Abstract
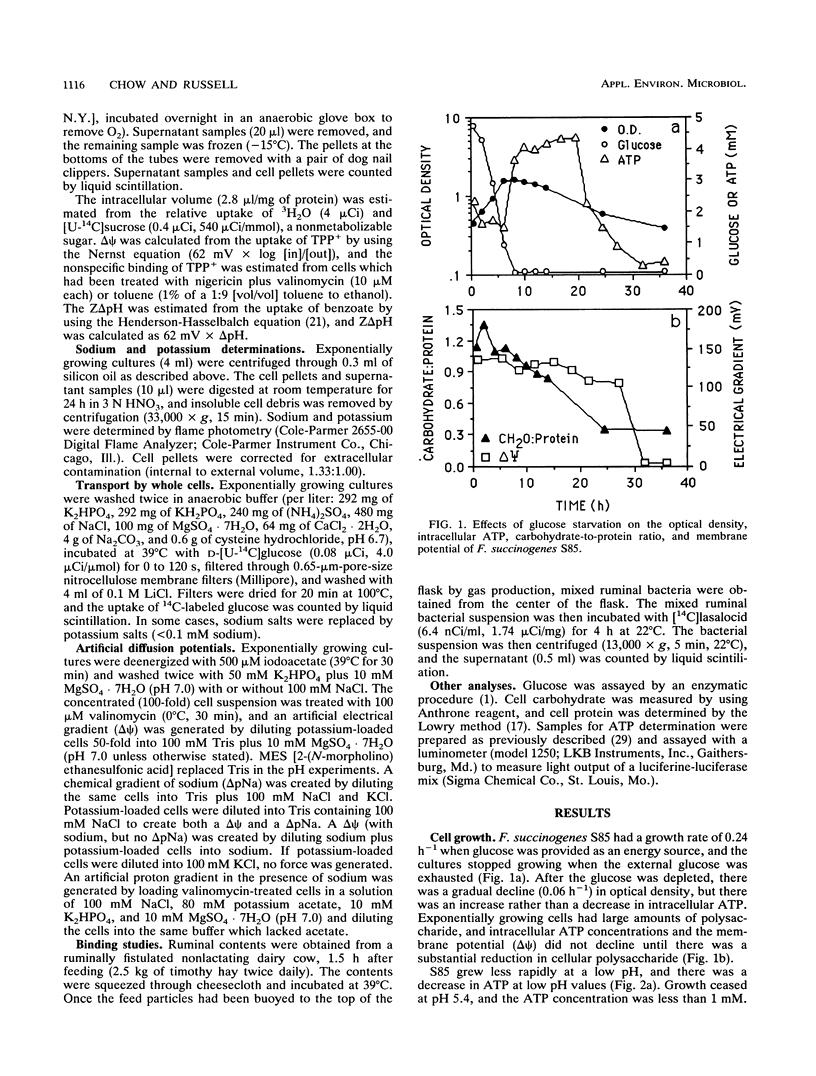
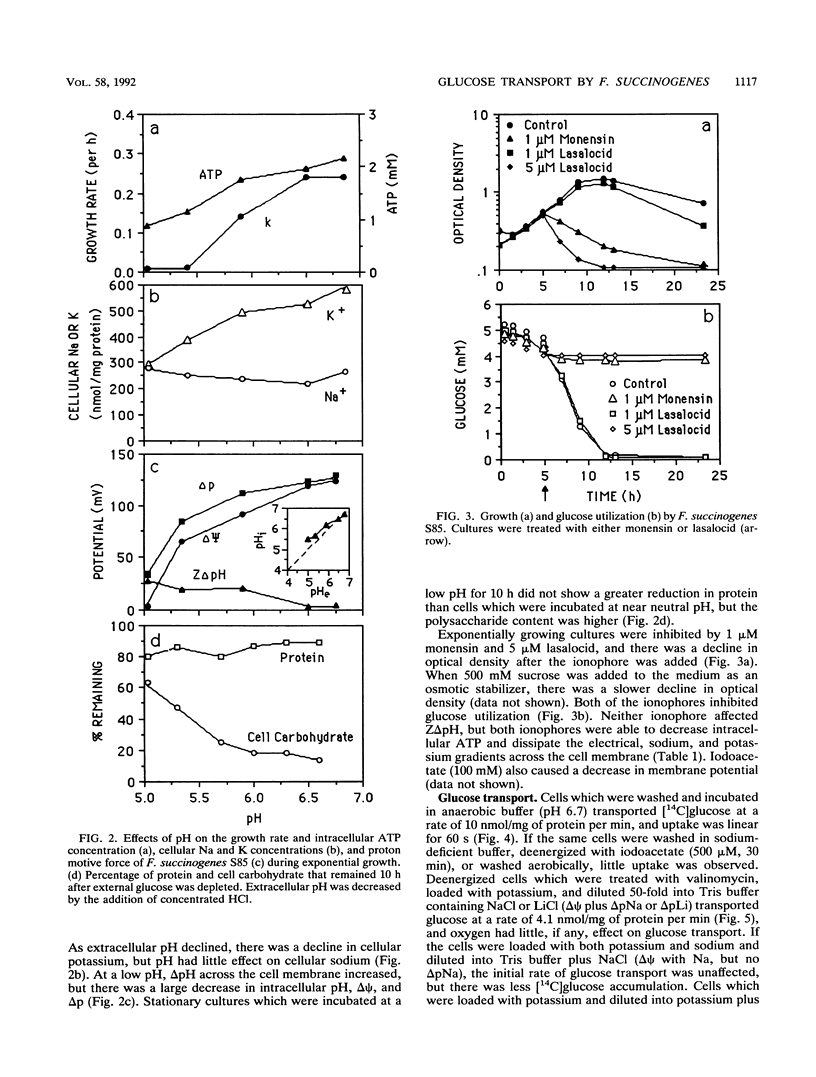
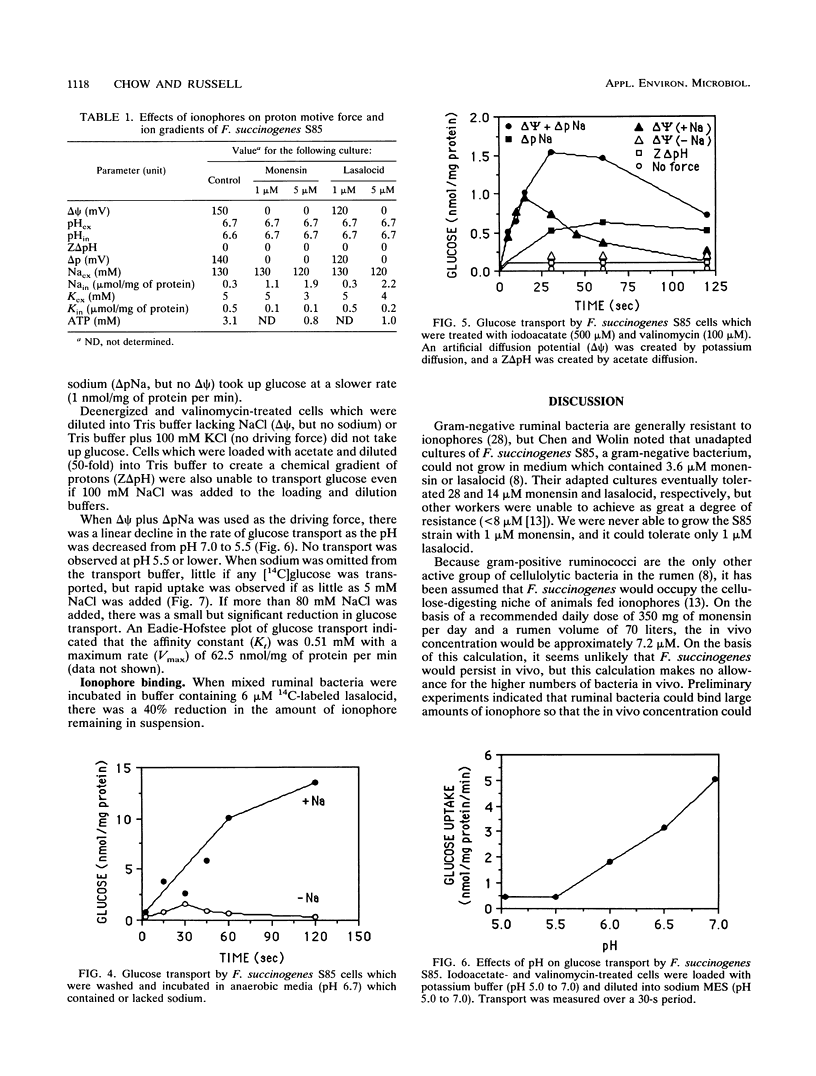
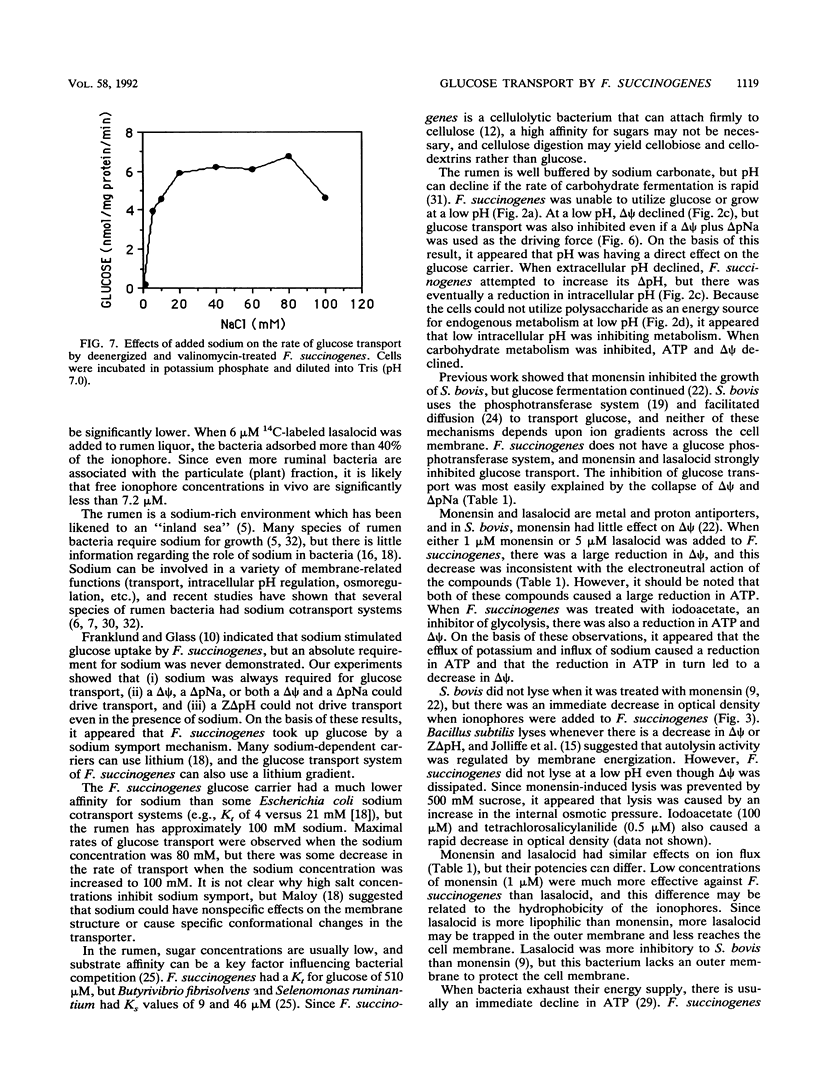
Fibrobacter succinogenes S85, a cellulolytic ruminal bacterium, required sodium for growth and glucose uptake. Cells which were deenergized with iodoacetate (500 μM) could not take up [14C]glucose. However, deenergized cells which were treated with valinomycin, loaded with potassium, and diluted into sodium or sodium plus potassium to create an artificial electrical gradient (ΔΨ) plus a chemical gradient of sodium (ΔpNa) or ΔpNa alone transported glucose at a rapid rate. Cells which were loaded with potassium plus sodium and diluted into sodium (ΔΨ with sodium, but no ΔpNa) also took up glucose at a rapid rate. Potassium-loaded cells that were diluted into buffers which did not contain sodium (ΔΨ without sodium) could not take up glucose. An artificial ZΔpH which was created by acetate diffusion could not drive glucose transport even if sodium was present. The maximum rate and affinity of glucose transport (pH 6.7) were 62.5 nmol/mg of protein per min and 0.51 mM, respectively. S85 was unable to grow at a pH of less than 5.5, and there was little glucose transport at this pH. When the extracellular pH was decreased, the glucose carrier was inhibited, intracellular pH declined, the cells were no longer able to metabolize glucose, and ΔΨ declined. Monensin (1 μM) or lasalocid (5 μM) decreased intracellular ATP and dissipated both the ΔΨ and ΔpNa. Since there was no driving force for transport, glucose transport was inhibited. These results indicated that F. succinogenes used a pH-sensitive sodium symport mechanism to take up glucose and that either a ΔΨ or a ΔpNa was required for glucose transport.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caldwell D. R., Bryant M. P. Medium without rumen fluid for nonselective enumeration and isolation of rumen bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Sep;14(5):794–801. doi: 10.1128/am.14.5.794-801.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell D. R., Hudson R. F. Sodium, an obligate growth requirement for predominant rumen bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Mar;27(3):549–552. doi: 10.1128/am.27.3.549-552.