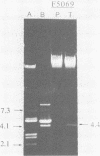
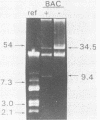
Abstract
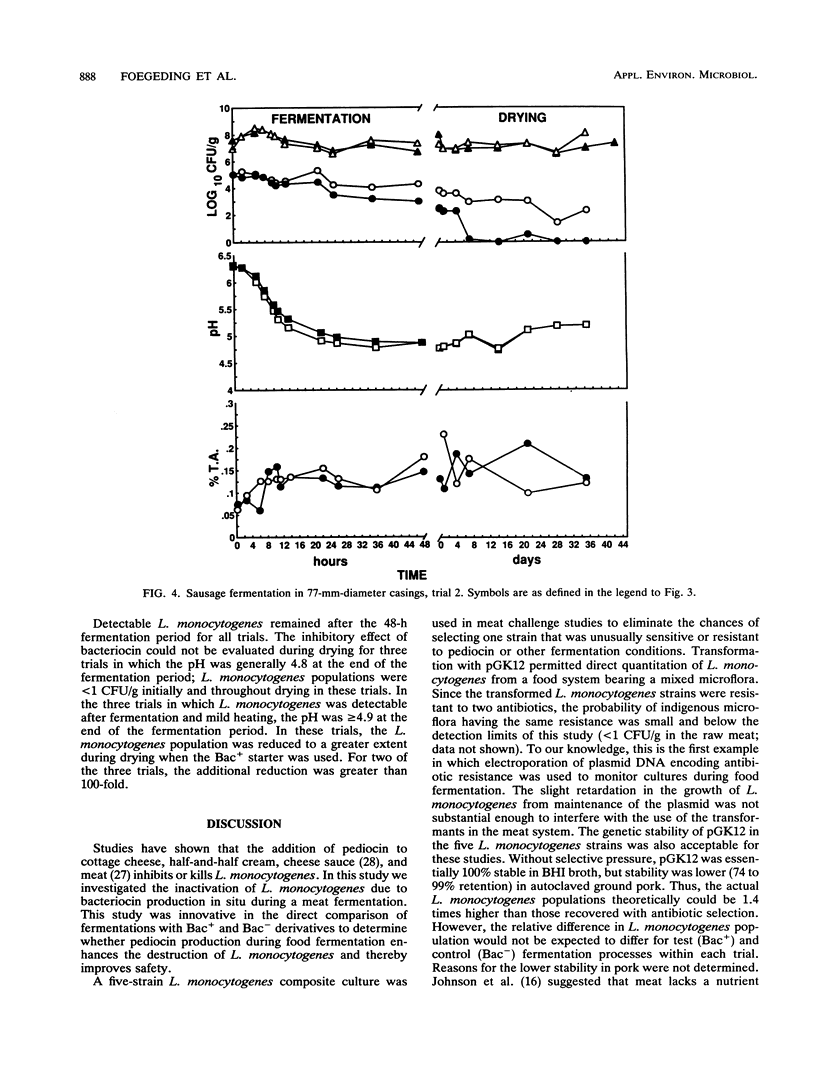
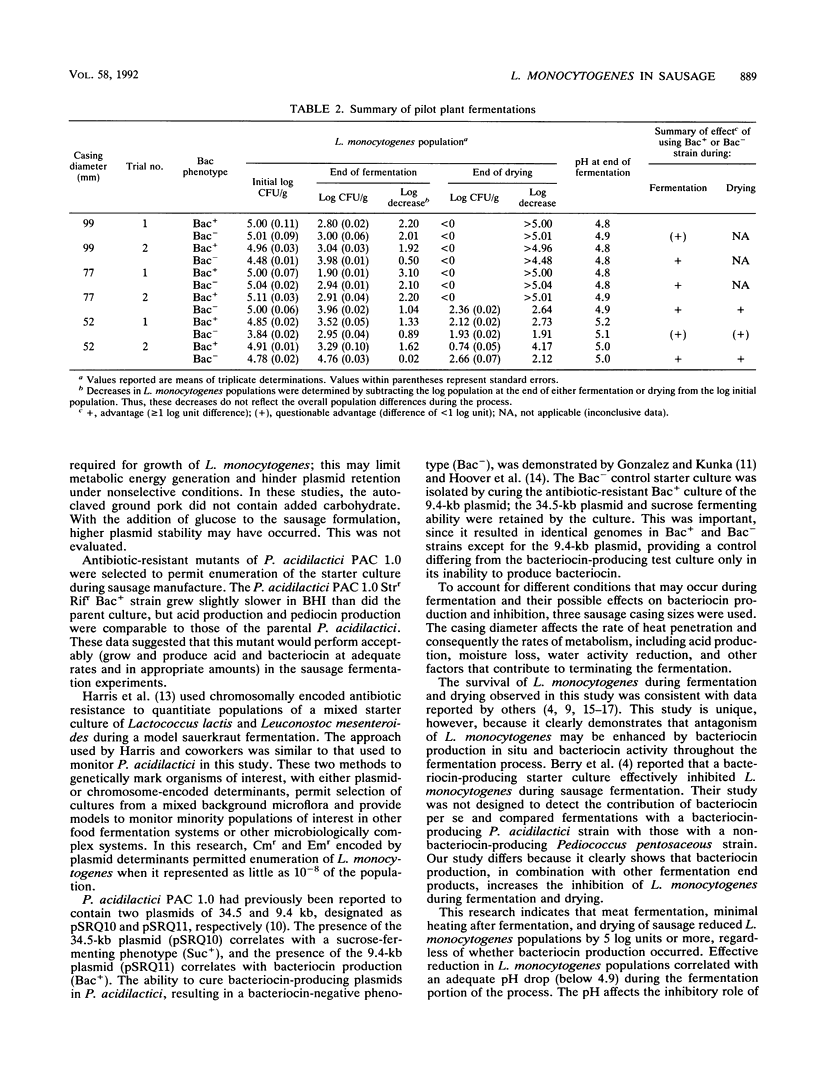
To determine whether pediocin is produced and has effective antilisterial activity during food fermentation, six sausage fermentation trials were conducted with antibiotic-resistant, pediocin-producing (Bac+) Pediococcus acidilactici PAC 1.0 (Strr Rifr) and an isogenic pediocin-negative (Bac-) derivative used as a control. Meat was inoculated (ca. 10(5) CFU/g) with a composite of five Listeria monocytogenes strains, each electrotransformed with pGK12 (Cmr Emr). P. acidilactici and L. monocytogenes populations were selectively enumerated by plating on media with antibiotics. This study indicated that the dry sausage fermentation process can reduce L. monocytogenes populations. Effective inactivation of L. monocytogenes was observed when the pH at the end of the fermentation portion of the process was less than 4.9. Pediocin was responsible for part of the antilisterial activity during the fermentation in each of the six trials. Furthermore, inhibition of L. monocytogenes during drying was enhanced in the presence of pediocin in the three trials in which L. monocytogenes could be detected throughout the drying process. Thus, pediocin production contributed to an increase in safety during both the fermentation and drying portions of sausage manufacturing.
