Abstract
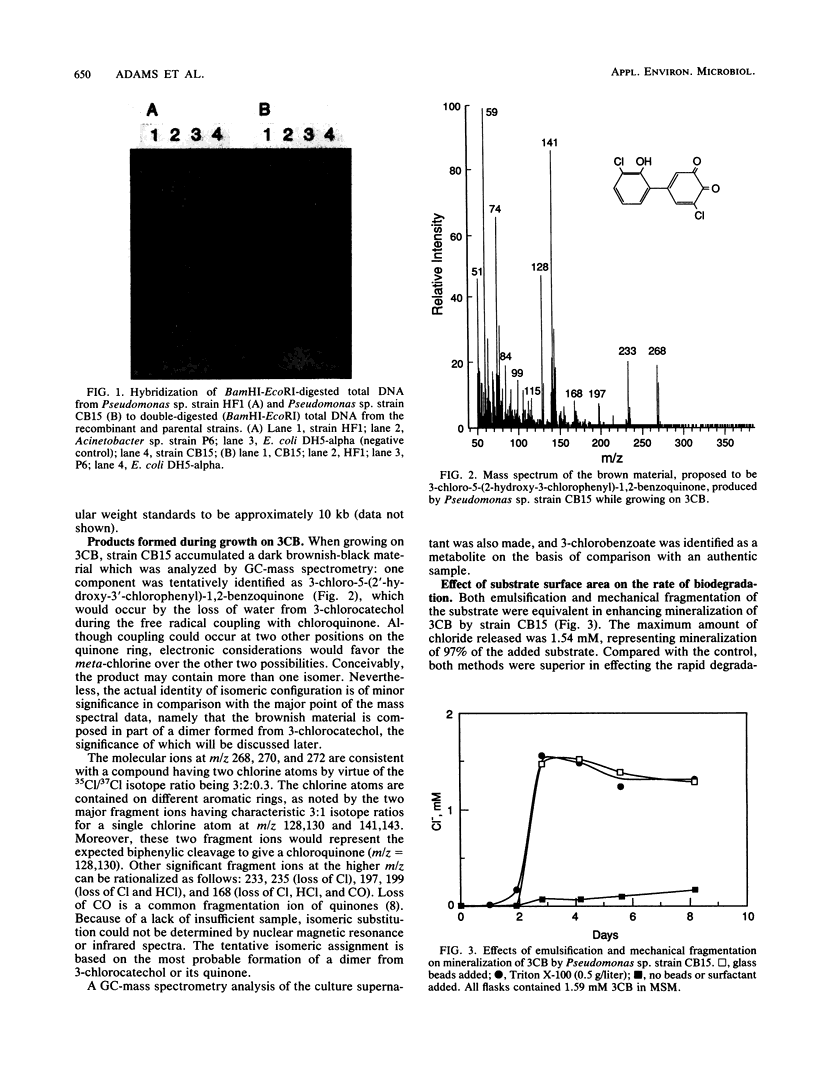
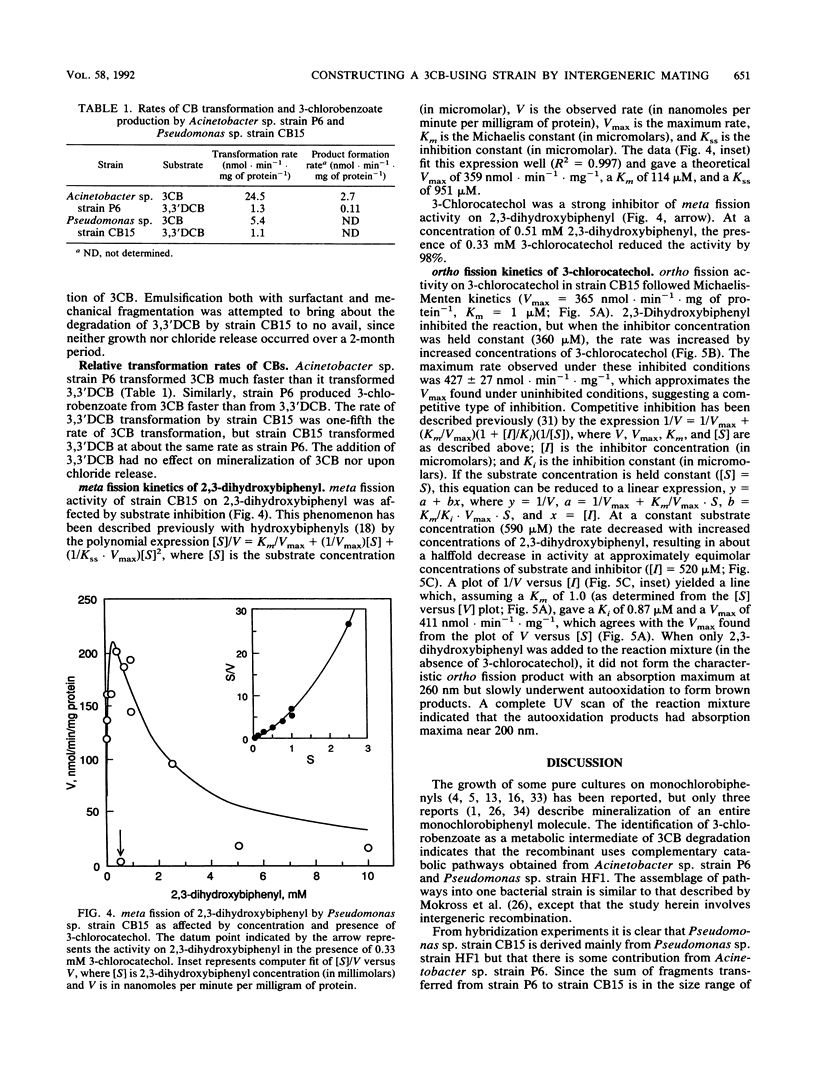
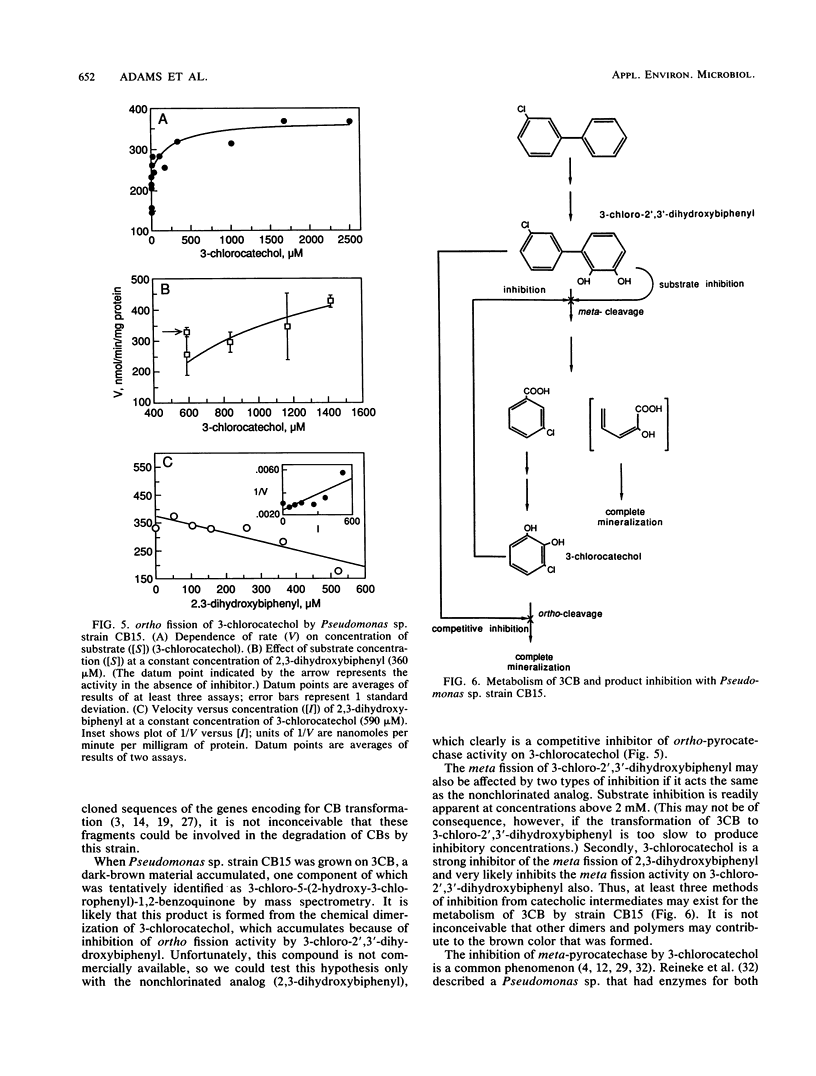
Recombinant Pseudomonas sp. strain CB15, which grows on 3-chlorobiphenyl (3CB), was constructed from Pseudomonas sp. strain HF1, which grows on 3-chlorobenzoate, and from Acinetobacter sp. strain P6, which grows on biphenyl, by using a continuous amalgamated culture apparatus. DNA from strains CB15 and HF1 hybridized very strongly to each other, while hybridization between both parental strains, HF1 and P6, was negligible. However, DNA from the recombinant CB15 hybridized moderately to strongly with three specific fragments of parental strain P6. Strains HF1 and P6 did not grow on 3CB, but recombinant strain CB15 mineralized this compound and released inorganic chloride. When growing on 3CB, strain CB15 accumulated brown products, one of which was identified as 3-chloro-5-(2'-hydroxy-3'-chlorophenyl)-1,2-benzoquinone by mass spectrometry. Emulsification and mechanical fragmentation greatly increased the rate of 3CB mineralization by strain CB15. At least three methods of inhibition from catecholic intermediates may account for slow growth on 3CB. The meta fission of 2,3-dihydroxybiphenyl (the nonchlorinated analog of the metabolic intermediate 3-chloro-2',3'-dihydroxybiphenyl) was affected by substrate inhibition (Vmax = 359 nmol.min-1.mg-1, Km = 114 microM, Kss [the inhibition constant] = 951 microM) and was also inhibited by 3-chlorocatechol. The ortho fission of 3-chlorocatechol, a degradation product, followed Michaelis-Menten kinetics (Vmax = 365 nmol.min-1.mg-1, Km = 1 microM), but the addition of 2,3-dihydroxybiphenyl inhibited the reaction (Ki = 0.87 microM).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adriaens P., Kohler H. P., Kohler-Staub D., Focht D. D. Bacterial dehalogenation of chlorobenzoates and coculture biodegradation of 4,4'-dichlorobiphenyl. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Apr;55(4):887–892. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.4.887-892.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad D., Massé R., Sylvestre M. Cloning and expression of genes involved in 4-chlorobiphenyl transformation by Pseudomonas testosteroni: homology to polychlorobiphenyl-degrading genes in other bacteria. Gene. 1990 Jan 31;86(1):53–61. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90113-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed M., Focht D. D. Degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls by two species of Achromobacter. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Jan;19(1):47–52. doi: 10.1139/m73-007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton M. R., Crawford R. L. Novel biotransformations of 4-chlorobiphenyl by a Pseudomonas sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):594–595. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.594-595.