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen G. J., Russell J. B. Sodium-dependent transport of branched-chain amino acids by a monensin-sensitive ruminal peptostreptococcus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Oct;55(10):2658–2663. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.10.2658-2663.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen G., Russell J. B. Transport and deamination of amino acids by a gram-positive, monensin-sensitive ruminal bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jul;56(7):2186–2192. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.7.2186-2192.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M., Wolin M. J. Effect of monensin and lasalocid-sodium on the growth of methanogenic and rumen saccharolytic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jul;38(1):72–77. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.1.72-77.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow J. M., Russell J. B. Effect of ionophores and pH on growth of Streptococcus bovis in batch and continuous culture. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1588–1593. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1588-1593.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklund C. V., Glass T. L. Glucose uptake by the cellulolytic ruminal anaerobe Bacteroides succinogenes. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):500–506. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.500-506.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich R. D., Garrett J. E., Gast D. R., Kirick M. A., Larson D. A., Meiske J. C. Influence of monensin on the performance of cattle. J Anim Sci. 1984 Jun;58(6):1484–1498. doi: 10.2527/jas1984.5861484x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLIWELL G., BRYANT M. P. THE CELLULOLYTIC ACTIVITY OF PURE STRAINS OF BACTERIA FROM THE RUMEN OF CATTLE. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Sep;32:441–448. doi: 10.1099/00221287-32-3-441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hungate R. E. Studies on Cellulose Fermentation: III. The Culture and Isolation for Cellulose-decomposing Bacteria from the Rumen of Cattle. J Bacteriol. 