Abstract
Background
Lupus nephritis is characterised by intrarenal inflammation and lymphocyte activation.
Aim
To examine the profile of cytokine gene expression in glomerulus and tubulointerstitium in patients with lupus nephritis.
Methods
36 consecutive patients with systemic lupus erythematosus having active renal disease were recruited, and they were required to undergo kidney biopsy. Glomerular and tubulointestitial cytokine expression of interleukin (IL)2, 4, 10, 12, 18, interferon γ (IFN)γ, T‐bet (the Th1 transcription factor), GATA‐3 (the Th2 transcription factor), transforming growth factorβ and monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)1 were studied by laser microdissection of the renal biopsy specimen, followed by real‐time quantitative PCR.
Results
There were 13 patients with World Health Organization class III nephritis, 14 patients with class IV nephritis and 9 patients with class V nephritis. There was a significant correlation between serum C3, C4 and anti‐double strand DNA antibody level with glomerular expression of T‐bet, IFNγ and IL2. There was a significant correlation between histological activity index and glomerular expression of IL12, IL18, IL10 and MCP1. In addition, the degree of glomerular leucocyte infiltration significantly correlated with glomerular expression of IFNγ, IL10, IL12 and IL18. By contrast, histological chronicity index correlated with the tubulointerstitial expression of IL2, MCP1 and GATA‐3.
Conclusions
Intraglomerular expression of certain target genes correlate with the severity of systemic as well as histological activity, whereas the tubulointerstitial expression of other target genes correlate with the degree of chronic kidney scarring. This result may shed light on the immunopathogenesis of lupus nephritis.
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease characterised by aberrant cytokines milieu and multiple organ involvement.1 Extensive studies have focused on cytokine profile in the peripheral blood of patients with SLE . However, reports on cytokine production in patients with SLE have been inconsistent.2,3,4,5 Cytokine assay of peripheral blood suggests that SLE is a Th2 mediated disease at the early stage,2 but the Th1 pathway may become predominant with the progression of disease and development of active nephritis.6
It is, however, important to note that the organ involvement in SLE is highly variable, and study of peripheral blood mononuclear cells may not be representative of the local immunopathogenesis at specific sites. In the case of lupus nephritis, kidney biopsy is the ideal method to study intrarenal immunologic disturbance. Unfortunately, quantification of cytokine gene expression in kidney tissue could not distinguish glomerular origin, the major site of pathological interest, from tubulointerstitial origin of the cytokines;7 immunohistochemical study allows accurate localisation of the site of cytokine production,8,9 but concomitant analysis of a large number of cytokines is not possible.
Laser‐manipulated microdissection has been developed as a method to cut out a single cell or limited tiny region from a specimen under microscopic observation by a laser beam, and subsequent laser pressure catapulting could push up and collect samples that are microdissected using a strong laser.10 The methods to isolate glomeruli from standard histochemical specimens by laser‐manipulated microdissection and laser pressure catapulting, and to quantify messenger RNA (mRNA) expression in the targeted glomeruli using real‐time quantitative PCR (RT‐QPCR) has been established.10 Recently, Peterson et al11 studied the transcriptional profiles of patients with lupus nephritis by laser‐captured microdissection and complementary DNA microarray analysis of glomeruli from clinical biopsy specimens. However, the expression of many cytokine genes was not specifically examined, and gene expression in tubulointerstitium was not considered. In the present study, we examine the profile of cytokine gene expression in glomerulus and tubulointerstitium in patients with lupus nephritis, and explore its relationship with histological morphology, degree of acute activity and chronic damage.
Patients and methods
Patient selection
We recruited 36 consecutive patients with SLE having active renal disease and required kidney biopsy. All patients fulfilled the American College of Rheumatology diagnostic criteria of SLE.12 The uninvolved pole of five kidneys, which were removed for renal cell carcinoma and had no morphological evidence of renal disease, were used as control.
