Abstract
The complex response of murine macrophages to infection with Streptococcus pyogenes was investigated at the level of gene expression with a high-density oligomer microarray. More than 400 genes were identified as being differentially regulated. Many of the up-regulated genes encode molecules involved in the immune response and in inflammation, transcription, signaling, apoptosis, the cell cycle, electron transport, and cell adhesion. Of particular interest was the up-regulation of proinflammatory cytokines, typical of the classically activated macrophages (M1 phenotype), such as tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 1 (IL-1), and IL-6, and as well as the up-regulation of anti-inflammatory mediators, such as IL-1 decoy receptor and IL-10, associated with alternative macrophage activation (M2 phenotype). Furthermore, the gene encoding inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), an enzyme typically implicated in classical activation, was not induced in infected macrophages. Instead, the gene encoding arginase, a competitor for the iNOS substrate arginine involved in the alternative activation pathway, was up-regulated in S. pyogenes-infected cells. Thus, the microarray-based gene expression analysis demonstrated that S. pyogenes induces an atypical activation program in macrophages, with some but not all features of the classical or alternative activation phenotypes. The microarray data also suggested that the bactericidal activity of macrophages against S. pyogenes is mediated by phagocyte oxidase, as p47phox was up-regulated in infected cells. Indeed, the in vivo and in vitro killing of S. pyogenes was markedly diminished in the absence of functional phagocyte (p47phox−/−) but not in the absence of iNOS (iNOS−/−). An understanding of how macrophages respond to S. pyogenes at the molecular level may facilitate the development of new therapeutic paradigms.
Streptococcus pyogenes (group A streptococcus) is a prevalent human pathogen responsible for a broad spectrum of clinical manifestations, including infections of the skin and upper respiratory tract, bacteremia, and occasionally sepsis and septic shock (9). Streptococcal septic shock is the most severe form of streptococcal disease and is characterized by an intense inflammatory reaction (25). The severity and outcome of the infections caused by S. pyogenes are likely to depend on the ability of host innate immune mechanisms to control bacterial growth and to limit further spread of the pathogen beyond the site of infection.
Previous studies examining host responses to S. pyogenes in a mouse model of infection have shown the importance of resident macrophages for controlling infection (18, 19). Macrophages are capable of recognizing, phagocytosing, and destroying S. pyogenes in order to eliminate the invading pathogen, while also producing cytokines and chemokines that are crucial in controlling the recruitment and activation of inflammatory cells at the site of infection (18, 19). Although it is assumed that the activation of macrophages is directed toward the elimination of the invading pathogens, it is equally likely that the excessive and unregulated stimulation of macrophages can lead to a continuous release of inflammatory mediators that act synergistically and thus lead to sepsis and septic shock (12). Therefore, the functional activities of macrophages during S. pyogenes infection may greatly influence the character, course, and outcome of the pathogenic process.
To improve our understanding of the complex response of macrophages to S. pyogenes and to identify new targets for which therapeutic options might be possible, we have analyzed the global gene expression profile of murine resident peritoneal macrophages after in vivo infection with this pathogen by gene array technology. We have identified more than 400 genes differentially transcribed in macrophages following 1 h of infection with S. pyogenes. Infection-induced genes fell into several functional categories, including immune response and inflammation, transcription, signaling, apoptosis, cell cycle, electronic transport, and cell adhesion; other induced genes have unknown functions.
Macrophages are plastic cells that respond to microenvironmental signals with distinct activation programs (16, 20, 30). Classically activated macrophages (M1 phenotype) are induced by inflammatory molecules such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and gamma interferon (IFN-γ). These M1 macrophages produce proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines, such as tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interleukin 1β (IL-1β), IL-6, IL-12, and macrophage inflammatory protein 1α (MIP-1α), and generate reactive nitrogen species, such as nitric oxide (NO), via expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) (16, 20, 30). Alternatively activated macrophages (M2 phenotype) are generated after exposure to certain stimuli, such as IL-4, IL-13, transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β), or glucocorticoids (16, 20). The M2 macrophages express anti-inflammatory molecules, such as IL-10 and IL-1 decoy receptor (IL-1ra), and metabolize arginine through arginase rather than iNOS (16, 20). Arginase blocks iNOS activity by a variety of mechanisms, including competing for the arginine substrate that is required for NO production (5). Classically activated M1 macrophages are potent effector cells integrated into Th1 responses, which kill microorganisms and tumor cells and produce copious amounts of proinflammatory cytokines (29). In contrast, M2 macrophages tune the inflammatory responses, promoting angiogenesis and tissue remodeling and repair. However, the M1 and M2 phenotypes seem to represent the two extremes of a spectrum of possible forms of macrophage activation, and different versions of the M2 phenotype—M2a, M2b, and M2c—with different functional properties have been described. Specifically, M2a macrophages are induced by IL-4 or IL-13 and are involved in promotion of Th2 responses; M2b macrophages are induced by exposure to agonists of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) or IL-1 receptor and play a role in suppression and regulation of inflammation and immunity; and the M2c phenotype, induced by IL-10 and glucocorticoid hormones, participates in matrix deposition and tissue remodeling (1, 26, 27).
The phenotype of macrophages activated by S. pyogenes is currently unknown but may be important in understanding the contribution of these phagocytic cells to disease pathogenesis. In this regard, we have shown here that S. pyogenes induces an atypical activation phenotype in macrophages that includes markers characteristic of both M1 and some of the M2 activation pathways.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacteria.
The S. pyogenes strains used in this study were S. pyogenes strain A20 (M-type 23), a human isolate obtained from the German Collection of Microorganisms and Cell Cultures (DSMZ 2071), and the sequenced M-type 1 strain SF370 (14). Stocks were maintained at −70°C and were routinely cultured at 37°C in Todd-Hewitt broth (Oxoid, Basingstoke, United Kingdom) supplemented with 1% yeast extract. Bacteria were collected in mid-log phase, washed twice with sterile phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), and diluted to the required inoculum, and the number of viable bacteria was determined by counting of CFU after dilution and plating in blood agar plates (GIBCO, Karlsruhe, Germany) containing 5% sheep blood.
Mice.
Inbred female C3H/HeN and BALB/c mice were purchased from Harlan-Winkelmann (Borchen, Germany). Mice with either a targeted disruption in the iNOS gene (B6.129P2-Nos2tm1Lau/J) (iNOS−/−) or a targeted deletion in the cytosolic p47phox gene [B6(Cg)-Ncf1m1J/J] (p47phox−/−), as well as wild-type control mice (C57BL/6J), were purchased from Jackson Laboratories (Bar Harbor, ME). Animals were housed in microisolator cages and given food and water ad libitum. All studies were approved by the local ethics board.
In vivo infection of peritoneal macrophages.
Mice were intraperitoneally infected with 5 × 107 CFU of S. pyogenes and euthanized 1 h thereafter, and the peritoneum was lavaged with sterile PBS. Macrophages present in the lavage samples were labeled with anti-F4/80 antibodies, further purified by positive selection with miniMACS magnetic microbeads, according to the manufacture's instructions (Miltenyi Biotec Inc., Germany), and used for the cDNA microarray analysis or reverse transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR).
For macrophage killing assays, peritoneal macrophages isolated from infected mice (1 h postinoculation) were seeded into 48-well microtiter plates and cultured at 37°C, 5% CO2, in Dulbecco modified Eagle medium (GIBCO) containing 10 mM HEPES, 2 mM l-glutamine, and 100 μg/ml of gentamicin. At several time points, the macrophages were lysed with distilled water (dH2O) and surviving bacteria were enumerated by plating of serial dilutions in blood agar.