Full text
PDF

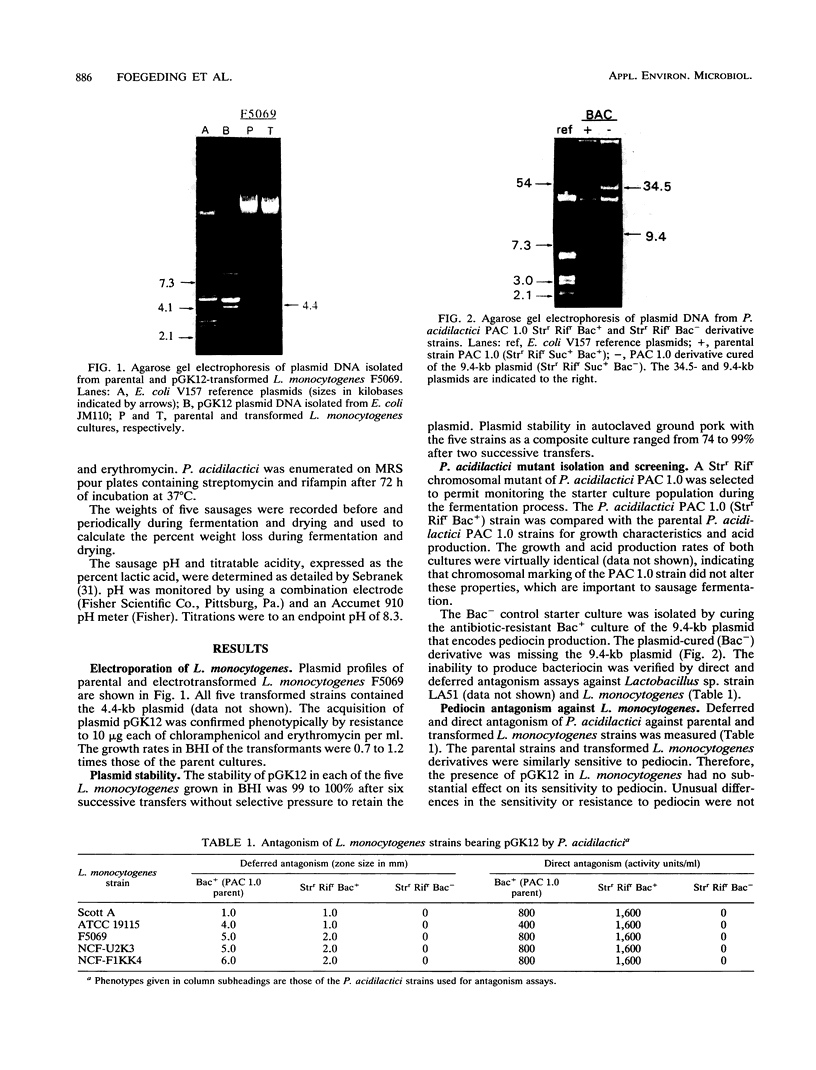
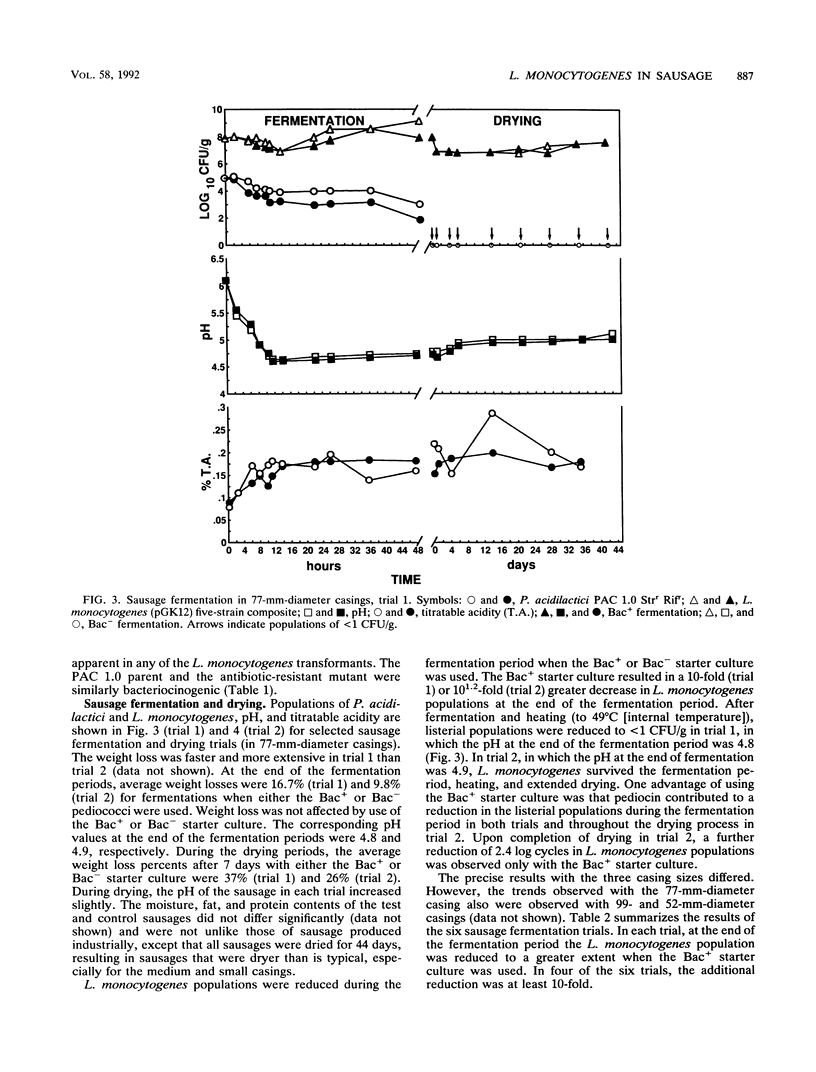

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. G., McKay L. L. Simple and rapid method for isolating large plasmid DNA from lactic streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Sep;46(3):549–552. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.3.549-552.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhunia A. K., Johnson M. C., Ray B. Purification, characterization and antimicrobial spectrum of a bacteriocin produced by Pediococcus acidilactici. J Appl Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;65(4):261–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1988.tb01893.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming D. W., Cochi S. L., MacDonald K. L., Brondum J., Hayes P. S., Plikaytis B. D., Holmes M. B., Audurier A., Broome C. V., Reingold A. L. Pasteurized milk as a vehicle of infection in an outbreak of listeriosis. N Engl J Med. 1985 Feb 14;312(7):404–407. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198502143120704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass K. A., Doyle M. P. Fate of Listeria monocytogenes in processed meat products during refrigerated storage. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1565–1569. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1565-1569.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez C. F., Kunka B. S. Evidence for Plasmid Linkage of Raffinose Utilization and Associated alpha-Galactosidase and Sucrose Hydrolase Activity in Pediococcus pentosaceus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jan;51(1):105–109. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.1.105-109.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez C. F., Kunka B. S. Plasmid-Associated Bacteriocin Production and Sucrose Fermentation in Pediococcus acidilactici. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Oct;53(10):2534–2538. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.10.2534-2538.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. L., Doyle M. P., Cassens R. G., Schoeni J. L. Fate of Listeria monocytogenes in tissues of experimentally infected cattle and in hard salami. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):497–501. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.497-501.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr K. G., Dealler S. F., Lacey R. W. Materno-fetal listeriosis from cook-chill and refrigerated food. Lancet. 1988 Nov 12;2(8620):1133–1133. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90543-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kok J., van der Vossen J. M., Venema G. Construction of plasmid cloning vectors for lactic streptococci which also replicate in Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Oct;48(4):726–731. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.4.726-731.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kékessy D. A., Piguet J. D. New method for detecting bacteriocin production. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Aug;20(2):282–283. doi: 10.1128/am.20.2.282-283.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luchansky J. B., Muriana P. M., Klaenhammer T. R. Application of electroporation for transfer of plasmid DNA to Lactobacillus, Lactococcus, Leuconostoc, Listeria, Pediococcus, Bacillus, Staphylococcus, Enterococcus and Propionibacterium. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Sep;2(5):637–646. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00072.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Kopecko D. J., Jones K. R., Ayers D. J., McCowen S. M. A multiple plasmid-containing Escherichia coli strain: convenient source of size reference plasmid molecules. Plasmid. 1978 Jun;1(3):417–420. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J. W., Dickson J. S., Crouse J. D. Use of a bacteriocin produced by Pediococcus acidilactici to inhibit Listeria monocytogenes associated with fresh meat. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jul;56(7):2142–2145. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.7.2142-2145.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pucci M. J., Vedamuthu E. R., Kunka B. S., Vandenbergh P. A. Inhibition of Listeria monocytogenes by using bacteriocin PA-1 produced by Pediococcus acidilactici PAC 1.0. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Oct;54(10):2349–2353. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.10.2349-2353.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlech W. F., 3rd, Lavigne P. M., Bortolussi R. A., Allen A. C., Haldane E. V., Wort A. J., Hightower A. W., Johnson S. E., King S. H., Nicholls E. S. Epidemic listeriosis--evidence for transmission by food. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jan 27;308(4):203–206. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198301273080407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skovgaard N., Morgen C. A. Detection of Listeria spp. in faeces from animals, in feeds, and in raw foods of animal origin. Int J Food Microbiol. 1988 May;6(3):229–242. doi: 10.1016/0168-1605(88)90015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]