Clinical and histological assessment
The disease activity of SLE was assessed clinically by the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI)13,14 that was scored on the day of kidney biopsy by an independent physician. Baseline serum creatinine, albumin, urea, complement levels (C3 and C4) and anti‐double strand (ds) DNA antibody titre were also measured. Glomerular filtration rate was estimated from a standard prediction equation.15
Kidney biopsy specimen were evaluated according to the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of lupus nephritis.16 The activity index (AI) and chronicity index (CI) of each biopsy specimen were scored by standard methods.17,18 AI is the sum of semiquantitative manual scores (0–3 each) of the following parameters: endocapillary hypercellularity; leucocyte infiltration, subendothelial hyaline deposits; interstitial inflammation, necrosis and cellular crescents.17 Scores of the last two parameters are counted double, making a total AI of 0–24. Evaluation of biopsy specimens was performed by a single pathologist (FM‐ML).
Laser microdissection
Cryosections of 14 μm thickness were prepared on a cryostat (Leica Microsystems, Wetzlar, Germany) using disposable microtome blades (Leica Microsystem) in RNase‐free conditions, and were mounted on glass slides covered with a polyethylene naphthalate membrane (PALM Microlaser Technologies, Bernried, Germany). All polyethylene naphthalate‐covered slides were treated with ultraviolet irradiation and RNase Away (Invitrogen Life Technologies, Carlsbad, California, USA) before use. Immediately after taking the slides out of the cryostat, the sections were fixed in 70% ethanol. After gentle washing in diethylpyrocarbonate‐treated water, sections were lightly stained with haematoxylin, followed by a short rinse in diethylpyrocarbonate‐treated water and dehydrated in increasing ethanol series. Sections were air‐dried at room temperature.
Laser microdissection of the snap‐frozen kidney biopsy specimens was performed using the PALM Microlaser System (PALM Microlaser Technologies), which is equipped with a pulsed high‐quality laser beam, computer‐controlled microscope stage and micromanipulator. Under direct visual control, areas of interest in the histological specimens were selected through the PALM RoboSoftware (PALM Microlaser Technologies) by moving the computer mouse, and microdissected by cutting the contour of the selected areas with the adjusted laser beam. The isolated tissue was then laser‐catapulted into a microcentrifuge cap filled with guanidine thiocyanate containing lysis buffer for the subsequent RNA isolation. Approximately 5–10 glomerulus and 20 randomly selected tubulointerstitial area were isolated from each specimen. The tissue lysate of glomerulus and tubulointerstitium were kept at −80°C until RNA extraction was performed with the RNeasy Micro Kit (Qiagen, Mississauga, Ontario, Canada), following manufacturer's instruction.
Quantification of intrarenal gene expression
The method of total RNA extraction and reverse transcription was described in our previous studies.8,19 As suggested by previous studies,8,19 we quantified the mRNA expression of interleukin (IL) 2, 4, 10, 12, 18, interferon (IFN)γ, T‐bet (the Th1 transcription factor), GATA‐3 (the Th2 transcription factor), transforming growth factor (TGF)β and monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP) 1 in glomerulus and tubulointerstitium by real‐time quantitative PCR (RT‐QPCR). Taqman primers and probes of each target were purchased from Applied Biosystems (Foster City, California, USA). The RT‐QPCR of IL2, IL4, IL10, IL12, IL18, IFNγ, TGFβ and MCP‐1 was performed by commercial kits (all from Applied Biosystems) following the manufacturer's instruction. The primer and probe sequence of T‐bet and GATA‐3 has been described in our previous study.20 The mRNA expression for each signal was calculated by using the ΔCt procedure according to manufacturer's instruction, with 18S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) used as the housekeeping gene for normalisation among samples. All primers and probes were tested with purified DNA as the template in RT‐QPCR to ensure that they do not amplify genomic DNA. All results were analysed by Sequence Detection Software V.1.7 (Applied Biosystems).