In some experiments, peritoneal macrophages were stimulated with 1 μg/ml of LPS from Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium (Sigma-Aldrich, Taufkirchen, Germany) plus 100 U/ml of recombinant murine IFN-γ (PeproTech, Rocky Hill, NJ).
Array analysis.
Total RNA was isolated from highly purified F4/80+ cells obtained from the peritoneal cavity of BALB/c or C3H/HeN infected and uninfected control mice with peqGold TriFast (Peqlab), according to the manufacturer's instructions, and hybridized to an Affymetrix GeneChip MOE430A by standard Affymetrix protocols, as described elsewhere (36). Two replicate chips per group were used with pooled macrophages harvested from 8 to 10 mice. The data set used in this study is available in a MIAME-compliant format at the NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database under accession number GSE7769 (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/). Normalized gene expression intensities were compared, and genes were considered to be differentially expressed between infected and uninfected samples when their fold change was greater than or equal to 2 or less than or equal to −2. The statistical parameter used to define significant change (P) was less than 0.001, and the difference between compared signal intensities of a certain gene was more than 200.
RT-PCR.
To independently confirm the microarray results, RT-PCR was carried out on arbitrarily selected genes that were found to be up-regulated in infected macrophages in the microarray analysis (Il-1α, Il-1β, Il-6, Csf2, Tnf-α, Mip-1α, Mip-1β) and two unaffected genes (Ifn-γ, Il-12p40). Total RNA was prepared as described above. RNA was reverse transcribed with RT (Hoffman La Roche), and cDNA synthesis was performed with a Gibco RT-PCR kit, according to the manufacturer's instructions. The single-stranded cDNA was then subjected to PCR under standard reaction conditions. The PCR primer sequences for these genes, as well as those of the housekeeping genes β-actin and Rsp9, are provided in Table 1. The resultant PCR products were electrophoresed on a 2% agarose gel, stained with ethidium bromide, and photographed.
TABLE 1.
Primers used for RT-PCR
| Gene | Primer sequencea | PCR product (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| IL-1α | 5′ CAGTTCTGCCATTGACCATC 3′ | 218 |
| 5′ TGGATAAGCAGCTGATGTGAAGTA 3′ | ||
| IL-1β | 5′ ACTACAGGCTCCGAGATGAACAAC 3′ | 163 |
| 5′ CCCAAGGCCACAGGTATTTT 3′ | ||
| IL-6 | 5′ CTGGTGACAACCACGGCCTTCCCTA 3′ | 600 |
| 5′ ATGCTTAGGCATAACGCACTAGGTT 3′ | ||
| IL-12 p40 | 5′ CGTGCTCATGGCTGGTGCAAAG 3′ | 280 |
| 5′ CTTCATCTGCAAGTTCTTGGGC 3′ | ||
| TNF-α | 5′ AGCCCACGTCGTAGCAAACCACCAA 3′ | 446 |
| 5′ ACACCCATTCCCTTCACAGAGCAAT 3′ | ||
| MIP-1α | 5′ CTCCCAGCCAGGTGTCATTTTC 3′ | 110 |
| 5′ CTCAGGCATTCAGTTCCAGGTCAG 3′ | ||
| MIP-1β | 5′ GCAAACCTAACCCCGAGCAACA 3′ | 127 |
| 5′ AGCAGGAAGTGGGAGGGTCAGAG 3′ | ||
| IFN-γ | 5′ AGGAACTGGCAAAAGGATGGTGA 3′ | 106 |
| 5′ TGTTGCTGATGGCCTGATTGTCTT 3′ | ||
| Csf2 | 5′ CATTGTGGTCTACAGCCTCTC 3′ | 278 |
| 5′ GGCAGTATGTCTGGTAGTAGC 3′ | ||
| Nos | 5′ CCCTTCCGAAGTTTCTGGCAGCAGC 3′ | 496 |
| 5′ GGCTGTCAGAGCCTCGTGGCTTTGG 3′ | ||
| Arg2 | 5′ CGC ACA GAA GAA GCT AGG AG 3′ | 174 |
| 5′ CCCACT GAA CGA GGA TAC AC 3′ | ||
| β-Actin | 5′ TGGAATCCTGTGGCATCCATGAAAC 3′ | 318 |
| 5′ TAAAACGCAGCTCAGTAACAGTCCG 3′ | ||
| Rsp9 | 5′ CTGGACGAGGGCAAGATGAAGC 3′ | 143 |
| 5′ TGACGTTGGCGGATGAGCACA 3′ |
For each pair of primers, the sense sequence is listed first, followed by the antisense sequence.
Detection of IL-6 production by ELISA.
Detection of IL-6 was performed by specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). In brief, 96-well microtiter plates were coated overnight at 4°C with purified rat anti-mouse anti-IL-6 capture antibody (Pharmingen, San Diego, CA) at 2 μg/ml in sodium bicarbonate buffer. The wells were washed and then blocked with 2% bovine serum albumin-PBS before the supernatant samples and the appropriate standard were added to each well. Biotinylated rat monoclonal anti-IL-6 (Pharmingen) at 2 μg/ml was added as the second antibody. Detection was carried out with streptavidin-peroxidase, and the plates were developed with 2,2′-azinobis(3-ethylbenzthiazolinesulfonic acid). A standard curve was generated with recombinant murine IL-6 (Pharmingen).
Measurement of NO.
The Griess reaction was used to determine NO concentrations in supernatants of S. pyogenes-infected macrophages, as previously described (11). Briefly, supernatant from cultured uninfected or S. pyogenes-infected macrophages was mixed with an equal volume of Griess's reagent (1% sulfanilamide, 0.1% naphthylethylenediamine dihydrochloride, 2.5% H3PO4). Absorbance at 550 nm was recorded. Serial dilutions of sodium nitrite were used to construct a standard curve.
Determination of ROS radicals.
For detection of reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated by S. pyogenes-infected macrophages, mice were intraperitoneally infected, as described above, with either unlabeled S. pyogenes or S. pyogenes labeled green with carboxyfluorescein (Molecular Probes, Göttingen, Germany). For labeling, a suspension of 5 ×108 bacteria was centrifuged, resuspended in 1 ml of Hanks balanced salt solution containing 0.2 mg/ml of carboxyfluorescein, and incubated 30 min 4°C in the dark. After incubation, labeled bacteria were washed several times to remove unbound dye. Infected mice were euthanized 1 h after bacterial inoculation and subjected to peritoneal lavage. Mice intraperitoneally injected with PBS were used as controls. Lavage samples were added to wells containing glass coverslips and incubated for 1 h at 37°C, 5% CO2. After a wash to remove nonadherent cells, macrophages were incubated with 1 mg/ml of Nitro Blue Tetrazolium (NBT) dissolved in Krebs-Ringer phosphate glucose buffer (KRPG) (144 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, 8.5 mM Na2HPO4, 1.4 mM NaH2PO4, 1.3 mM MgSO4, 5 mM glucose, 10 mM HEPES [pH 7.4]) for 45 min at 37°C. After incubation, the cells were washed twice with KRPG buffer, fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, and counterstained with Giemsa stain. Samples were examined by light and fluorescence microscopy for the presence of green-fluorescing bacteria and blue-black formazan precipitate.
Experimental infection of mice.
