Abstract
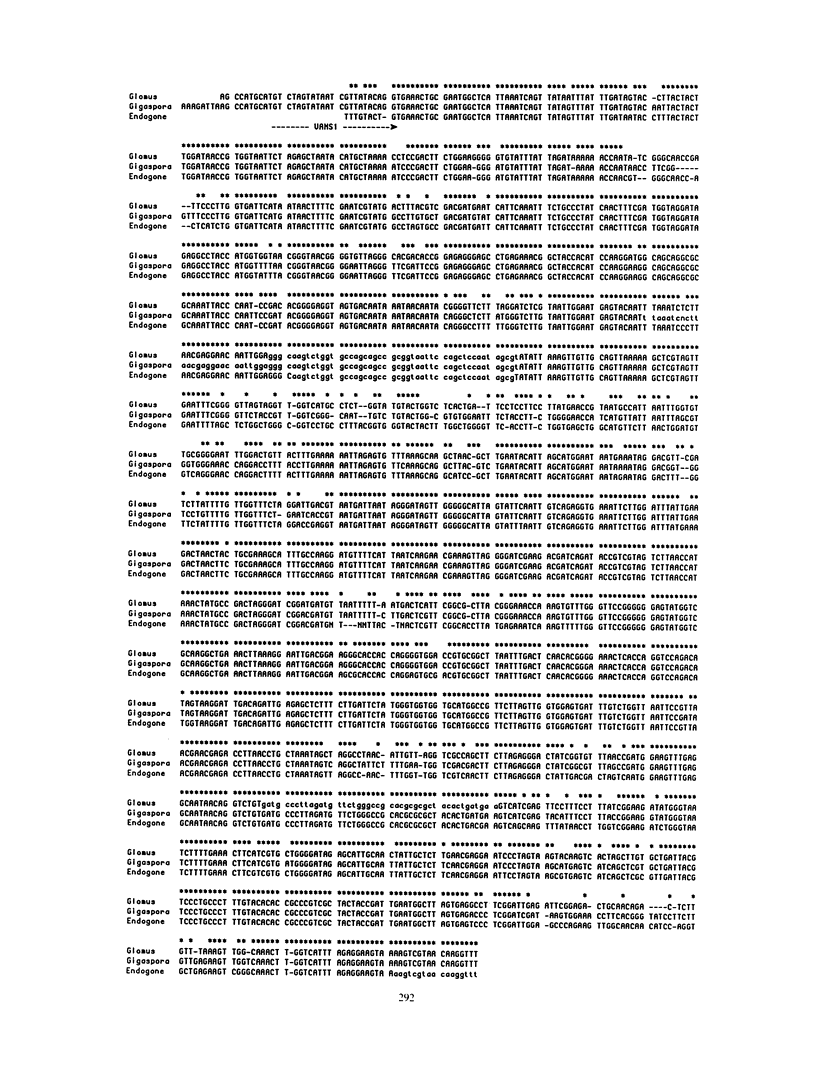
The first DNA sequences obtained from arbuscular endomycorrhizal fungi are reported. They were obtained by directly sequencing overlapping amplified fragments of the nuclear genes coding for the small subunit rRNA. These sequences were used to develop a polymerase chain reaction primer (VANS1) that enables the specific amplification of a portion of the vesicular-arbuscular endomycorrhizal fungus small subunit rRNA directly from a mixture of plant and fungal tissues. The specificity of this primer for arbuscular endomycorrhizal fungi was demonstrated by testing it on a number of organisms and by sequencing the fragment amplified from colonized leek (Allium porum) roots. This approach, coupled with other molecular techniques, will facilitate rapid detection, identification, and possibly quantitation of arbuscular endomycorrhizal fungi.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amann R., Springer N., Ludwig W., Görtz H. D., Schleifer K. H. Identification in situ and phylogeny of uncultured bacterial endosymbionts. Nature. 1991 May 9;351(6322):161–164. doi: 10.1038/351161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedergren R., Gray M. W., Abel Y., Sankoff D. The evolutionary relationships among known life forms. J Mol Evol. 1988 Dec;28(1-2):98–112. doi: 10.1007/BF02143501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLong E. F., Wickham G. S., Pace N. R. Phylogenetic stains: ribosomal RNA-based probes for the identification of single cells. Science. 1989 Mar 10;243(4896):1360–1363. doi: 10.1126/science.2466341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards U., Rogall T., Blöcker H., Emde M., Böttger E. C. Isolation and direct complete nucleotide determination of entire genes. Characterization of a gene coding for 16S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7843–7853. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Stackebrandt E., Hespell R. B., Gibson J., Maniloff J., Dyer T. A., Wolfe R. S., Balch W. E., Tanner R. S., Magrum L. J. The phylogeny of prokaryotes. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):457–463. doi: 10.1126/science.6771870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. W., Sankoff D., Cedergren R. J. On the evolutionary descent of organisms and organelles: a global phylogeny based on a highly conserved structural core in small subunit ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5837–5852. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen G. J., Lane D. J., Giovannoni S. J., Pace N. R., Stahl D. A. Microbial ecology and evolution: a ribosomal RNA approach. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:337–365. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.002005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson R. L., Piché Y., Plenchette C. Mycorrhizae and their potential use in the agricultural and forestry industries. Biotechnol Adv. 1984;2(1):101–120. doi: 10.1016/0734-9750(84)90243-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogin M. L., Gunderson J. H., Elwood H. J., Alonso R. A., Peattie D. A. Phylogenetic meaning of the kingdom concept: an unusual ribosomal RNA from Giardia lamblia. Science. 1989 Jan 6;243(4887):75–77. doi: 10.1126/science.2911720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubblefield S. P., Taylor T. N., Trappe J. M. Fossil mycorrhizae: a case for symbiosis. Science. 1987 Jul 3;237(4810):59–60. doi: 10.1126/science.237.4810.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Fox G. E. Phylogenetic structure of the prokaryotic domain: the primary kingdoms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5088–5090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]