Gene expression of each target was calculated by using the difference‐in‐threshold‐cycle (ΔCt) procedure, according to manufacturer's instruction. For 18S rRNA and each target, the relative efficiency of amplification over various starting template concentrations was determined. Approximately equal efficiencies for other targets with 18S rRNA amplifications were verified by an absolute value of <0.1 for the slope of log input complementary DNA amount versus ΔCt, which was obtained by subtracting the threshold cycle (Ct) value of 18S rRNA from that of the target. Therefore, it was possible to detect 18S rRNA in the same tube with other targets. The relative quantification of using multiplex reaction with a comparative method was determined by the formula 2−(ΔΔCt), where the ΔΔCt was calculated by the subtraction of ΔCt of the calibrator from ΔCt of the sample.21
Quantification of gene expression in urinary sediment
We further studied the relationship between intrarenal and urinary cytokine gene expression. The methods of urinary sediment isolation and mRNA extraction have been described previously.8,19,20 Briefly, the urine specimen was centrifuged at 3000g for 30 min at 4°C. Total RNA was extracted by the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen), following manufacturer's instruction. Cytokine mRNA expressions were quantified by RT‐QPCR using ABI Prism 7700 Sequence Detector System (Applied Biosystems). Taqman primers and probe of T‐bet, GATA‐3, IFNγ and IL4 were purchased from Applied Biosystems. Level of mRNA expression was normalised to 18S rRNA as housekeeping gene (Applied Biosystems). Results were analysed using Sequence Detection Software V.1.9a (Applied Biosystems). As the amount of mRNA was limited, we did not quantify the expression of other cytokines in the urinary sediment.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed by SPSS V.10.0 for Windows software. The results are presented as mean (SD) unless otherwise specified. As the data were highly skewed, correlations of intrarenal mRNA expression with the SLEDAI scores and other serological, urinary or histological parameters were determined by Spearman's rank correlation coefficient. Comparison of intrarenal mRNA expression between groups was performed by Kruskal–Wallis test or Mann–Whitney U test as appropriate. A p value of <0.05 was considered as significant. All probabilities were two‐tailed.
Results
We studied 36 patients with SLE . Table 1 shows the baseline demographic and clinical data of these patients. All patients had at least 5 mm of renal cortex and 5 non‐sclerosed glomeruli for histological study. Their histological diagnoses were WHO class III (n = 13), class IV (n = 14) and class V (n = 9) nephritis. The mean (SD) histological activity and chronicity indices were 6.2 (3.9) and 4.2 (3.1), respectively.
Table 1 Baseline demographic and clinical data.
| Sex (M:F) | 1:35 |
| Age (years) | 37.2 (11.4) |
| SLEDAI score | 13.2 (6.7) |
| Level of serum creatinine (μmol/l) | 132.1 (101.8) |
| Level of serum albumin (g/l) | 24.7 (5.8) |
| Level of proteinuria (g/day) | 4.7 (3.2) |
| Glomerular filtration rate (ml/min/1.73 m2) | 63.5 (34.3) |
| Renal histology | |
| Cortical fibrosis (%) | 22.1 (22.7) |
| Glomerosclorosis (%) | 16.1 (18.8) |
| Prednisolone (mg/day)* | 26.9 (13.6) |
F, female; M, male; SLEDAI, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index.
*At the time of renal biopsy.
Values are given as mean (SD).
For the negative controls, the intrarenal expression of all target genes varied from 0 to 3.5‐fold of the median expression (details not shown). Table 2 gives the intrarenal expression of the target genes of the 36 patients. There was a marked upregulation of glomerular expression of T‐bet in patients with lupus nephritis compared to controls. By contrast, there was a marked downregulation of glomerular expression of IL2, IL18, IL4 and MCP‐1. There was a close internal correlation between glomerular expression of IFNγ, IL10, IL12, IL18, TGFβ and MCP‐1, but not with other target genes (details not shown). A similar pattern of internal correlation was observed between the tubulointerstitial expressions of these genes (details not shown).
Table 2 Intrarenal mRNA expression of target genes.
| Glomerulus | Tubulointerstitium | Internal correlation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Th1 response | |||
| T‐bet | 2.9 (0.19–24.12) | 1.53 (0.28–24.97) | r = 0.59, p<0.001 |
| IFNγ | 1.1 (0–15.6) | 46.5 (0.4–567.7) | r = 0.37, p = 0.021 |
| IL2 | 0 (0–17.9) | 9.3 (0–300.8) | r = 0.18, p = 0.282 |
| IL12 | 0.6 (0–5.6) | 3.3 (0–35.5) | r = −0.08, p = = 0.625 |
| IL18 | 0.07 (0–0.4) | 2.6 (0.03–7.2) | r = −0.05, p = 0.766 |
| Th2 response | |||
| GATA‐3 | 1.33 (0.11–8.82) | 0.23 (0.07–1.92) | r = 0.69, p<0.001 |
| IL4 | 0 (0–21.3) | 0 (0–115.7) | r = 0.24, p = 0.144 |
| IL10 | 0.54 (0–17.92) | 3.7 (0.4–59.7) | r = −0.04, p = 0.792 |
| Other cytokines | |||
| TGFβ | 0.4 (0–1.8) | 2.5 (0.04–16.3) | r = −0.13, p = 0.455 |
| MCP‐1 | 0.01 (0–0.06) | 0.07 (0–1.2) | r = 0.06, p = 0.702 |
IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; MCP, monocyte chemoattractant protein; TGF, transforming growth factor.