A previously described murine model of S. pyogenes infection was used (17). In brief, mice were inoculated with 105 CFU of S. pyogenes in 0.2 ml of PBS via a lateral tail vein. Viable bacterial counts were determined in the blood of infected mice by collecting blood samples from the tail vein at 24 h postinoculation and plating serial dilutions in blood agar.
Statistical analysis.
Statistical significance between samples was determined by analysis of variance (ANOVA) and the Mann-Whitney (Wilcoxon) W test, with a P value of <0.05 considered significant.
RESULTS
Transcriptome analysis of murine macrophages infected with S. pyogenes.
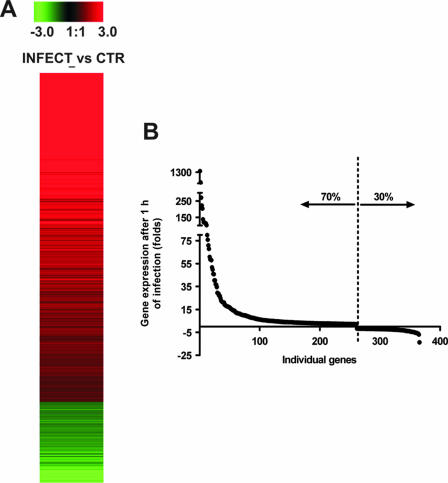
Analysis of the relative expression levels of 22,623 genes showed that more than 400 genes were differentially expressed in resident peritoneal macrophages after in vivo infection with S. pyogenes (Fig. 1A). Approximately 70% of the differentially induced genes were up-regulated, and 30% were down-regulated (Fig. 1B). To facilitate subsequent analysis, the differentially expressed genes with known functions were divided into several categories, based on biological activities. Table 2 lists some of the genes that demonstrated at least a twofold increase or decrease in expression of infected macrophages compared with uninfected control cells (P < 0.001). After 1 h of infection, many of the up-regulated genes were those that encode proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1α, IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6), chemokines (monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 [MCP-1], MCP-3, MIP-1α, MIP-1β, and MIP-2α), and growth factors (granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor [GM-CSF], G-CSF). Genes encoding anti-inflammatory molecules (Ilrn and Il10) were also induced in macrophages upon stimulation with S. pyogenes. Also, the gene encoding type II arginase (Arg2) and the gene encoding the p47phox component of the NADPH oxidase (Ncf1), were both up-regulated after infection.
FIG. 1.
Transcriptional profile of resident murine macrophages after 1 h of infection with S. pyogenes. (A) Expression pattern of cDNAs representing differentially regulated genes analyzed by microarray. Gene regulation was expressed as signal log ratios (calculated by Affymetrix MAS5 software) from the comparison of infected versus uninfected control macrophages. Induced gene expression by S. pyogenes is indicated in red, whereas suppressed gene expression is indicated in green. The degree of red intensity represents the level of induction, whereas that of green intensity represents the level of repression. (B) After 1 h infection with S. pyogenes, more than 400 genes were found to be differentially expressed with respect to the uninfected state; 70% were induced while 30% were repressed.
TABLE 2.
Genes differentially expressed in resident macrophages at 1 h postinfection with S. pyogenes
| Function and gene designation | GI no. | Description | GenBank accession no. | Fold change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immune response and inflammation | ||||
| Ptgs2 | 19225 | Prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 | M88242 | 1,357.75 |
| Il6 | 13624310 | IL-6 | NM_031168 | 427.86 |
| Tnfsf9 | 141803209 | TNF (ligand) superfamily, member 9 | NM_009404 | 366.33 |
| Csf2 | 51100 | Colony stimulating factor 2 (granulocyte-macrophage) | X03019 | 141.24 |
| Ccl7 | 6652905 | Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 7 | AF128193 | 110.66 |
| Il1b | 15030320 | IL-1β | BC011437 | 108.84 |
| Ccl2 | 6531370 | Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 | AF065933 | 79.89 |
| Il1a | 13277631 | IL-1α | BC003727 | 72.35 |
| Ccl3 | 126432552 | Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 3 | NM_011337 | 71.36 |
| IL23a | 133892789 | IL-23α subunit p19 | NM_031252 | 69.50 |
| Ccl4 | 6652955 | Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 4 | AF128218 | 68.55 |
| Il1rn | 145301622 | IL-1 receptor antagonist | NM_031167 | 53.82 |
| Cxcl1 | 141802720 | Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 | NM_008176 | 45.73 |
| Csf3 | 6753535 | Colony stimulating factor 3 (granulocyte) | NM_009971 | 35.53 |
| Lif | 16354736 | Leukemia inhibitory factor | BB235045 | 29.88 |
| Tnf | 133892368 | TNF | NM_013693 | 26.35 |
| Il10 | 6754317 | IL-10 | NM_010548 | 21.53 |
| Cxcl2 | 118130527 | Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 2 | NM_009140 | 19.04 |
| Tlr2 | 31981332 | Toll-like receptor 2 | NM_011905 | 15.61 |
| Cxcl10 | 10946575 | Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 10 | NM_021274 | 8.19 |
| Cd80 | 2412318 | CD80 antigen | AA596883 | 7.73 |
| Icosl | 118131092 | Icos ligand | NM_015790 | 6.97 |
| Ncf1 | 3061281 | Neutrophil cytosolic factor 1 | AB002663 | 5.14 |
| Cd14 | 118129882 | CD14 antigen | NM_009841 | 3.85 |
| Irf1 | 6680466 | IFN regulatory factor 1 | NM_008390 | 3.63 |
| Cd86 | 15489434 | CD86 antigen | BC013807 | 3.61 |
| Ccl24 | 11181621 | Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 24 | AF281075 | 2.98 |
| Transcription | ||||
| Maff | 18605754 | V-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene family, protein F (avian) | BC022952 | 113.06 |
| Egr2 | 52812 | Early growth response 2; protein containing zinc fingers | X06746 | 66.63 |
| Crem | 4320936 | Camp-responsive element modulator | AI467599 | 48.00 |
| Nr4a1 | 6754215 | Nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 1 | NM_010444 | 47.31 |
| Ets2 | 13529535 | E26 avian leukemia oncogene 2; 3′ domain | BC005486 | 25.02 |
| Egr1 | 76559936 | Early growth response 1 | NM_007913 | 24.37 |
| Rel | 112181203 | Reticuloendotheliosis oncogene | NM_009044 | 17.56 |
| Tgif | 31982824 | TG interacting factor | NM_009372 | 11.03 |
| Atf3 | 18044779 | Activating transcription factor 3 | BC019946 | 10.85 |
| Nr4a2 | 7305324 | Nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 2 | NM_013613 | 8.88 |
| Jundm2 (pending) | 31982607 | Jun dimerization protein 2 | NM_030887 | 8.66 |
| Relb | 31982052 | Avian reticuloendotheliosis viral (v-rel) oncogene related B | NM_009046 | 6.41 |
| Junb | 6680511 | Jun-B oncogene | NM_008416 | 3.81 |
| Sra1 | 40106182 | Steroid receptor RNA activator 1 | BG074964 | 3.49 |
