Abstract
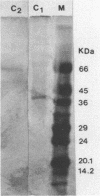
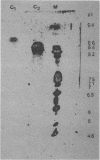
A nonsporulating strain of Streptomyces diastaticus producing alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase activity (EC 3.2-1.55) was isolated from soil. Two alpha-L-arabinosidases were purified by ion-exchange chromatography and chromatofocusing. The enzymes had molecular weights of 38,000 (C1) and 60,000 (C2) and pIs of 8.8 and 8.3, respectively. The optimum pH range of activity for both enzymes was between 4 and 7. The apparent Km values with p-nitrophenyl arabinofuranoside as the substrate were 10 mM (C1) and 12.5 mM (C2). C1 retained 50% of its activity after 8 h of incubation at 25 degrees C, while C2 retained 80% activity. After 3 h of incubation at 50 degrees C, C1 lost 90% of its initial activity while C2 lost only 40%. The purified enzymes hydrolyzed p-nitrophenyl alpha-L-arabinofuranoside and liberated arabinose from arabinoxylan and from a debranched beta-1,5-arabinan.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greve L. C., Labavitch J. M., Hungate R. E. alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase from Ruminococcus albus 8: purification and possible role in hydrolysis of alfalfa cell wall. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 May;47(5):1135–1140. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.5.1135-1140.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaji A., Saheki T. Endo-arabinanase from Bacillus subtilis F-11. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Dec 18;410(2):354–360. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90237-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaji A., Tagawa K. Purification, crystallization and amino acid composition of alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase from Aspergillus niger. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jun 23;207(3):456–464. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2795(70)80008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., Link T. A., Engel W. D., von Jagow G. Isolation of the eleven protein subunits of the bc1 complex from beef heart. Methods Enzymol. 1986;126:224–237. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(86)26024-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Uchida T. Purification and properties of alpha-l-arabinofuranosidase from plant Scopolia japonica calluses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 10;522(2):531–540. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90085-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]