1947 May;53(5):631–645. doi: 10.1128/jb.53.5.631-645.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolliffe L. K., Doyle R. J., Streips U. N. The energized membrane and cellular autolysis in Bacillus subtilis. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):753–763. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90183-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K. The role of Na+ in transport processes of bacterial membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 20;559(4):377–397. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(79)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. A., Russell J. B. Transport and phosphorylation of disaccharides by the ruminal bacterium Streptococcus bovis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Oct;53(10):2388–2393. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.10.2388-2393.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressman B. C. Biological applications of ionophores. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:501–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riebeling V., Thauer R. K., Jungermann K. The internal-alkaline pH gradient, sensitive to uncoupler and ATPase inhibitor, in growing Clostridium pasteurianum. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jul 1;55(2):445–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02181.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B. A proposed mechanism of monensin action in inhibiting ruminal bacterial growth: effects on ion flux and protonmotive force. J Anim Sci. 1987 May;64(5):1519–1525. doi: 10.2527/jas1987.6451519x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B., Baldwin R. L. Comparison of substrate affinities among several rumen bacteria: a possible determinant of rumen bacterial competition. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):531–536. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.531-536.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B., Dombrowski D. B. Effect of pH on the efficiency of growth by pure cultures of rumen bacteria in continuous culture. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Mar;39(3):604–610. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.3.604-610.