| Nfe2l2 | 76573877 | Nuclear factor, erythroid-derived 2, like 2 | NM_010902 | 3.21 |
| Nfkb1 | 468361 | Nuclear factor of kappa light chain gene enhancer in B-cells 1, p105 | L28118 | 2.76 |
| Copeb | 4092799 | Core promoter element binding protein | AF072403 | 2.63 |
| Cebpd | 17009389 | CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP), delta | BB831146 | 2.31 |
| Cebpg | 31486229 | CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP), gamma | BM228675 | −2.24 |
| Gilz | 116517341 | Glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper | NM_010286 | −2.68 |
| Gata6 | 31537073 | GATA binding protein 6 | BM214048 | −4.41 |
| Tieg | 118130846 | TGFB-inducible early growth response | NM_013692 | −5.27 |
| Cebpa | 15029793 | CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP), alpha | BC011118 | −5.02 |
| Klf2 | 6680579 | Kruppel-like factor 2 (lung) | NM_008452 | −6.95 |
| Signaling | ||||
| Rab20 | 40013469 | RAB20; member of RAS oncogene family | BG066967 | 15.96 |
| Cd3e | 141803351 | CD3 antigen, epsilon polypeptide | NM_007648 | 15.92 |
| Socs3 | 31982458 | Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 | NM_007707 | 13.27 |
| Ralgds | 6677734 | Ral guanine nucleotide dissociation stimulator | NM_009058 | 12.49 |
| Rgs1 | 7657511 | Regulator of G-protein signaling 1 | NM_015811 | 11.85 |
| Cmkor1 | 15929639 | Chemokine orphan receptor 1 | BC015254 | 9.13 |
| Cish | 118129844 | Cytokine-inducible SH2-containing protein, cytokine-inducible SH2-containing protein | NM_009895 | 3.99 |
| Gpr35 | 142356082 | G-protein-coupled receptor 35 | NM_022320 | 3.99 |
| Plaur | 53277 | Urokinase plasminogen activator receptor | X62701 | 2.41 |
| Csk | 12576639 | c-src tyrosine kinase | BG094076 | −2.85 |
| Il16 | 20070724 | IL-16 | BC026894 | −4.86 |
| Apoptosis | ||||
| Gadd45b | 12845848 | Growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible 45 beta | AK010420 | 188.84 |
| Pmaip1 | 118130467 | Phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate-induced protein 1 | NM_021451 | 38.91 |
| Tnfaip3 | 31543879 | TNF-α-induced protein 3 | NM_009397 | 33.59 |
| Gadd45g | 12840945 | Growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible 45 gamma | AK007410 | 22.50 |
| Casp4 | 6671681 | Caspase 4, apoptosis-related cysteine protease | NM_007609 | 5.10 |
| Birc2 | 141803312 | Baculoviral IAP repeat-containing 2 | NM_007464 | 4.68 |
| Bcl2a1a | 293273 | B-cell leukemia/lymphoma 2-related protein a1a | L16462 | 4.66 |
| Bcl2l11 | 16399030 | BCL2-like 11 (apoptosis facilitator) | BB667581 | 3.05 |
| Cflar | 131889125 | CASP8 and FADD-like apoptosis regulator | NM_009805 | 2.92 |
| Cell cycle | ||||
| Gadd45a | 6681148 | Growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible 45 alpha | NM_007836 | 10.54 |
| Cdkn1a | 12841291 | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A (P21) | AK007630 | 8.88 |
| Fosb | 110350004 | FBJ osteosarcoma oncogene B | NM_008036 | 8.86 |
| Mapk6 | 19353313 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 6 | BC024684 | 4.73 |
| Map3k8 | 118131172 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 8 | NM_007746 | 4.26 |
| Junb | 6680511 | Jun-B oncogene | NM_008416 | 3.81 |
| Ccnl | 31505036 | Cyclin L | BM250672 | 3.24 |
| Dusp1 | 145301574 | Dual-specificity phosphatase 1 | NM_013642 | 2.80 |
| Ccng2 | 2149913 | Cyclin G2 | U95826 | 2.53 |
| Electron transport | ||||
| Mt2 | 2859721 | Metallothionein 2 | AA796766 | 32.65 |
| Arg2 | 4779068 | Arginase type II | AV002218 | 12.76 |
| Slc20a1 | 7657578 | Solute carrier family 20, member 1 | NM_015747 | 11.73 |
| Txnrd1 | 110224443 | Thioredoxin reductase 1 | NM_015762 | 5.21 |
| Sod2 | 76253932 | Superoxide dismutase 2, mitochondrial | NM_013671 | 4.22 |
| Fabp4 | 14149634 | Fatty acid binding protein 4, adipocyte | NM_024406 | 3.72 |
| Hbb-b1 | 20071755 | Hemoglobin beta adult major chain | BC027434 | 2.72 |
| Abca1 | 15411280 | ATP binding cassette, subfamily A (ABC1), member 1 | BB305534 | 2.62 |
| Lcn2 | 49710 | Lipocalin 2 | X14607 | 2.58 |
| Clic4 | 16987473 | Chloride intracellular channel 4 (mitochondrial) | BB814844 | 2.17 |
| Por | 6679420 | P450 (cytochrome) oxidoreductase | NM_008898 | 2.03 |
| Cell adhesion | ||||
| Icam1 | 14250386 | Intercellular adhesion molecule | BC008626 | 28.72 |
| Cd44 | 53677 | CD44 antigen | X66083 | 2.89 |
| Thbs1 | 4803484 | Thrombospondin 1 | AV026492 | 2.51 |
A set of genes up-regulated in response to the infection encoded cell surface receptors involved in the recognition of gram-positive cell wall components, such as TLR-2 and CD14 (47); costimulatory molecules involved in the induction of antigen-specific immune responses (CD80 and CD86) (7); and cell adhesion molecules critical for the entry of immune cells into sites of infection (ICAM-1 and CD44) (31).
Other genes whose expression was greatly increased were associated with the cell cycle (Gadd45a, Cdkn1a, Fosb), transcription (Maff, Egr2, Relb, Nfkb1), or cell signaling (Rab20, Socs3 or Plaur). Elevated mRNA levels were also observed for apoptosis-regulating genes (Gadd45b, Bcl2a1a, Birc2, Cflar), as well as for apoptosis-associated genes (Pmaip1, Casp4, Bcl211).
Among the down-regulated genes were transcription factors such as Gata 6, which has been shown to regulate innate immune responses (39), and Tieg (TGFB-inducible early growth response) and signaling genes such as Il16.
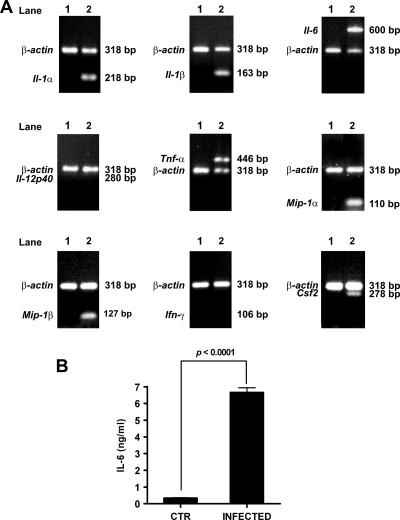
To independently confirm the microarray results, RT-PCR was carried out on seven arbitrarily selected genes that were found to be up-regulated in infected macrophages in the microarray analysis (Il-1α, Il-1β, Il-6, Csf2, Tnf-α, Mip-1α, and Mip-1β) and on two unaffected genes (Ifn-γ and Il-12p40). As shown in Fig. 2A, expression of mRNA was detected by RT-PCR for IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, MIP-1α, MIP-1β, and GM-CSF in infected macrophages but not in uninfected cells. The levels of mRNA for IL-12 p40 and IFN-γ were undetectable in both S. pyogenes-infected and uninfected control macrophages in the microarray data and were also undetectable by RT-PCR (Fig. 2A). Similar results were obtained when the transcription of these genes was investigated in resident macrophages after exposure to a different strain of S. pyogenes (M-type 1 strain SF370) (data not shown).
