Abstract
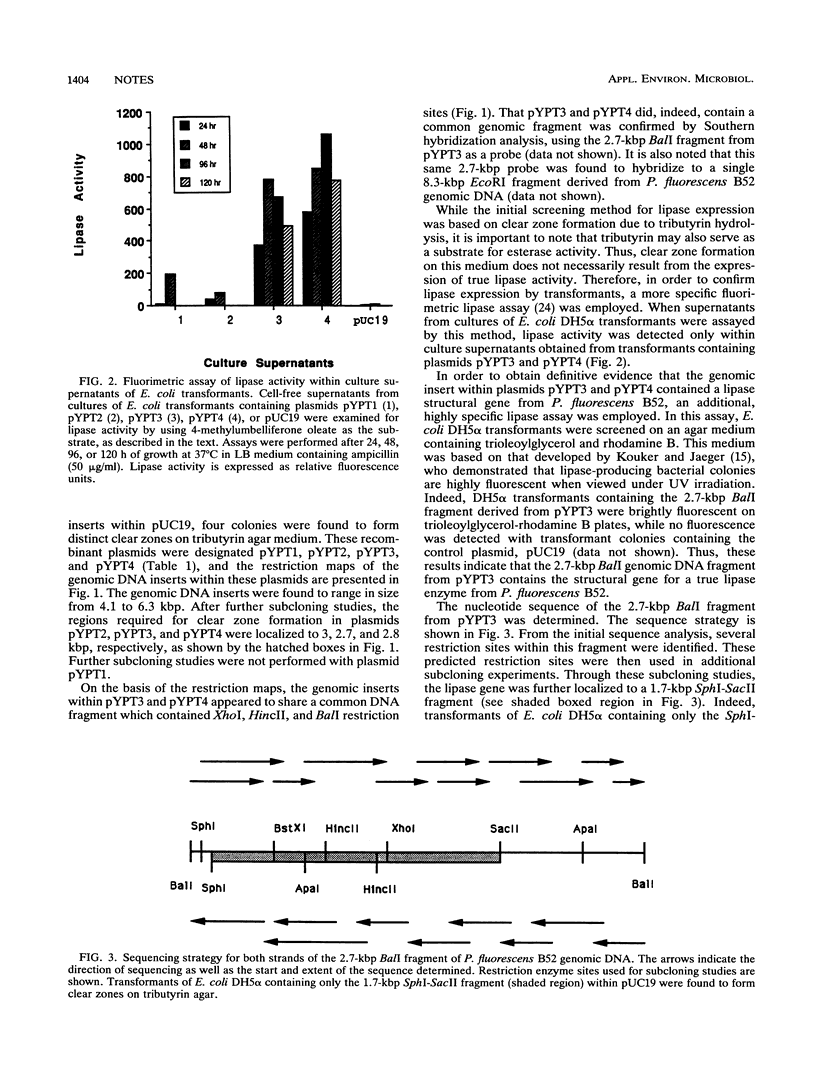
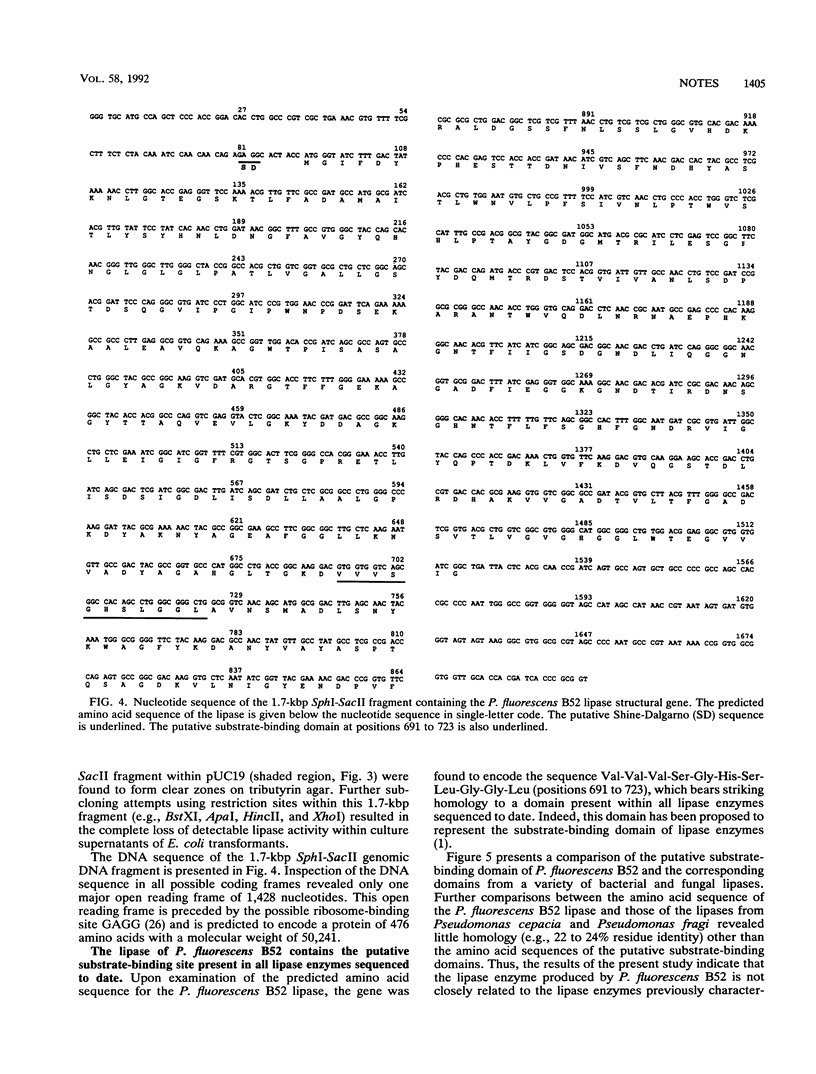
In this study, we report the cloning and expression of lipase gene from Pseudomonas fluorescens B52, a psychrotrophic spoilage bacterium isolated from refrigerated raw milk. Sequence analysis revealed one major open reading frame of 1,428 nucleotides that was predicted to encode a protein with a molecular weight of 50,241. The predicted enzyme was found to contain an amino acid sequence highly homologous to the putative substrate-binding domain present within all lipases examined to date.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonian E. Recent advances in the purification, characterization and structure determination of lipases. Lipids. 1988 Dec;23(12):1101–1106. doi: 10.1007/BF02535273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoyama S., Yoshida N., Inouye S. Cloning, sequencing and expression of the lipase gene from Pseudomonas fragi IFO-12049 in E. coli. FEBS Lett. 1988 Dec 19;242(1):36–40. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80980-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boel E., Huge-Jensen B., Christensen M., Thim L., Fiil N. P. Rhizomucor miehei triglyceride lipase is synthesized as a precursor. Lipids. 1988 Jul;23(7):701–706. doi: 10.1007/BF02535672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung G. H., Lee Y. P., Jeohn G. H., Yoo O. J., Rhee J. S. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of thermostable lipase gene from Pseudomonas fluorescens SIK W1. Agric Biol Chem. 1991 Sep;55(9):2359–2365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feller G., Thiry M., Arpigny J. L., Gerday C. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of three lipase-encoding genes from the psychrotrophic antarctic strain Moraxella TA144. Gene. 1991 Jun 15;102(1):111–115. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90548-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feller G., Thiry M., Gerday C. Sequence of a lipase gene from the antarctic psychrotroph Moraxella TA144. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6431–6431. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Götz F., Popp F., Korn E., Schleifer K. H. Complete nucleotide sequence of the lipase gene from Staphylococcus hyicus cloned in Staphylococcus carnosus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 26;13(16):5895–5906. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.16.5895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M. J., Allen J., Berka T. R. Cloning, expression and characterization of a cDNA encoding a lipase from Rhizopus delemar. Gene. 1991 Dec 20;109(1):107–113. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90594-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood J. The versatility of lipases for industrial uses. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Apr;14(4):125–126. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90140-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihara F., Kageyama Y., Hirata M., Nihira T., Yamada Y. Purification, characterization, and molecular cloning of lactonizing lipase from Pseudomonas species. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18135–18140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen S., Skov K. W., Diderichsen B. Cloning, sequence, and expression of a lipase gene from Pseudomonas cepacia: lipase production in heterologous hosts requires two Pseudomonas genes. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):559–567. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.559-567.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi Y., Honda H., Taniguchi-Morimura J., Iwasaki S. The codon CUG is read as serine in an asporogenic yeast Candida cylindracea. Nature. 1989 Sep 14;341(6238):164–166. doi: 10.1038/341164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouker G., Jaeger K. E. Specific and sensitive plate assay for bacterial lipases. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jan;53(1):211–213. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.1.211-213.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kugimiya W., Otani Y., Hashimoto Y., Takagi Y. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of the lipase gene from Pseudomonas fragi. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Nov 26;141(1):185–190. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80352-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Y., Iandolo J. J. Lysogenic conversion of staphylococcal lipase is caused by insertion of the bacteriophage L54a genome into the lipase structural gene. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):385–391. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.385-391.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura A., Morita M., Nishimura Y., Sugino Y. A rapid and highly efficient method for preparation of competent Escherichia coli cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6169–6169. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada Y., Sugihara A., Iizumi T., Tominaga Y. cDNA cloning and characterization of Geotrichum candidum lipase II. J Biochem. 1990 May;107(5):703–707. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stead D. Microbial lipases: their characteristics, role in food spoilage and industrial uses. J Dairy Res. 1986 Aug;53(3):481–505. doi: 10.1017/s0022029900025103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D., Schneider T. D., Gold L. M. Characterization of translational initiation sites in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2971–2996. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