Data are presented as median (range).
Level of gene expression represents the ratio to control specimen.
Table 3 summarises the relationship between intrarenal cytokine gene expression and serological markers of lupus activity. Serum C3 level had significant inverse correlation with the glomerular expression of T‐bet, IFNγ, IL2, MCP‐1, as well as the tubulointerstitial expression of T‐bet, IFNγ and IL2. Similarly, serum C4 level had significant inverse correlation with the glomerular expression of T‐bet, IFNγ, IL2, IL10, IL12, MCP‐1 and tubulointerstitial expression of T‐bet. Serum anti‐ds‐DNA antibody titre significantly correlated with glomerular expression of T‐bet, IFNγ, GATA‐3, IL2, as well as the tubulointerstitial expression of T‐bet and IL2. By contrast, there was no correlation between the overall SLEDAI score and the expression of any target gene in glomerulus or tubulointerstitium. The baseline glomerular filtration rate inversely correlated with the tubulointerstitial expression of IL10 (r = −0.34, p = 0.04) and MCP1 (r = −0.39, p = 0.014), but not with the expression of any target gene in the glomerulus. The degree of proteinuria did not correlate with the expression of any target gene in the glomerulus or tubulointerstitium.
Table 3 Relationship between intrarenal gene expression and serological markers of lupus activity.
| C3 | C4 | anti‐ds‐DNA antibody | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glomerular | Tubulointerstitial | Glomerular | Tubulointerstitial | Glomerular | Tubulointerstitial | |
| T‐bet | r = −0.725 | r = −0.451 | r = −0.809 | r = −0.513 | r = 0.976 | r = 0.613 |
| p<0.001 | p = 0.006 | p<0.001 | p = 0.001 | p<0.001 | p<0.001 | |
| GATA‐3 | r = −0.225 | r = −0.003 | r = −0.202 | r = −0.123 | r = 0.607 | r = 0.327 |
| p = 0.2 | p = 0.9 | p = 0.2 | p = 0.5 | p<0.001 | p = 0.052 | |
| IFNγ | r = −0.545 | r = −0.396 | r = −0.394 | r = −0.057 | r = 0.369 | r = −0.008 |
| p<0.001 | p = 0.014 | p = 0.014 | p = 0.7 | p = 0.023 | p = 0.9 | |
| IL2 | r = −0.352 | r = −0.335 | r = −0.419 | r = −0.220 | r = 0.234 | r = 0.371 |
| p = 0.03 | p = 0.04 | p = 0.011 | p = 0.2 | p = 0.16 | p = 0.022 | |
| IL4 | r = −0.199 | r = −0.217 | r = −0.099 | r = −0.199 | r = 0.154 | r = 0.234 |
| p = 0.231 | p = 0.2 | p = 0.6 | p = 0.2 | p = 0.4 | p = 0.16 | |
| IL10 | r = −0.302 | r = −0.165 | r = −0.323 | r = −0.056 | r = 0.254 | r = 0.234 |
| p = 0.065 | p = 0.3 | p = 0.048 | p = 0.7 | p = 0.12 | p = 0.16 | |
| IL12 | r = −0.156 | r = 0.101 | r = −0.323 | r = 0.143 | r = 0.254 | r = −0.152 |
| p = 0.3 | p = 0.5 | p = 0.048 | p = 0.4 | p = 0.12 | p = 0.4 | |
| IL18 | r = −0.200 | r = 0.113 | r = −0.237 | r = 0.309 | r = 0.178 | r = −0.277 |
| p = 0.2 | p = 0.5 | p = 0.2 | p = 0.059 | p = 0.3 | p = 0.09 | |
| TGFβ | r = −0.172 | r = 0.063 | r = −0.232 | r = 0.163 | r = 0.161 | r = −0.133 |
| p = 0.3 | p = 0.7 | p = 0.2 | p = 0.3 | p = 0.3 | p = 0.4 | |
| MCP‐1 | r = −0.405 | r = −0.068 | r = −0.374 | r = 0.127 | r = 0.311 | r = −0.043 |
| p = 0.014 | p = 0.7 | p = 0.021 | p = 0.4 | p = 0.057 | p = 0.8 | |
ds, double strand; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; TGF, transforming growth factor.