FIG. 2.
Confirmation of microarray data by RT-PCR and protein expression. (A) RT-PCR analysis of selected gene transcription in resident macrophages uninfected or infected with S. pyogenes. Uninfected samples were loaded in lanes 1, and infected samples were loaded in lanes 2. β-Actin expression served as a control. (B) IL-6 protein expression by S. pyogenes-infected macrophages. Resident macrophages were isolated from the peritoneal cavity of mice after 1 h of infection with S. pyogenes and cultured in vitro for 2 h. Noninfected macrophages were used as a control. The levels of IL-6 in the supernatants were determined by ELISA. Each column represents the mean ± standard deviation of triplicate samples obtained from three independent experiments. P < 0.0001 (ANOVA).
The array data were further demonstrated by detection of protein expression. The gene encoding IL-6 (Il6) was found to be strongly up-regulated in the microarray analysis (Table 2). Accordingly, high levels of IL-6 were detected in the supernatant of S. pyogenes-infected macrophages (Fig. 2B).
Activation phenotype of S. pyogenes-infected macrophages.
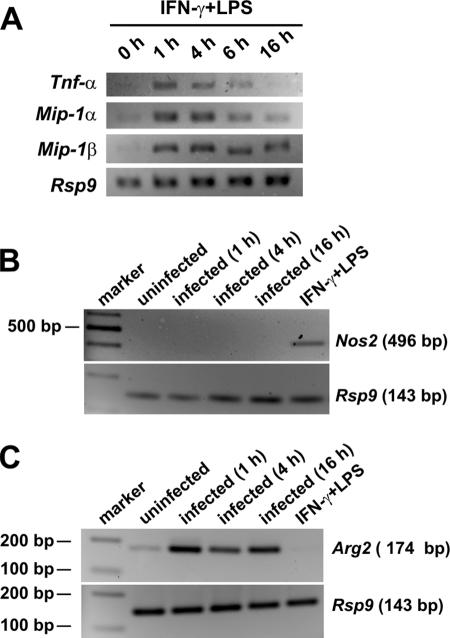
Some markers of classical activation (M1 phenotype) and some markers compatible with alternative activation (M2 phenotype) were induced in macrophages after exposure to S. pyogenes. Thus, the levels of transcripts encoding cytokines and chemokines, such as TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, IP-10, MIP-1α, and MCP-1, implicated in the classical activation phenotype were significantly increased after infection (Table 2). On the other hand, several transcripts typical of the alternative activation phenotype (e.g., IL-1ra and IL-10) were also up-regulated in infected macrophages. As classically activated macrophages are developed in response to IFN-γ, along with exposure to a microbe or microbial product such as LPS (30), peritoneal macrophages stimulated with IFN-γ plus LPS were used for comparison. Treatment of murine macrophages with LPS plus IFN-γ also resulted in up-regulation of inflammatory genes, such as the TNF-α, Mip-1α, and Mip-1β genes, typical of the classical activation pathway (Fig. 3A).
FIG. 3.
Effects of S. pyogenes on the regulation of Nos2 and Arg2 gene transcription. (A) RT-PCR analysis of inflammatory gene transcription (Tnf-α, Mip-1α, and Mip-1β) in resident macrophages unstimulated (0 h) or stimulated with IFN-γ plus LPS for 1 h, 4 h, 6 h, or 16 h. Rsp9 expression served as an internal control (B) RT-PCR analysis of Nos2 gene transcription in resident macrophages uninfected or after 1 h, 4 h, or 16 h of infection with S. pyogenes. Macrophages stimulated with IFN-γ plus LPS were used as a positive control. Rsp9 expression served as an internal control. (C) RT-PCR analysis of Arg2 gene transcription in resident macrophages uninfected or after 1 h, 4 h, or 16 h of infection with S. pyogenes. Macrophages stimulated with IFN-γ plus LPS were used as a negative control. Rsp9 expression served as an internal control.
Classical activation and alternative activation have also been associated with the activities of the enzymes iNOS and arginase, respectively (30). While S. pyogenes-infected macrophages showed increased expression of the gene encoding arginase (Arg2) after 1 h of infection, Nos2 was not induced. We then determined whether Nos2 was induced in S. pyogenes-infected macrophages at later times after infection. Results in Fig. 3B show that while stimulation of macrophages with IFN-γ and LPS resulted in induction of Nos2 within 1 h of exposure, Nos2 transcripts were undetectable in macrophages both at 1 h and at 4 h or 16 h after infection. For that reason, NO was undetectable in the supernatant of cultured S. pyogenes-infected macrophages at the selected time points (data not shown).
The up-regulation of Arg2 observed in the array data was then confirmed by RT-PCR. As shown in Fig. 3C, Arg2 was induced in infected macrophages as early as 1 h of infection, and gene transcription is maintained after 4 h and 16 h of infection (Fig. 3C). The Arg2 gene was not induced in macrophages stimulated with IFN-γ and LPS (Fig. 3C).
NADPH oxidase is involved in the S. pyogenes-killing activity of murine macrophages.
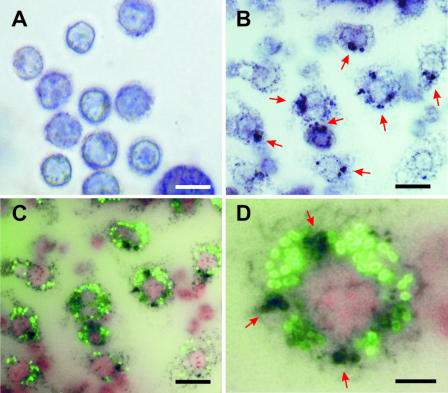
Since NO produced by iNOS and ROS produced by phagocyte oxidase (phox) are the major antimicrobial mechanisms involved in host defense (4, 22, 34), we hypothesized that production of oxygen radicals may play a major role in the elimination of phagocytosed S. pyogenes by murine macrophages. To confirm this hypothesis, the production of ROS by S. pyogenes-infected macrophages was determined with the NBT reaction. Uninfected macrophages were used as a control (Fig. 4A). As shown in Fig. 4B, significantly high levels of NBT-reducing activity (dark blue precipitate) were detected in infected macrophages (red arrows). Similar experiments were performed with S. pyogenes labeled with fluorescein to determine whether production of ROS takes place in macrophages that are associated with bacteria. Figure 4C shows that the oxidative response (black precipitate) largely occurred in macrophages with associated S. pyogenes (green). Colocalization of ROS and S. pyogenes was also evident in infected macrophages (Fig. 4D, red arrows).
FIG. 4.
Production of oxygen radicals by peritoneal macrophages after infection with S. pyogenes. Uninfected macrophages (A) or S. pyogenes-infected macrophages (B) were incubated with NBT for 45 min and examined by light microscopy. NBT precipitates as a blue-purple formazan when reduced by superoxide (red arrows). (C) Macrophages infected with green fluorescence-labeled S. pyogenes and incubated with NBT for 45 min. Production of ROS by macrophages is evidenced by black precipitation. (D) Colocalization of ROS and S. pyogenes (red arrows). Bars represent 15 μm in panels A to C and 5 μm in panel D.
