Abstract
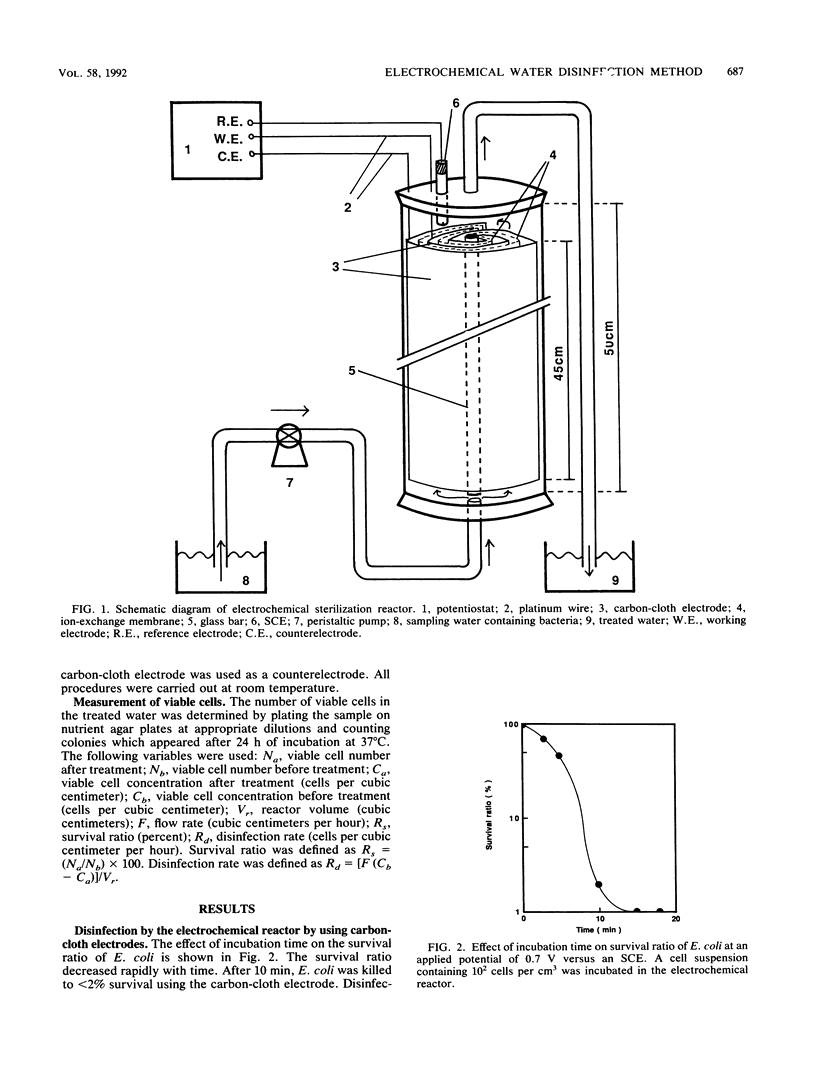
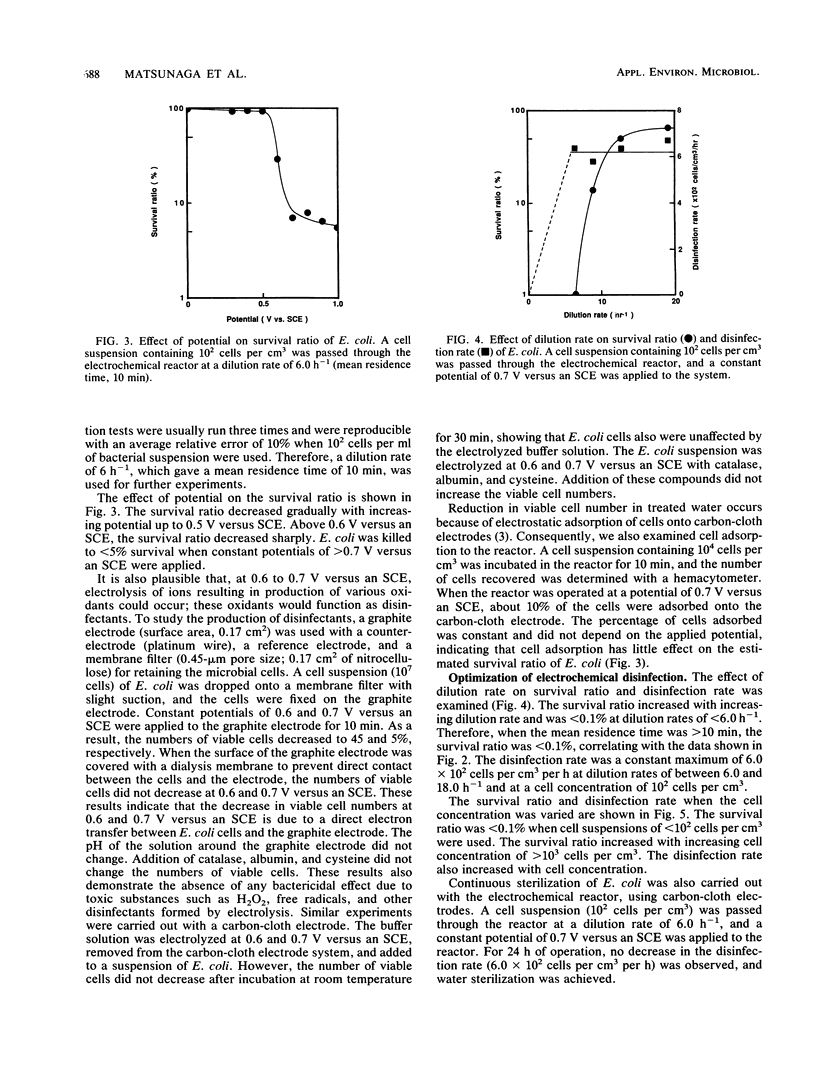
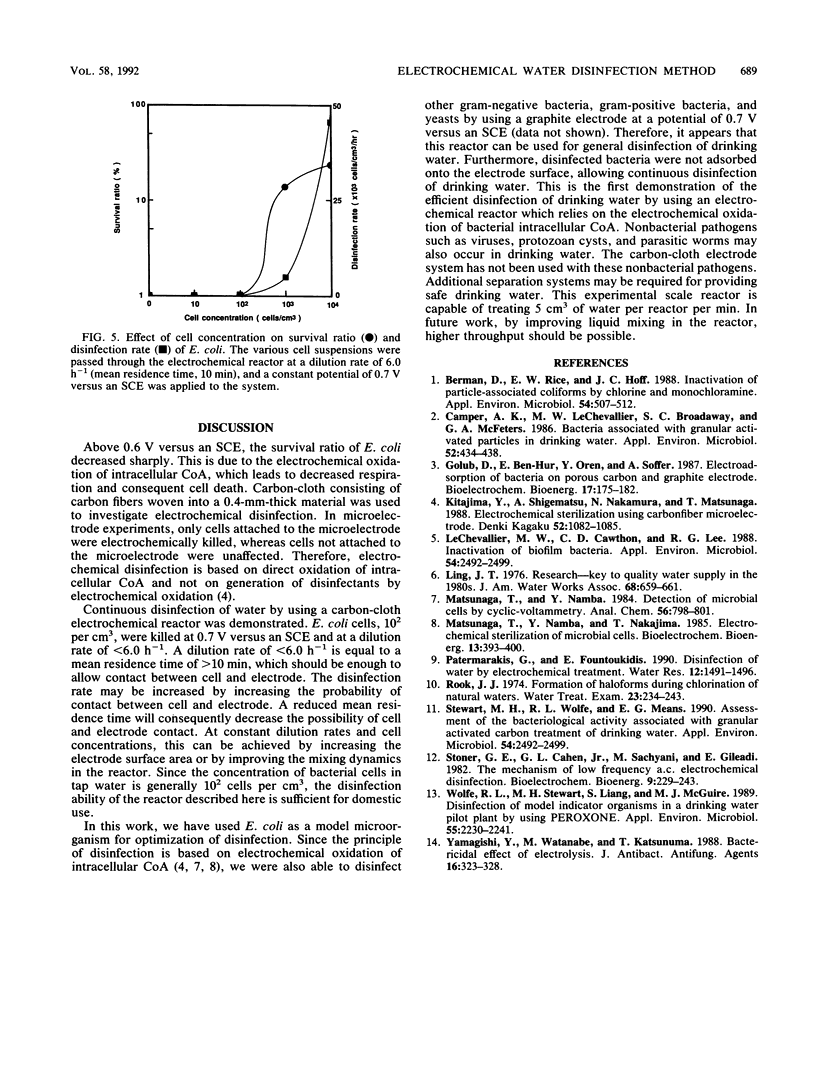
A novel electrochemical reactor employing carbon-cloth electrodes was constructed for disinfection of drinking water. Escherichia coli K-12 (10(2) cells per cm3) was sterilized when a cell suspension was passed through the reactor at a dilution rate of 6.0 h-1, and a potential of 0.7 V versus a saturated calomel electrode was applied to an electrode. The survival ratio increased with increasing dilution rate but was less than 0.1% at dilution rates of less than 6.0 h-1. Although the survival ratio increased with increasing cell concentration above 10(3) cells per cm3, the disinfection rate also increased. The disinfection rate was 6.0 x 10(2) cells per cm3 per h at a cell concentration of 10(2) cells per cm3. Continuous sterilization of E. coli cells was carried out for 24 h. Sterilization is based on an electrochemical reaction between the electrode and the cell which is mediated by intracellular coenzyme A. Sterilization of drinking water by using this reactor was successfully performed, demonstrating the potential of such a reactor for clean and efficient water purification.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berman D., Rice E. W., Hoff J. C. Inactivation of particle-associated coliforms by chlorine and monochloramine. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):507–512. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.507-512.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camper A. K., LeChevallier M. W., Broadaway S. C., McFeters G. A. Bacteria associated with granular activated carbon particles in drinking water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Sep;52(3):434–438. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.3.434-438.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeChevallier M. W., Cawthon C. D., Lee R. G. Inactivation of biofilm bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Oct;54(10):2492–2499. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.10.2492-2499.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga T., Namba Y. Detection of microbial cells by cyclic voltammetry. Anal Chem. 1984 Apr;56(4):798–801. doi: 10.1021/ac00268a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe R. L., Stewart M. H., Liang S., McGuire M. J. Disinfection of model indicator organisms in a drinking water pilot plant by using PEROXONE. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Sep;55(9):2230–2241. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.9.2230-2241.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


