Abstract
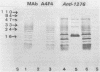
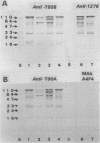
Immunomagnetic beads (IMB) were used to recover thermophilic sulfate-reducing bacteria from oil field waters from oil production platforms in the Norwegian sector of the North Sea. IMB coated with polyclonal antibodies against whole-cell antigens of the thermophilic Thermodesulfobacterium mobile captured strains GFA1, GFA2, and GFA3. GFA1 was serologically and morphologically identical to T. mobile. GFA2 and GFA3 were spore forming and similar to the Desulfotomaculum strains T90A and T93B previously isolated from North Sea oil field waters by a classical enrichment procedure. Western blots (immunoblots) of whole cells showed that GFA2, GFA3, T90A, and T93B are different serotypes of the same Desulfotomaculum species. Monoclonal antibodies (MAb) against T. mobile type strain cells were produced and used as capture agents on IMB. These MAb, named A4F4, were immunoglobulin M; they were specific to T. mobile and directed against lipopolysaccharides. The prevailing cells immunocaptured with MAb A4F4 were morphologically and serologically similar to T. mobile type strain cells. T. mobile was not detected in these oil field waters by classical enrichment procedures. Furthermore, extraction with antibody-coated IMB allowed pure strains to be isolated directly from primary enrichment cultures without prior time-consuming subculturing and consecutive transfers to selective media.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratthall D., Gahnberg L., Krasse B. Method for detecting IgA antibodies to Streptococcus mutans serotypes in parotid saliva. Arch Oral Biol. 1978;23(10):843–849. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(78)90285-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfrè G., Milstein C. Preparation of monoclonal antibodies: strategies and procedures. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):3–46. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton W. A. Sulphate-reducing bacteria and anaerobic corrosion. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:195–217. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.001211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoff K. A. Rapid and simple method for double staining of bacteria with 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole and fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled antibodies. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Dec;54(12):2949–2952. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.12.2949-2952.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lea T., Vartdal F., Davies C., Ugelstad J. Magnetic monosized polymer particles for fast and specific fractionation of human mononuclear cells. Scand J Immunol. 1985 Aug;22(2):207–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1985.tb01873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luk J. M., Lindberg A. A. Rapid and sensitive detection of Salmonella (O:6,7) by immunomagnetic monoclonal antibody-based assays. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Mar 1;137(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90387-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund A., Hellemann A. L., Vartdal F. Rapid isolation of K88+ Escherichia coli by using immunomagnetic particles. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Dec;26(12):2572–2575. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.12.2572-2575.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. A., Winstanley C., Pickup R. W., Saunders J. R. Rapid Immunocapture of Pseudomonas putida Cells from Lake Water by Using Bacterial Flagella. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Feb;57(2):503–509. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.2.503-509.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosnes J. T., Torsvik T., Lien T. Spore-forming thermophilic sulfate-reducing bacteria isolated from north sea oil field waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Aug;57(8):2302–2307. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.8.2302-2307.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skjerve E., Rørvik L. M., Olsvik O. Detection of Listeria monocytogenes in foods by immunomagnetic separation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Nov;56(11):3478–3481. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.11.3478-3481.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]