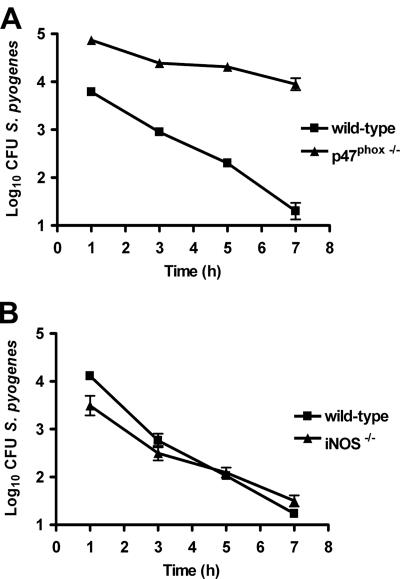
The contribution of phagocyte oxidase to macrophage-mediated in vitro killing of S. pyogenes was further demonstrated with macrophages from p47phox−/− mice. As shown in Fig. 5A, macrophages from p47phox−/− mice exerted less antimicrobial activity on S. pyogenes than did macrophages from wild-type control animals. In fact, while macrophages from wild-type animals eliminated >99.9% of the original inoculum during the first 7 h of infection, macrophages lacking phagocyte oxidase activity did not reduce the original inoculum but were still able to maintain the bacterial burden at a steady level over time (Fig. 5A). In contrast, macrophages deficient in iNOS were as efficient at killing S. pyogenes as were the wild-type macrophages (Fig. 5B). These results clearly indicate that the antimicrobial activity of macrophages is dependent of phagocyte oxidase but not of iNOS.
FIG. 5.
Roles of iNOS and phagocyte oxidase in the killing of S. pyogenes by peritoneal macrophages. (A) Killing activity of S. pyogenes by peritoneal macrophages isolated from wild-type or p47phox−/− mice. (B) Killing activity of S. pyogenes by peritoneal macrophages from wild-type or iNOS−/− mice. Macrophages were isolated from the peritoneal cavity of mice after 1 h of intraperitoneal infection with 5 × 107 CFU of S. pyogenes and were cultured at 37°C, 5% CO2. At several time points, the macrophages were lysed with dH2O, and surviving bacteria were enumerated by plating serial dilutions in blood agar. Data presented are means ± standard deviations for triplicate samples from one experiment representative of three independent determinations.
NADPH oxidase is involved in S. pyogenes killing during in vivo infection.
The in vivo relevance of these findings was determined by evaluating the ability of iNOS−/− and p47phox−/− mice to control bacterial growth after intravenous infection with S. pyogenes. The amount of bacteria recovered from the blood of infected p47phox−/− mice was significantly higher than the amount of bacteria present in the blood of wild-type control mice (Fig. 6A). No significant differences were found between the levels of bacteria in the blood of iNOS−/− and wild-type mice (Fig. 6B).
FIG. 6.
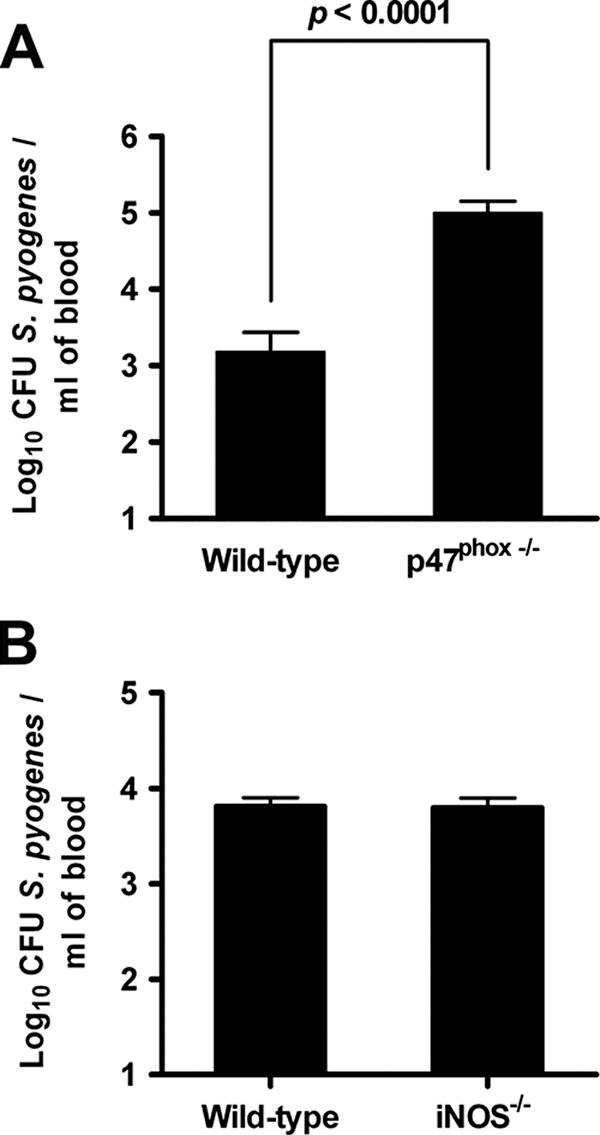
Levels of bacteria in the blood of mice at 24 h after intravenous infection with S. pyogenes. Wild-type, p47phox−/− (A), or iNOS−/− (B) mice were inoculated with 105 CFU of S. pyogenes in 0.2 ml of PBS via a lateral tail vein. Viable bacterial counts were determined in the blood of infected mice by collecting blood samples from the tail vein at 24 h postinoculation. Each column represents the mean ± standard deviation of 10 mice per group. P < 0.0001 (ANOVA).
DISCUSSION
The results reported here show that S. pyogenes induces an unusual activation phenotype in murine macrophages. The type of macrophage activation initiated upon phagocytosis of a particular pathogen is important since it strongly influences the pathogenesis and outcome of the infection. Thus, in the current paradigm of macrophage polarization, the proinflammatory properties of classically activated M1 macrophages directed to promote inflammation and kill the invading pathogens are in contrast with the anti-inflammatory activities of alternatively activated M2 macrophages, which provide regulatory signals to protect the host from overzealous inflammatory responses (19, 20, 30). Interestingly, the transcriptional response of S. pyogenes-infected macrophages revealed features of classically activated M1 macrophages, as increased expression of genes involved in the recruitment and activation of inflammatory cells, such as those encoding proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and colony stimulation factors, was observed. On the other hand, several transcripts implicated in anti-inflammatory responses typical of alternatively activated M2 macrophages (e.g., IL-1ra and IL-10) were also up-regulated.
Another important difference between M1 and M2 macrophages involves the balance between arginase and iNOS activities. Classically activated murine macrophages undergo a respiratory burst and express iNOS, whereas alternatively activated macrophages metabolize arginine through arginase rather than iNOS. Arginase and iNOS both utilize l-arginine as a substrate (46). However, while iNOS generates reactive NO species with microbicidal and proinflammatory effects important in immune responses, arginase competes with iNOS for arginine as a substrate and generates l-ornithine, an important precursor for proline that enhances collagen biosynthesis, promoting cell growth and tissue repair (21). The induction of either iNOS or arginase is usually associated with suppression of the opposing enzyme, indicating a competitive nature in these alternative states of macrophage metabolism. We report in this study that during experimental S. pyogenes infection, arginase II mRNA, but not iNOS mRNA, was up-regulated in macrophages. These results also suggest that the bactericidal activity of macrophages against S. pyogenes is mediated by phagocyte oxidase and not by iNOS. This assumption was further confirmed by the impaired capacity of macrophages with dysfunctional phagocyte oxidase (p47phox−/−) to kill S. pyogenes. In contrast, this capability was preserved in macrophages deficient in iNOS expression. Besides S. pyogenes, oxygen radical formation has been shown to participate in the killing of a diverse group of pathogens, including the promastigote form of Leishmania donovani (32), Toxoplasma gondii (33), Plasmodium falciparum (45), and Staphylococcus aureus (24). The critical role of the phagocyte oxidase for control of S. pyogenes infection in humans is reflected by the enhanced susceptibility of patients with chronic granulomatous disease, an inherited disease characterized by deficient functional activity of phagocyte oxidase complex, to recurrent pyogenic infections (15, 37).