Relationship with gene expression in urinary sediment
The expression of T‐bet in urinary sediment significantly correlated with that in the glomerulus (r = 0.445, p = 0.007) but not with that in tubulointerstitial space (r = 0.188, p = 0.3). Similarly, the expression of IFNγ in urinary sediment correlated significantly with that in glomerulus (r = 0.505, p = 0.001) but not with that in tubulointerstitial space (r = 0.214, p = 0.2). By contrast, the expression of GATA‐3 in urinary sediment correlated significantly with that in glomerulus (r = 0.400, p = 0.016) as well as with that in tubulointerstitial space (r = 0.367, p = 0.028). The expression of IL4 in urinary sediment also had significant correlation with expressions in both the glomerulus (r = 0.398, p = 0.013) and in tubulointerstitial space (r = 0.336, p = 0.039).
Relationship with histology
In essence, there was no significant difference in the glomerular expression of any target gene between WHO classes (details not shown). Although there was a trend of higher glomerular expression of T‐bet in class IV nephritis (6.8 (4.7) vs 4.7 (4.8), p = 0.3), and lower glomerular expression of IL18 (0.065 (0.058) vs 0.106 (0.094), p = 0.1) and MCP‐1 (0.009 (0.010) vs 0.015 (0.015), p = 0.16) in class V nephritis, the difference was not statistically significant after adjusting for multiple comparison.
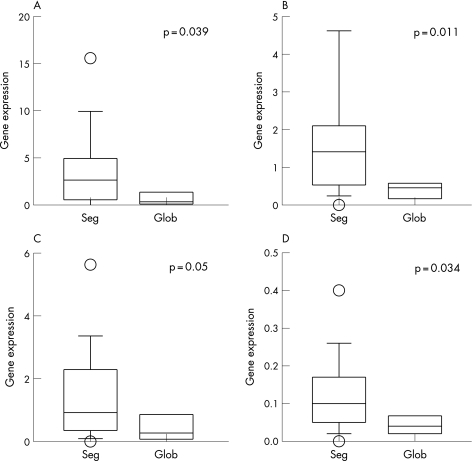
For patients with WHO class III and IV nephritis, we also compared the glomerular gene expression between patients with segmental and global glomerular lesions. Patients with segmental lesions had significantly higher glomerular expression of IFNγ, IL12, IL18, as well as IL10 (fig 1). Expression of T‐bet, IL2 and IL4 were similar between the groups. Glomerular expression of GATA‐3 was marginally higher in patients with global lesions, but the result was not statistically significant. In patients with segmental lesions, we found no difference in the glomerular expression of any target gene between those with necrotising and sclerosis lesions (details not shown), although the number of cases was small in each group. Relationship between glomerular pathology and target gene expression in tubulointerstitium was considered physiologically irrelevant and therefore not analysed.
Figure 1 Comparison of gene expression in the glomerulus between patients with segmental versus global glomerular lesions: (A) interferon γ; (B) interleukin (IL)10; (C) IL12 and (D) IL18. Gene expressions are expressed as ratio to the control. Data are presented as the whisker‐box plot and compared by Kruskal–Wallis test. The boxes indicate median, 25 and 75 centile; whisker caps indicate 5 and 95 centile; open circles indicate outliers. seg, segmental lesions; glob, global lesions.
