partially released from the cells during fermentation in defined medium with 5% (wt/vol) soybean oil. Approximately one-half of the total culture activity remained in solution after removal of cells. More than 95% of the activity was found in culture supernatant after mild detergent treatment (10 mM sodium deoxycholate) or after shifting the carbon source during the fermentation from triglyceride to a free fatty acid. The enzyme was recovered from an acetone precipitate of the whole culture and purified by hydrophobic interaction chromatography, yielding a preparation having a specific activity of about 1,300 mumol of fatty acid mg-1 h-1. The lipase (molecular size, approximately 40 kDa) hydrolyzes a variety of fatty acid esters and has an optimum pH of about 7. The enzyme retained its full activity at 20 to 55 degrees C, even after prolonged exposure (more than 30 days) to different concentrations of water-miscible organic solvents such as alcohols, glycols, pyridine, acetonitrile, dimethyl formamide, and dimethyl sulfoxide. The hydrolysis of 4-nitrophenyl laurate ester and of triglyceride emulsified in water was slightly accelerated with increasing concentrations of alcohols and glycols up to about 20% but was abolished with a further increase in alcohol concentration or in the presence of acetonitrile. In contrast, the rate of hydrolysis of these substrates in concentrated solutions of dimethyl formamide or dimethyl sulfoxide was markedly increased, by more than twofold and more than fivefold, respectively.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Breuil C., Shindler D. B., Sijher J. S., Kushner D. J. Stimulation of lipase production during bacterial growth on alkanes. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):601–606. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.601-606.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsack D. E. Relation of the hydrophobicity index to the thermal stability of homologous proteins. Biopolymers. 1970 Feb;9(2):247–252. doi: 10.1002/bip.1970.360090209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isobe M., Sugiura M. Studies on the lipase of Chromobacterium viscosum. V. Physical and chemical properties of the lipases. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1977 Aug;25(8):1980–1986. doi: 10.1248/cpb.25.1980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shabtai Y. Isolation and characterization of a lipolytic bacterium capable of growing in a low-water-content oil-water emulsion. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jun;57(6):1740–1745. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.6.1740-1745.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shabtai Y. Production of exopolysaccharides by Acinetobacter strains in a controlled fed-batch fermentation process using soap stock oil (SSO) as carbon source. Int J Biol Macromol. 1990 Apr;12(2):145–152. doi: 10.1016/0141-8130(90)90066-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuer W., Jaeger K. E., Winkler U. K. Purification of extracellular lipase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1070–1074. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1070-1074.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler U. K., Stuckmann M. Glycogen, hyaluronate, and some other polysaccharides greatly enhance the formation of exolipase by Serratia marcescens. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;138(3):663–670. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.3.663-670.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaks A., Klibanov A. M. Enzyme-catalyzed processes in organic solvents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3192–3196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]