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B. Effect of extracellular pH on growth and proton motive force of Bacteroides succinogenes, a cellulolytic ruminal bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Oct;53(10):2379–2383. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.10.2379-2383.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B. Low-affinity, high-capacity system of glucose transport in the ruminal bacterium Streptococcus bovis: evidence for a mechanism of facilitated diffusion. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Nov;56(11):3304–3307. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.11.3304-3307.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B., Strobel H. J. ATPase-dependent energy spilling by the ruminal bacterium, Streptococcus bovis. Arch Microbiol. 1990;153(4):378–383. doi: 10.1007/BF00249009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B., Strobel H. J., Driessen A. J., Konings W. N. Sodium-dependent transport of neutral amino acids by whole cells and membrane vesicles of Streptococcus bovis, a ruminal bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3531–3536. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3531-3536.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B., Strobel H. J. Effect of ionophores on ruminal fermentation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jan;55(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.1.1-6.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B., Strobel H. J. Effects of additives on in vitro ruminal fermentation: a comparison of monensin and bacitracin, another gram-positive antibiotic. J Anim Sci. 1988 Feb;66(2):552–558. doi: 10.2527/jas1988.662552x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slyter L. L. Influence of acidosis on rumen function. J Anim Sci. 1976 Oct;43(4):910–929. doi: 10.2527/jas1976.434910x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel H. J., Russell J. B. Role of sodium in the growth of a ruminal selenomonad. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jun;57(6):1663–1668. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.6.1663-1668.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