Relationship with histological activity and chronicity
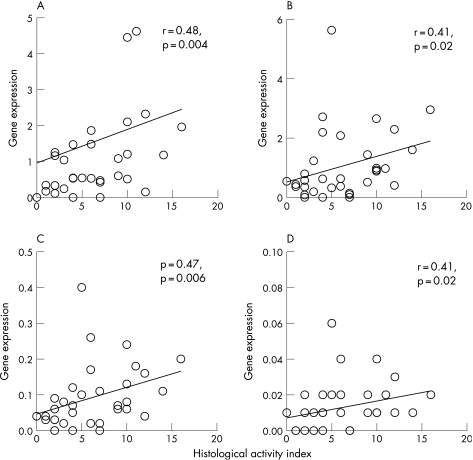
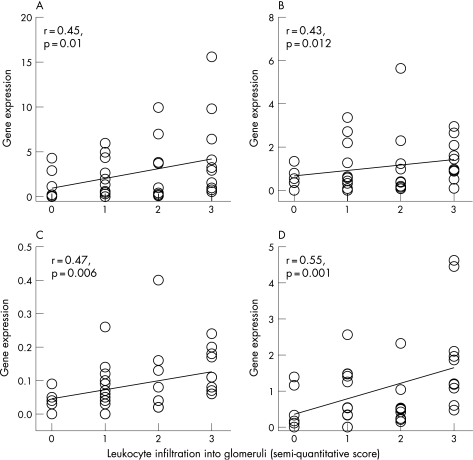
There was a close correlation between AI and glomerular expression of IL12, IL18, IL10 and MCP‐1 (fig 2). The AI had significant but only modest correlation with the expression of IFNγ (r = 0.34, p = 0.05) and TGFβ (r = 0.35, p = 0.05). By contrast, AI did not correlate with the expression of T‐bet, GATA‐3, IL2 or IL4. Among the six items of the AI, leucocyte infiltration showed the best correlation with the expression of target genes in glomerulus, including IFNγ (r = 0.45, p = 0.01), IL12 (r = 0.43, p = 0.012), IL18 (r = 0.47, p = 0.006) and IL10 (r = 0.55, p = 0.001; (fig 3). Glomerular expression did not correlate with the percentage of glomerulosclerosis, degree of cortical scarring or histological CI for all of the target genes (details not shown).
Figure 2 Relationship between histological activity index and glomerular expression of: (A) interleukin (IL)10; (B) IL12; (C) IL18; and (D) monocyte chemoattractant protein‐1. Gene expressions are depicted as ratio to the control.
Figure 3 Relationship between leucocyte infiltration and glomerular expression of: (A) interferon γ; (B) interleukin (IL)12; (C) IL18; and (D) IL10. Gene expressions are depicted as ratio to those in control.
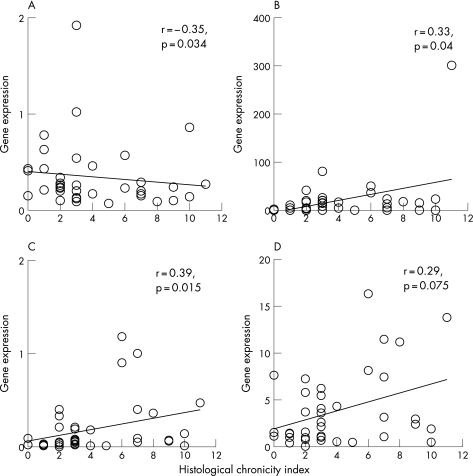
By contrast, CI correlated with the tubulointerstitial expression of IL2 (r = 0.33, p = 0.04) and MCP‐1 (r = 0.39, p = 0.015), and inversely with the tubulointerstitial expression of GATA‐3 (r = −0.35, p = 0.034; fig 4). Similarly, percentage of cortical fibrosis correlated with the tubulointerstitial expression of IL2 (r = 0.38, p = 0.025) and MCP‐1 (r = 0.45, p = 0.008), and inversely with the tubulointerstitial expression of GATA‐3 (r = −0.43, p = 0.015). There was also an insignificant correlation between the tubulointerstitial expression of TGFβ and CI (r = 0.29, p = 0.075) and percentage of cortical fibrosis (r = 0.33, p = 0.059).