Little is known regarding the interaction of S. pyogenes with human macrophages. Thulin et al. (42) recently reported that some S. pyogenes microorganisms are capable of surviving intracellularly in human macrophages during acute invasive infection, as well as in in vitro-infected human monocytes/macrophages. In contrast to this observation, murine macrophages infected in vivo with S. pyogenes were refractory to bacterial persistence. However, Thulin et al. (42) also showed that the percentage of human monocytes associated with viable microorganisms was reduced to almost 50% between 4 and 12 h after in vitro infection. This observation clearly indicates that, although some human monocytes allowed S. pyogenes persistence, other infected monocytes were also capable of efficiently eliminating ingested S. pyogenes. Whether the killing of S. pyogenes by human monocytes/macrophages is mediated by the phagocyte oxidase system or by iNOS remains to be elucidated.
The phagocyte oxidase system produces superoxide after bacterial phagocytosis, which is rapidly converted to other potent ROS, such as hydrogen peroxide, within forming phagosomes (3). In addition to participating in bacterial killing, ROS released in high levels by overstimulated immune cells have been implicated in inflammation and tissue injury (13). In blood, ROS can be neutralized by the antioxidant activity of red cell and plasma components (44). However, local generation of ROS can cause tissue injury, as has been shown in Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia (41), pneumococcal meningitis (2), and Helicobacter pylori gastritis (35). Therefore, immune cells also require adequate levels of antioxidants in order to avoid the harmful effects of an excessive production of ROS. The excess of oxygen radicals can be neutralized by a wide array of antioxidant molecules, including superoxide dismutase (28). In this regard, our array data show that the genes encoding metallothioneins (Mt1 and Mt2), thioredoxin reductase (Txnrd1), and superoxidismutase 2 (Sod2), which are reactive oxygen scavengers and play an important role in the detoxification of free radicals (38, 43), were up-regulated in S. pyogenes-infected macrophages. The up-regulation of these genes may be critical for protection against the potential harmful effects for cells of high levels of oxygen radicals.
The gene encoding prostaglandin-endoperoxidase synthase 2 (Ptgs2) was also strongly induced following S. pyogenes infection, with an average increase of more than 1,000-fold. While the role of Ptgs2 expression in response to S. pyogenes is unknown, it may serve as a potent regulator of inflammation. Up-regulation of this gene is responsible for the increased production of inflammatory prostaglandins implicated in the pathogenesis of many inflammatory diseases, including sepsis (6).
Of particular interest was the up-regulation of Gadd45 family proteins, which have been implicated in DNA repair following stress (40), and the cytoprotective Tnfaip3 protein, which is antiapoptotic through inhibition of the caspase cascade at the level of the initiator caspase 8 (10). These cytoprotective molecules may be critical for maintenance of cellular homeostasis under the severe stress conditions associated with streptococcal infection. Interestingly, the gene encoding the suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (Socs3) was also strongly up-regulated. Socs3 protein is a key negative regulator of cytokine signaling (8). Up-regulation of Socs3 may constitute a negative feedback mechanism for the maintenance of homeostasis.
Taken together, these data strongly suggest that resident macrophages activate an array of specific survival pathways after infection with S. pyogenes directed at maintaining cell integrity and ensuring survival. In contrast to this survival program activated in macrophages, exposure of human neutrophils to S. pyogenes results in the induction of apoptotic genes and acceleration of apoptosis (23). This divergence in response between these two phagocytic cells may most likely reflect fundamental differences either in the cellular receptors recognizing S. pyogenes or in their phagocytic pathways.
In summary, the results of our study indicate that S. pyogenes induces an uncommon activation profile in murine macrophages that does not strictly fit either the M1 or M2 activation phenotype. This profile can be explained by the high plasticity of the mononuclear phagocyte system. Thus, the activation response of macrophages to S. pyogenes infection may be the result of exposure to a multiplicity of polarizing signals emerging from the pathogen (e.g., cell wall components and exotoxins, etc.), yielding either a mixed M1/M2 activation phenotype or a mixed population of macrophages belonging to the M1 and M2 phenotypes. The characterization of the transcriptional profile adds a new dimension to the analysis of the macrophage response to S. pyogenes with the identification of potential fingerprints useful for defining states within the complex infection process.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by Nationales Genomforschungsnetz II (grant 01GS0404) and in part by “Impuls und Vernetzungsfond,” HGF Präsidentenfonds.
We thank Tanja Toepfer and Sabine Lehne for excellent technical work.
Editor: D. L. Burns
Footnotes
Published ahead of print on 25 May 2007.
REFERENCES
- 1.Anderson, C. F., and D. M. Mosser. 2002. A novel phenotype for an activated macrophage: the type 2 activated macrophage. J. Leukoc. Biol. 72:101-106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Auer, M., L. A. Pfister, D. Leppert, M. G. Tauber, and S. L. Leib. 2000. Effects of clinically used antioxidants in experimental pneumococcal meningitis. J. Infect. Dis. 182:347-350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Babior, B. M. 1999. NADPH oxidase: an update. Blood 93:1464-1476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bogdan, C. 2001. Nitric oxide and the immune response. Nat. Immunol. 2:907-916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bronte, V., and P. Zanovello. 2005. Regulation of immune responses by l-arginine metabolism. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 5:641-654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bulger, E. M., and R. V. Maier. 2000. Lipid mediators in the pathophysiology of critical illness. Crit. Care Med. 28:N27-36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Collins, M., V. Ling, and B. M. Carreno. 2005. The B7 family of immune-regulatory ligands. Genome Biol. 6:223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Croker, B. A., D. L. Krebs, J. G. Zhang, S. Wormald, T. A. Willson, E. G. Stanley, L. Robb, C. J. Greenhalgh, I. Forster, B. E. Clausen, N. A. Nicola, D. Metcalf, D. J. Hilton, A. W. Roberts, and W. S. Alexander. 2003. SOCS3 negatively regulates IL-6 signalling in vivo. Nat. Immunol. 4:540-545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cunningham, M. W. 2000. Pathogenesis of group A streptococcal infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 13:470-511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Daniel, S., M. B. Arvelo, V. I. Patel, C. R. Longo, G. Shrikhande, T. Shukri, J. Mahiou, D. W. Sun, C. Mottley, S. T. Grey, and C. Ferran. 2004. A20 protects endothelial cells from TNF-, Fas-, and NK-mediated cell death by inhibiting caspase 8 activation. Blood 104:2376-2384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ding, A. H., C. F. Nathan, and D. J. Stuehr. 1988. Release of reactive nitrogen intermediates and reactive oxygen intermediates from mouse peritoneal macrophages. Comparison of activating cytokines and evidence for independent production. J. Immunol. 141:2407-2412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Evans, T. J. 1996. The role of macrophages in septic shock. Immunobiology 195:655-659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fang, F. C. 2004. Antimicrobial reactive oxygen and nitrogen species: concepts and controversies. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2:820-832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ferretti, J. J., W. M. McShan, D. Ajdic, D. J. Savic, G. Savic, K. Lyon, C. Primeaux, S. Sezate, A. N. Suvorov, S. Kenton, H. S. Lai, S. P. Lin, Y. Qian, H. G. Jia, F. Z. Najar, Q. Ren, H. Zhu, L. Song, J. White, X. Yuan, S. W. Clifton, B. A. Roe, and R. McLaughlin. 