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedard D. L., Wagner R. E., Brennan M. J., Haberl M. L., Brown J. F., Jr Extensive degradation of Aroclors and environmentally transformed polychlorinated biphenyls by Alcaligenes eutrophus H850. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):1094–1102. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.1094-1102.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catelani D., Colombi A., Sorlini C., Treccani V. Metabolism of biphenyl. 2-Hydroxy-6-oxo-6-phenylhexa-2,4-dienoate: the meta-cleavage product from 2,3-dihydroxybiphenyl by Pseudomonas putida. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;134(4):1063–1066. doi: 10.1042/bj1341063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. R., Chian E. S., Griffin R. A. Degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls by mixed microbial cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Apr;37(4):680–685. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.4.680-685.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Focht D. D., Alexander M. Aerobic cometabolism of DDT analogues by Hydrogenomonas sp. J Agric Food Chem. 1971 Jan-Feb;19(1):20–22. doi: 10.1021/jf60173a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa K., Chakrabarty A. M. Involvement of plasmids in total degradation of chlorinated biphenyls. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Sep;44(3):619–626. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.3.619-626.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa K., Miyazaki T. Cloning of a gene cluster encoding biphenyl and chlorobiphenyl degradation in Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):392–398. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.392-398.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa K., Tomizuka N., Kamibayashi A. Effect of chlorine substitution on the bacterial metabolism of various polychlorinated biphenyls. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):301–310. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.2.301-310.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa K., Tonomura K., Kamibayashi A. Effect of chlorine substitution on the biodegradability of polychlorinated biphenyls. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Feb;35(2):223–227. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.2.223-227.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higson F. K., Focht D. D. Bacterial metabolism of hydroxylated biphenyls. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Apr;55(4):946–952. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.4.946-952.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A., Walia S. Cloning of bacterial genes specifying degradation of 4-chlorobiphenyl from Pseudomonas putida OU83. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Apr;55(4):798–805. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.4.798-805.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler H. P., Kohler-Staub D., Focht D. D. Cometabolism of polychlorinated biphenyls: enhanced transformation of Aroclor 1254 by growing bacterial cells. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Aug;54(8):1940–1945. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.8.1940-1945.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kröckel L., Focht D. D. Construction of chlorobenzene-utilizing recombinants by progenitive manifestation of a rare event. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Oct;53(10):2470–2475. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.10.2470-2475.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutsuna M., Someda K., Morita K., Yamanouchi Y., Kurimoto T., Kawamura Y., Matsumura H. [Ischemic cerebral symptoms after subarachnoid hemorrhage due to aneurysmal rupture (author's transl)]. No Shinkei Geka. 1978 Jun;6(6):543–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mokross H., Schmidt E., Reineke W. Degradation of 3-chlorobiphenyl by in vivo constructed hybrid pseudomonads. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Sep 1;59(1-2):179–185. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90053-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondello F. J. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of Pseudomonas strain LB400 genes encoding polychlorinated biphenyl degradation. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1725–1732. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1725-1732.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nies L., Vogel T. M. Effects of organic substrates on dechlorination of aroclor 1242 in anaerobic sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Sep;56(9):2612–2617. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.9.2612-2617.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettigrew C. A., Breen A., Corcoran C., Sayler G. S. Chlorinated biphenyl mineralization by individual populations and consortia of freshwater bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jul;56(7):2036–2045. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.7.2036-2045.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettigrew C. A., Haigler B. E., Spain J. C. Simultaneous biodegradation of chlorobenzene and toluene by a Pseudomonas strain. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jan;57(1):157–162. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.1.157-162.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reineke W., Jeenes D. J., Williams P. A., Knackmuss H. J. TOL plasmid pWW0 in constructed halobenzoate-degrading Pseudomonas strains: prevention of meta pathway. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):195–201. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.195-201.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields M. S., Hooper S. W., Sayler G. S. Plasmid-mediated mineralization of 4-chlorobiphenyl. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):882–889. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.882-889.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]