Abstract
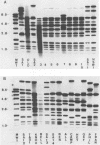
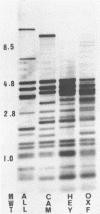
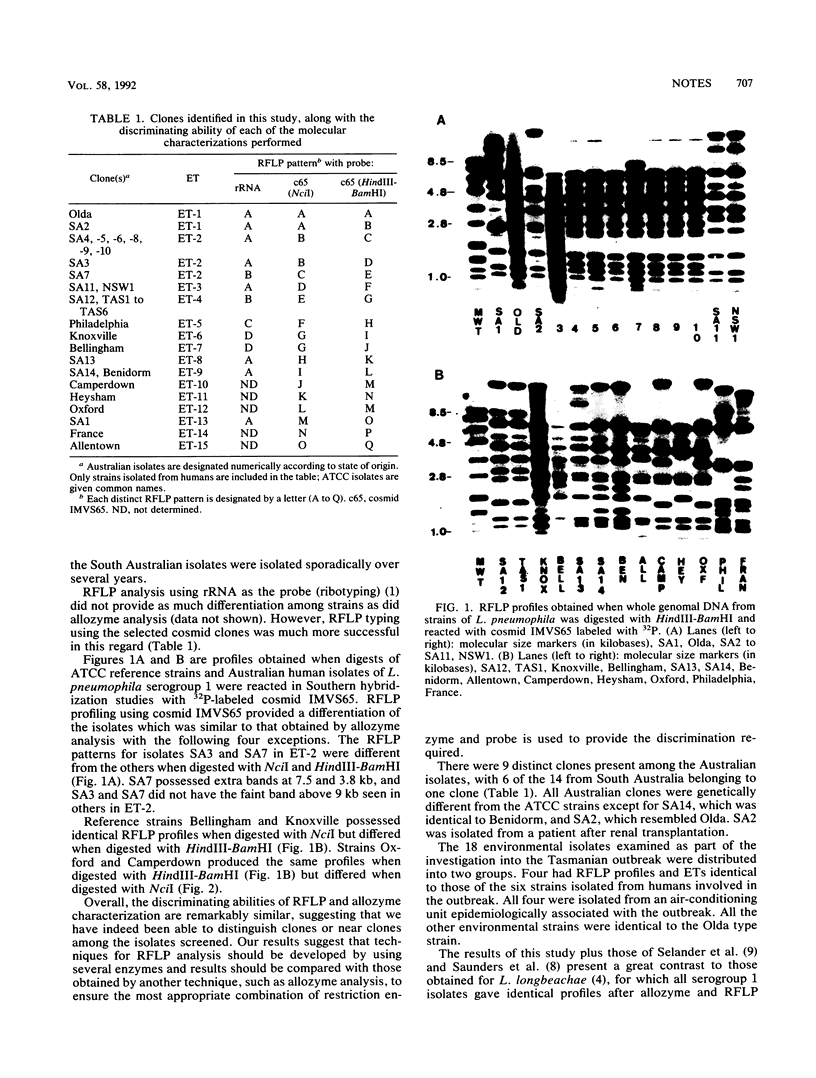
Techniques were developed for genetic characterization of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 by using restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis. Allozyme analysis provided an index of the discrimination achieved by restriction fragment length polymorphism. Isolates from human cases of legionellosis were examined by both methods, and their profiles were compared with reference strains of L. pneumophila serogroup 1 obtained from the American Type Culture Collection. Eighteen distinct clones were evident among the isolates examined. Both methods could be used to trace the source of an outbreak of legionellosis caused by L. pneumophila serogroup 1.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Grimont F., Grimont P. A. Ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene restriction patterns as potential taxonomic tools. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Sep-Oct;137B(2):165–175. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly J. R., McKinney R. M., Tobin J. O., Bibb W. F., Watkins I. D., Ramsay D. Development of a standardized subgrouping scheme for Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 using monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Apr;23(4):768–771. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.4.768-771.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanser J. A., Adams M., Doyle R., Sangster N., Steele T. W. Genetic relatedness of Legionella longbeachae isolates from human and environmental sources in Australia. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Sep;56(9):2784–2790. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.9.2784-2790.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim I., Sangster N., Reid D. P., Lanser J. A. Legionella longbeachae pneumonia: report of two cases. Med J Aust. 1989 May 15;150(10):599–601. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1989.tb136700.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning P. A., Heuzenroeder M. W., Yeadon J., Leavesley D. I., Reeves P. R., Rowley D. Molecular cloning and expression in Escherichia coli K-12 of the O antigens of the Inaba and Ogawa serotypes of the Vibrio cholerae O1 lipopolysaccharides and their potential for vaccine development. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):272–277. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.272-277.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders N. A., Harrison T. G., Haththotuwa A., Kachwalla N., Taylor A. G. A method for typing strains of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 by analysis of restriction fragment length polymorphisms. J Med Microbiol. 1990 Jan;31(1):45–55. doi: 10.1099/00222615-31-1-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., McKinney R. M., Whittam T. S., Bibb W. F., Brenner D. J., Nolte F. S., Pattison P. E. Genetic structure of populations of Legionella pneumophila. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1021–1037. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1021-1037.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele T. W., Lanser J., Sangster N. Isolation of Legionella longbeachae serogroup 1 from potting mixes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jan;56(1):49–53. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.1.49-53.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]