Figure 4 Relationship between histological chronicity index and tubulointerstitial expression of: (A) GATA‐3; (B) interleukin 2; (C) monocyte chemoattractant protein‐1; and (D) transforming growth factor β. Gene expressions are depicted as ratio to the control.
Discussion
In this study, we found that the pattern of intraglomerular cytokine gene expression was not related to the WHO class of lupus nephritis. We did, however, identify a marked difference in the pattern of cytokine gene expression between segmental and global lesions, irrespective of the WHO class (fig 2). Briefly, segmental lesions had significantly higher intraglomerular expression of IFNγ, IL12, IL18 and IL10; and the glomerular expression of these genes correlated with the histological AI. By contrast, chronic renal damage, as represented by histological CI and percentage of cortical fibrosis, was associated with tubulointerstitial expression of IL2, MCP‐1, and possibly of TGFβ, which is consistent with the current understanding of the pathophysiology of chronic kidney diseases.22,23
The glomerular expression of T‐bet, IFNγ and IL2 correlated with serological markers of lupus activity, such as serum complement levels and anti‐ds‐DNA antibody titre. The pattern of glomerular cytokine gene expression suggests a predominantly Th1 pathway of lymphocyte activation, an observation that is consistent with our previous study on urinary cytokine gene expression.20 It is interesting, however, to note that neither the overall SLEDAI score nor the dosage of corticosteroid treatment correlated with the expression of any of the target genes. In other words, the profile of intrarenal gene expression is not a marker of systemic disease activity, but actually the disease process within the kidney.
Although most of the target genes being examined were different, our results share some similarities to that reported by Peterson et al.11 We found that glomerular expressions of IFNγ and other Th1 cytokines were upregulated in patients with segmental but not global lesions, whereas Peterson et al11 found that type I interferon‐inducible transcripts were upregulated in a subset of patients. It is important, however, to note that global and segmental lesions were not separately analysed in the report of Peterson et al.11 Contrary to usual expectations, we could not observe any change in glomerular TGFβ expression, whereas Peterson et al11 actually found that glomerular TGFβ expression was downregulated in patients with lupus nephritis.
We observed that glomerular GATA‐3 expression was fivefold higher than that of the tubulointerstitium (table 2). Although GATA‐3 is generally regarded as a marker of Th2 lymphocyte differentiation, the interpretation of GATA‐3 expression in the kidney could be problematic because of the critical constitutive expression of this transcription factor in the kidney, at least during embryogenesis.24
In this study, we could not affirm the cellular origin of the detected mRNA. We believe that the expression of most of the target genes came from the infiltration of mononuclear leucocytes, with possible contribution from endothelium and tubular epithelial cells in the tubulointerstitium. In fact, the gene expression level in our study closely correlated with the leucocyte infiltration subscore of the histological AI. Previous immunohistochemical studies also showed that most of the target genes we studied are expressed exclusively or largely by mononuclear inflammatory cells.25,26
In summary, we found that segmental and global proliferative lupus nephritis had distinct patterns of intraglomerular cytokine gene expression. Segmental lupus nephritis is characterised by a predominantly Th1 pattern of cytokine gene expression, the degree of which correlates with the histological AI.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by the CUHK research accounts 6901031 and 7101215.
We thank Ms Lee Wai Ching for her clerical assistance.
Abbreviations
AI - activity index
CI - chronicity index
ds - double strand
IFN - interferon
IL - interleukin
MCP - monocyte chemoattractant protein
mRNA - messenger RNA
RT‐QPCR - real‐time quantitative PCR
rRNA - ribosomal RNA
SLE - systemic lupus erythematosus
SLEDAI - Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index
WHO - World Health Organization
Footnotes
Competing interests: None.