2001. Complete genome sequence of an M1 strain of Streptococcus pyogenes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:4658-4663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gallin, J. I., E. S. Buescher, B. E. Seligmann, J. Nath, T. Gaither, and T. Katz. 1983. NIH conference. Recent advances in chronic granulomatous disease. Ann. Intern. Med. 99:657-674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Goerdt, S., and C. E. Orfanos. 1999. Other functions, other genes: alternative activation of antigen-presenting cells. Immunity 10:137-142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Goldmann, O., G. S. Chhatwal, and E. Medina. 2003. Immune mechanisms underlying host susceptibility to infection with group A streptococci. J. Infect. Dis. 187:854-861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Goldmann, O., A. Lengeling, J. Bose, H. Bloecker, R. Geffers, G. S. Chhatwal, and E. Medina. 2005. The role of the MHC on resistance to group A streptococci in mice. J. Immunol. 175:3862-3872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Goldmann, O., M. Rohde, G. S. Chhatwal, and E. Medina. 2004. Role of macrophages in host resistance to group A streptococci. Infect. Immun. 72:2956-2963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gordon, S. 2003. Alternative activation of macrophages. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 3:23-35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hesse, M., M. Modolell, A. C. La Flamme, M. Schito, J. M. Fuentes, A. W. Cheever, E. J. Pearce, and T. A. Wynn. 2001. Differential regulation of nitric oxide synthase-2 and arginase-1 by type 1/type 2 cytokines in vivo: granulomatous pathology is shaped by the pattern of l-arginine metabolism. J. Immunol. 167:6533-6544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hibbs, J. B., Jr. 2002. Infection and nitric oxide. J. Infect. Dis. 185(Suppl. 1):S9-S17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kobayashi, S. D., K. R. Braughton, A. R. Whitney, J. M. Voyich, T. G. Schwan, J. M. Musser, and F. R. DeLeo. 2003. Bacterial pathogens modulate an apoptosis differentiation program in human neutrophils. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100:10948-10953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Leijh, P. C., C. F. Nathan, M. T. van den Barselaar, and R. van Furth. 1985. Relationship between extracellular stimulation of intracellular killing and oxygen-dependent microbicidal systems of monocytes. Infect. Immun. 47:502-507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Low, D. E., B. Schwartz, and A. McGeer. 1998. The re-emergence of severe group A streptococcal diseases: an evolutionary perspective, p. 93-112. In Emerging pathogens. Proceedings of the 1996 International Congress on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC.
- 26.Mantovani, A., A. Sica, S. Sozzani, P. Allavena, A. Vecchi, and M. Locati. 2004. The chemokine system in diverse forms of macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol. 25:677-686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Mantovani, A., S. Sozzani, M. Locati, P. Allavena, and A. Sica. 2002. Macrophage polarization: tumor-associated macrophages as a paradigm for polarized M2 mononuclear phagocytes. Trends Immunol. 23:549-555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mates, J. M., and F. Sanchez-Jimenez. 1999. Antioxidant enzymes and their implications in pathophysiologic processes. Front. Biosci. 4:D339-D345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Mills, C. D., K. Kincaid, J. M. Alt, M. J. Heilman, and A. M. Hill. 2000. M-1/M-2 macrophages and the Th1/Th2 paradigm. J. Immunol. 164:6166-6173.10843666 [Google Scholar]
- 30.Mosser, D. M. 2003. The many faces of macrophage activation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 73:209-212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Muller, W. A., and G. J. Randolph. 1999. Migration of leukocytes across endothelium and beyond: molecules involved in the transmigration and fate of monocytes. J. Leukoc. Biol. 66:698-704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Murray, H. W. 1981. Susceptibility of Leishmania to oxygen intermediates and killing by normal macrophages. J. Exp. Med. 153:1302-1315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Murray, H. W., and Z. A. Cohn. 1979. Macrophage oxygen-dependent antimicrobial activity. I. Susceptibility of Toxoplasma gondii to oxygen intermediates. J. Exp. Med. 150:938-949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Nathan, C., and M. U. Shiloh. 2000. Reactive oxygen and nitrogen intermediates in the relationship between mammalian hosts and microbial pathogens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97:8841-8848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.O'Rourke, E. J., C. Chevalier, A. V. Pinto, J. M. Thiberge, L. Ielpi, A. Labigne, and J. P. Radicella. 2003. Pathogen DNA as target for host-generated oxidative stress: role for repair of bacterial DNA damage in Helicobacter pylori colonization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100:2789-2794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Pfoertner, S., A. Jeron, M. Probst-Kepper, C. A. Guzman, W. Hansen, A. M. Westendorf, T. Toepfer, A. J. Schrader, A. Franzke, J. Buer, and R. Geffers. 2006. Signatures of human regulatory T cells: an encounter with old friends and new players. Genome Biol. 7:R54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Roos, D. 1994. The genetic basis of chronic granulomatous disease. Immunol. Rev. 138:121-157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sato, M., and I. Bremner. 1993. Oxygen free radicals and metallothionein. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 14:325-337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Shapira, M., B. J. Hamlin, J. Rong, K. Chen, M. Ronen, and M. W. Tan. 2006. A conserved role for a GATA transcription factor in regulating epithelial innate immune responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103:14086-14091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Smith, M. L., J. M. Ford, M. C. Hollander, R. A. Bortnick, S. A. Amundson, Y. R. Seo, C. X. Deng, P. C. Hanawalt, and A. J. Fornace, Jr. 2000. p53-mediated DNA repair responses to UV radiation: studies of mouse cells lacking p53, p21, and/or gadd45 genes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20:3705-3714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Suntres, Z. E., A. Omri, and P. N. Shek. 2002. Pseudomonas aeruginosa-induced lung injury: role of oxidative stress. Microb. Pathog. 32:27-34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Thulin, P., L. Johansson, D. E. Low, B. S. Gan, M. Kotb, A. McGeer, and A. Norrby-Teglund. 2006. Viable group A streptococci in macrophages during acute soft tissue infection. PLoS Med. 3:e53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Van Remmen, H., W. Qi, M. Sabia, G. Freeman, L. Estlack, H. Yang, Z. Mao Guo, T. T. Huang, R. Strong, S. Lee, C. J. Epstein, and A. Richardson. 2004. Multiple deficiencies in antioxidant enzymes in mice result in a compound increase in sensitivity to oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 36:1625-1634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Victor, V. M., M. Rocha, and M. De la Fuente. 2004. Immune cells: free radicals and antioxidants in sepsis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 4:327-347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wozencraft, A. O., H. M. Dockrell, J. Taverne, G. A. Targett, and J. H. Playfair. 1984. Killing of human malaria parasites by macrophage secretory products. Infect. Immun. 43:664-669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Wu, G., and S. M. Morris, Jr. 1998. Arginine metabolism: nitric oxide and beyond. Biochem. J. 336:1-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Yoshimura, A., E. Lien, R. R. Ingalls, E. Tuomanen, R. Dziarski, and D. Golenbock. 1999. Cutting edge: recognition of Gram-positive bacterial cell wall components by the innate immune system occurs via Toll-like receptor 2. J. Immunol. 163:1-5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]