References
- 1.Horwitz D A, Jacob C O. The cytokine network in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus and possible therapeutic implications. Springer Semin Immunopathol 199416181–200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Horwitz D A, Gray J D, Behrendsen S C, Kubin M, Rengaraju M, Ohtsuka K.et al Decreased production of interleukin‐12 and other Th1‐type cytokines in patients with recent‐onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 199841838–844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wong C K, Ho C Y, Li E K, Lam C W. Elevation of proinflammatory cytokine (IL‐18, IL‐17, IL‐12) and Th2 cytokine (IL‐4) concentrations in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 20009589–593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Takahashi S, Fossati L, Iwamoto M, Merino R, Motta R, Kobayakawa T.et al Imbalance towards Th1 predominance is associated with acceleration of lupus‐like autoimmune syndrome in MRL mice. J Clin Invest 1996971597–1604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Peng S L, Szabo S J, Glimcher L H. T‐bet regulates IgG class switching and pathogenic autoantibody production. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002995545–5550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Akahoshi M, Nakashima H, Tanaka Y, Kohsaka T, Nagano S, Ohgami E.et al Th1/Th2 balance of peripheral T helper cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 1999421644–1648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Uhm W S, Na K, Song G W, Jung S S, Lee T, Park M H.et al Cytokine balance in kidney tissue from lupus nephritis patients. Rheumatology (Oxford) 200342935–938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chan R W, Lai F M, Li E K, Tam L S, Wong T Y, Szeto C Y.et al Messenger RNA expression of chemokine and fibrosing factor in the urinary sediment of patients with lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheum 2004502882–2890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lemay S, Mao C, Singh A K. Cytokine gene expression in the MRL/lpr model of lupus nephritis. Kidney Int 19965085–93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Nagasawa Y, Takenaka M, Matsuoka Y, Imai E, Hori M. Quantitation of mRNA expression in glomeruli using laser‐manipulated microdissection and laser pressure catapulting. Kidney Int 200057717–723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Peterson K S, Huang J F, Zhu J, D'Agati V, Liu X, Miller N.et al Characterization of heterogeneity in the molecular pathogenesis of lupus nephritis from transcriptional profiles of laser‐captured glomeruli. J Clin Invest 20041131722–1733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Finotto S, Neurath M F, Glickman J N, Qin S, Lehr H A, Green F H.et al Development of spontaneous airway changes consistent with human asthma in mice lacking T‐bet. Science 2002295336–338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hochberg M. Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 1997401725–1734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bombardier C, Gladman D D, Urowitz M B, Caron D, Chang C H. Derivation of the SLEDAI. Arthritis Rheum 199235630–640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Levey A S, Bosch J P, Lewis J B, Greene T, Rogers N, Roth D. A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine: a new prediction equation. Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Group. Ann Intern Med 1999130461–470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Weening J J, D'Agati V D, Schwartz M M, Seshan S V, Alpers C E, Appel G B.et al International Society of Nephrology Working Group on the Classification of Lupus Nephritis; Renal Pathology Society Working Group on the Classification of Lupus Nephritis. The classification of glomerulonephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus revisited. Kidney Int 200465521–530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Grande J P, Balow J E. Renal biopsy in lupus nephritis. Lupus 19987611–617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Austin H A, Muenz L R, Joyce K M, Antonovych T T, Kullick M E, Klippel J H.et al Prognostic factors in lupus nephritis. Contribution of renal histologic data. Am J Med 198375382–391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Chan R W, Tam L S, Li E K, Lai F M, Chow K M, Lai K B.et al Inflammatory cytokine gene expression in the urinary sediment of lupus nephritis patients. Arthritis Rheum 2003481326–1331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chan R W, Lai F M, Li E K, Tam L S, Chow K M, Li P K, Szeto C C. Imbalance of Th1/Th2 transcription factors in patients with lupus nephritis. Rheumatol 200645951–957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pfaffl M W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real‐time RT‐PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 2001292002–2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Remuzzi G, Bertani T. Pathophysiology of progressive nephropathies. N Engl J Med 19983391448–1456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Benigni A, Remuzzi G. How renal cytokines and growth factors contribute to renal disease progression. Am J Kidney Dis 200137(Suppl 2)S21–S24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Labastie M C, Catala M, Gregoire J M, Peault B. The GATA‐3 gene is expressed during human kidney embryogenesis. Kidney Int 1995471597–1603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Masutani K, Akahoshi M, Tsuruya K, Tokumoto M, Ninomiya T, Kohsaka T.et al Predominance of Th1 immune response in diffuse proliferative lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheum 2001442097–2106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Okada H, Konishi K, Nakazato Y, Kanno Y, Suzuki H, Sakaguchi H.et al Interleukin‐4 expression in mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis. Am J Kidney Dis 199423242–246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]