Abstract
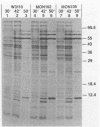
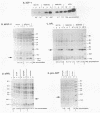
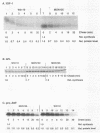
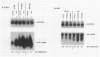
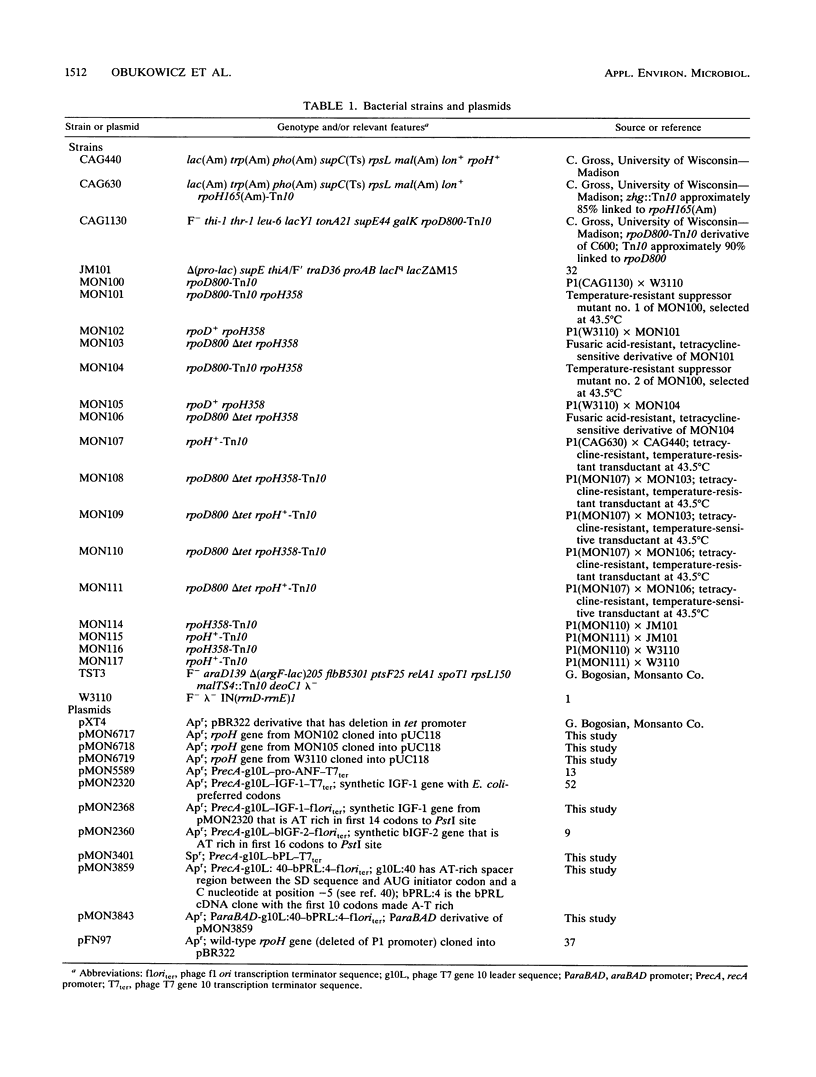
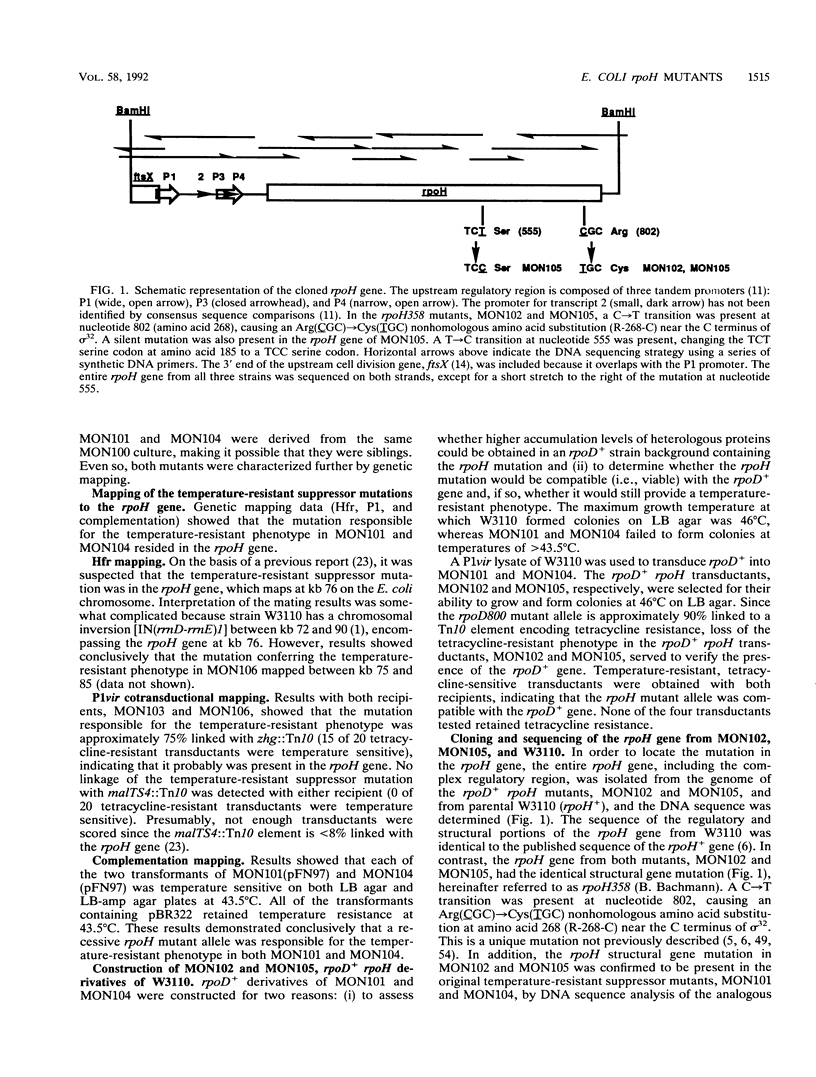
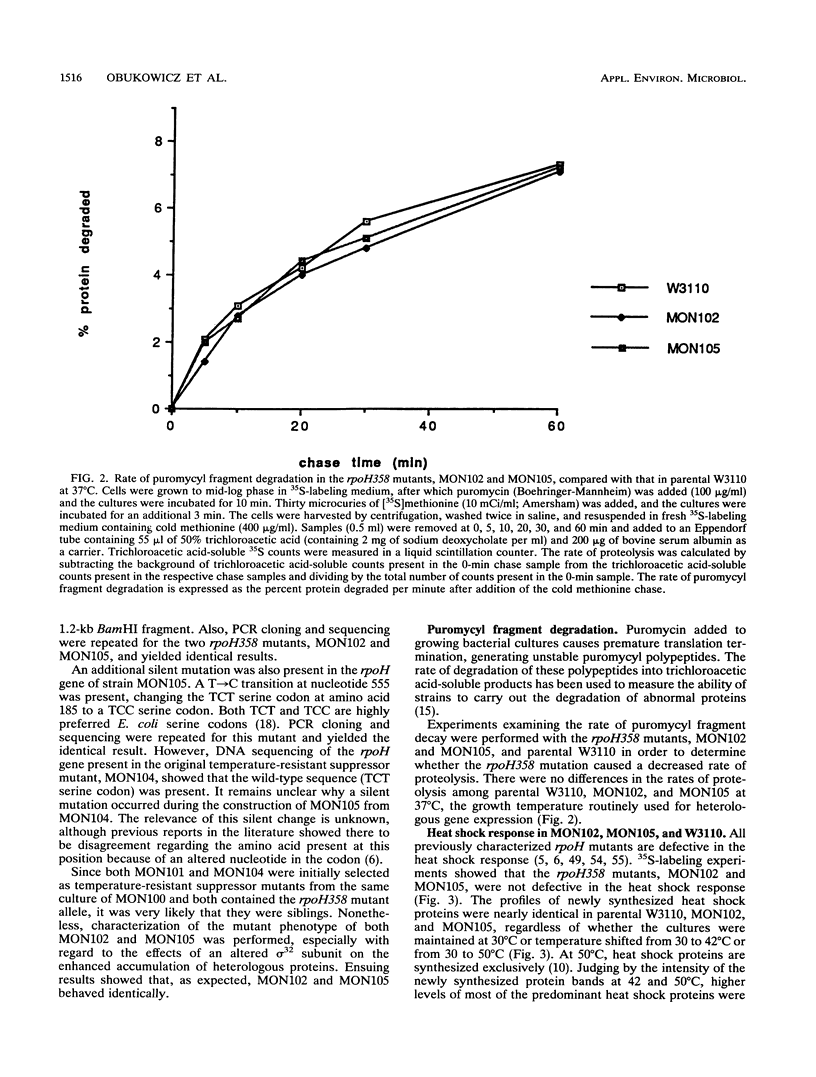
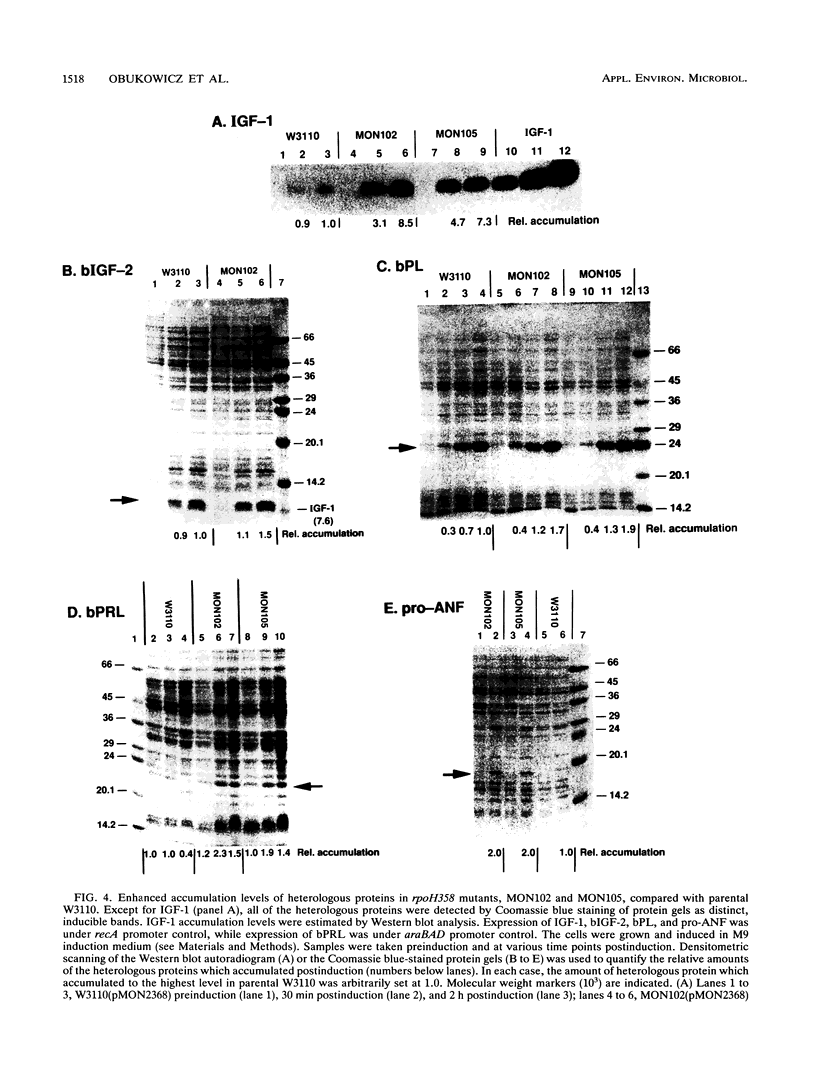
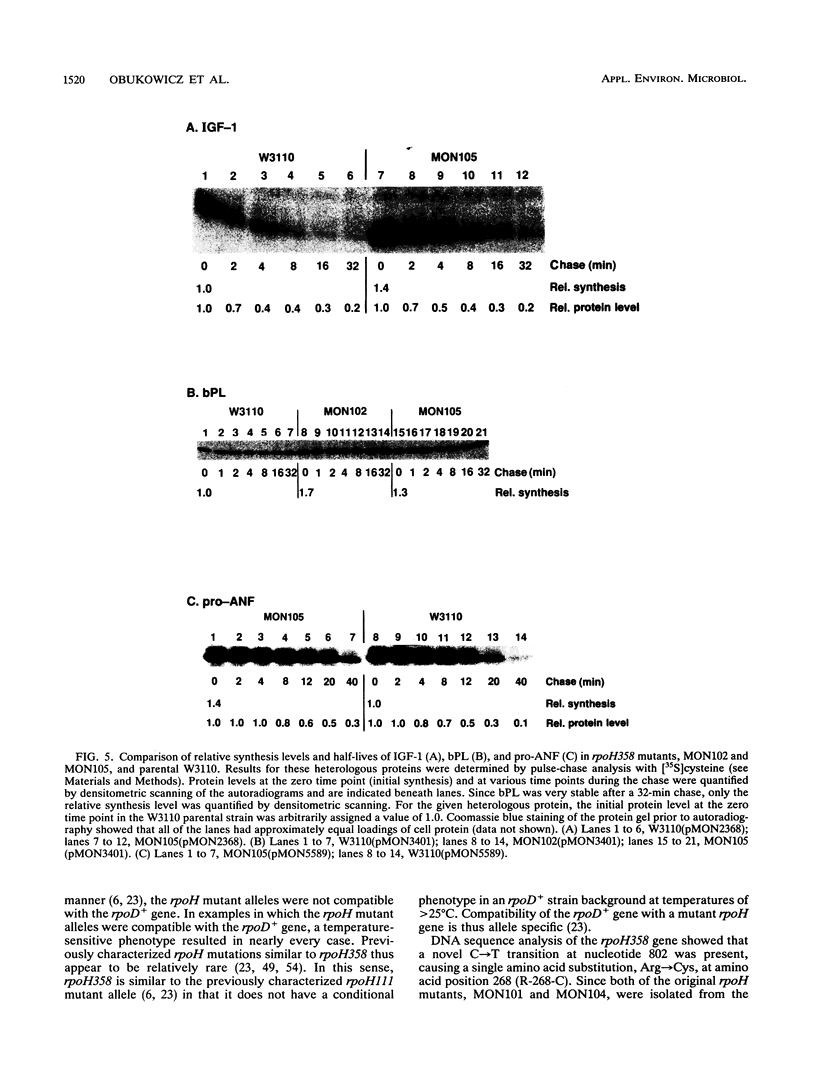
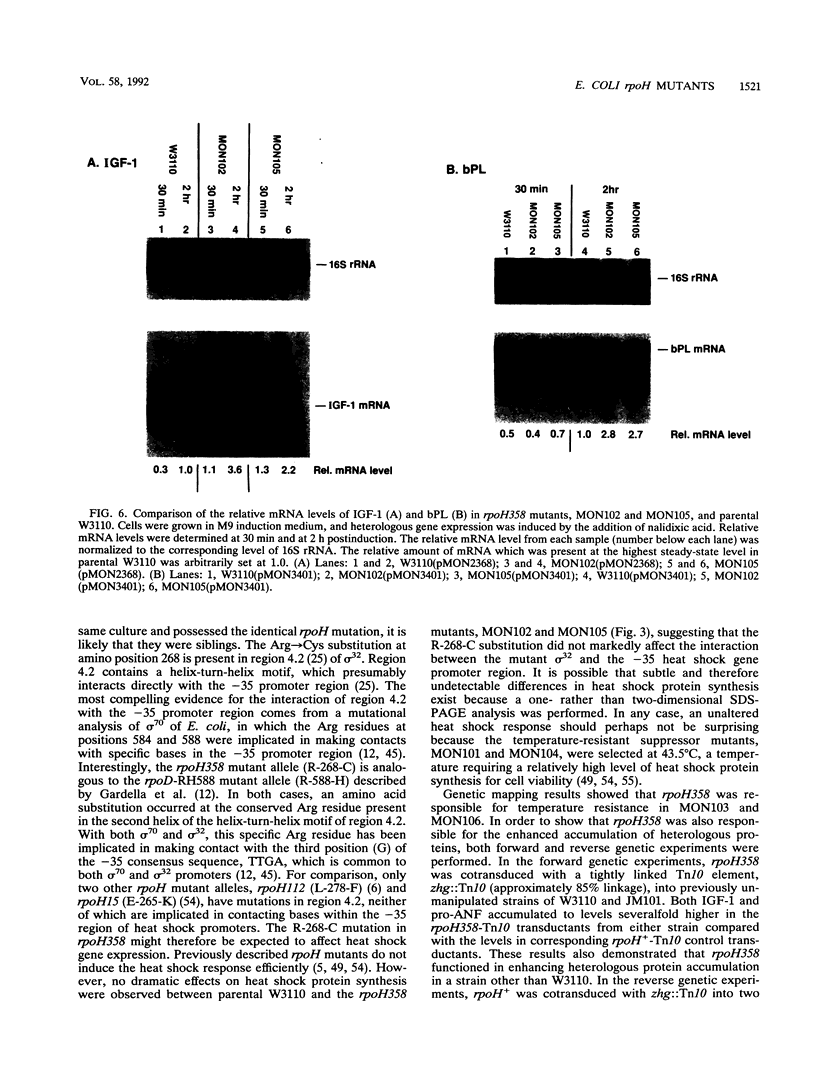
Extragenic temperature-resistant suppressor mutants of an rpoD800 derivative of Escherichia coli W3110 were selected at 43.5 degrees C. Two of the mutants were shown to have a phenotype of enhanced accumulation of heterologous proteins. Genetic mapping of the two mutants showed that the mutation conferring temperature resistance resided in the rpoH gene. P1-mediated transduction of the rpoD+ gene into both of the rpoD800 rpoH double mutants resulted in viable rpoH mutants, MON102 and MON105, that retained temperature resistance at 46 degrees C, the maximum growth temperature of W3110. The complete rpoH gene, including the regulatory region, from MON102, MON105, and the parental W3110 was cloned and sequenced. Sequencing results showed that a single C----T transition at nucleotide 802 was present in both MON102 and MON105, resulting in an Arg(CGC)----Cys(TGC) substitution at amino acid residue 268 (R-268-C; this gene was designated rpoH358). Heterologous protein accumulation levels in both MON102 and MON105, as well as in rpoH358 mutants constructed in previously unmanipulated W3110 and JM101, were assessed and compared with parental W3110 and JM101 levels. Expression studies utilizing the recA or araBAD promoter and the phage T7 gene 10L ribosome-binding site (g10L) showed that increased accumulation levels of a number of representative heterologous proteins (i.e., human or bovine insulin-like growth factor-1, bovine insulin-like growth factor-2, prohormone of human atrial natriuretic factor, bovine placental lactogen, and/or bovine prolactin) were obtained in the rpoH358 mutants compared with the levels in the parental W3110 and JM101. The mechanism of enhanced heterologous protein accumulation in MON102 and MON105 was unique compared with those of previously described rpoH mutants. Pulse-chase and Northern (RNA) blot analyses showed that the enhanced accumulation of heterologous proteins was not due to decreased proteolysis but was instead due to increased levels of the respective heterologous mRNAs accompanied by increased synthesis of the respective heterologous proteins. The plasmid copy number remained unaltered.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker T. A., Grossman A. D., Gross C. A. A gene regulating the heat shock response in Escherichia coli also affects proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6779–6783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgaize D. B., Phillips T. A., VanBogelen R. A., Jones P. G., Neidhardt F. C., Fournier M. J. Loss of 4.5S RNA induces the heat shock response and lambda prophage in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):1151–1154. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.1151-1154.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukau B., Walker G. C. Mutations altering heat shock specific subunit of RNA polymerase suppress major cellular defects of E. coli mutants lacking the DnaK chaperone. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):4027–4036. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07624.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calendar R., Erickson J. W., Halling C., Nolte A. Deletion and insertion mutations in the rpoH gene of Escherichia coli that produce functional sigma 32. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3479–3484. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3479-3484.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chew L. C., Tacon W. C. Simultaneous regulation of plasmid replication and heterologous gene expression in Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol. 1990 Jan;13(1):47–60. doi: 10.1016/0168-1656(90)90130-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper S., Ruettinger T. A temperature sensitive nonsense mutation affecting the synthesis of a major protein of Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Aug 5;139(2):167–176. doi: 10.1007/BF00264696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easton A. M., Gierse J. K., Seetharam R., Klein B. K., Kotts C. E. Production of bovine insulin-like growth factor 2 (bIGF2) in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1991 May 30;101(2):291–295. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90426-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson J. W., Gross C. A. Identification of the sigma E subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase: a second alternate sigma factor involved in high-temperature gene expression. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1462–1471. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson J. W., Vaughn V., Walter W. A., Neidhardt F. C., Gross C. A. Regulation of the promoters and transcripts of rpoH, the Escherichia coli heat shock regulatory gene. Genes Dev. 1987 Jul;1(5):419–432. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.5.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardella T., Moyle H., Susskind M. M. A mutant Escherichia coli sigma 70 subunit of RNA polymerase with altered promoter specificity. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 20;206(4):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90567-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierse J. K., Olins P. O., Devine C. S., Marlay J. D., Obukowicz M. G., Mortensen L. H., McMahon E. G., Blaine E. H., Seetharam R. Expression, purification, and in vivo activity of atrial natriuretic factor prohormone produced in Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Jun;271(2):441–446. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90294-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. R., Hatfull G. F., Salmond G. P. A new cell division operon in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Oct;205(1):134–145. doi: 10.1007/BF02428043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L. Degradation of abnormal proteins in Escherichia coli (protein breakdown-protein structure-mistranslation-amino acid analogs-puromycin). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):422–426. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman S. Genetics of proteolysis in Escherichia coli*. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:163–198. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.001115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouy M., Gautier C. Codon usage in bacteria: correlation with gene expressivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7055–7074. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A. D., Burgess R. R., Walter W., Gross C. A. Mutations in the Ion gene of E. coli K12 phenotypically suppress a mutation in the sigma subunit of RNA polymerase. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):151–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90505-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A. D., Erickson J. W., Gross C. A. The htpR gene product of E. coli is a sigma factor for heat-shock promoters. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):383–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90493-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A. D., Straus D. B., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. Sigma 32 synthesis can regulate the synthesis of heat shock proteins in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):179–184. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A. D., Zhou Y. N., Gross C., Heilig J., Christie G. E., Calendar R. Mutations in the rpoH (htpR) gene of Escherichia coli K-12 phenotypically suppress a temperature-sensitive mutant defective in the sigma 70 subunit of RNA polymerase. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):939–943. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.939-943.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmann J. D., Chamberlin M. J. Structure and function of bacterial sigma factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:839–872. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A., Humbel R. E. Insulin-like growth factors I and II in fetal and adult bovine serum. Purification, primary structures, and immunological cross-reactivities. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):569–575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu J. C., Gross C. A. Marker rescue with plasmids bearing deletions in rpoD identifies a dispensable part of E. coli sigma factor. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;191(3):492–498. doi: 10.1007/BF00425768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroh H. E., Simon L. D. The ClpP component of Clp protease is the sigma 32-dependent heat shock protein F21.5. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):6026–6034. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.6026-6034.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusukawa N., Yura T. Heat shock protein GroE of Escherichia coli: key protective roles against thermal stress. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):874–882. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloy S. R., Nunn W. D. Selection for loss of tetracycline resistance by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):1110–1111. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.1110-1111.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. W., Wu H. C. Cotranscription of the Escherichia coli isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase (ileS) and prolipoprotein signal peptidase (lsp) genes. Fine-structure mapping of the lsp internal promoter. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):389–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. L., Coit D., Baxter J. D., Martial J. A. Cloning of bovine prolactin cDNA and evolutionary implications of its sequence. DNA. 1981;1(1):37–50. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1981.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., VanBogelen R. A., Lau E. T. Molecular cloning and expression of a gene that controls the high-temperature regulon of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):597–603. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.597-603.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., VanBogelen R. A., Vaughn V. The genetics and regulation of heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:295–329. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obukowicz M. G., Turner M. A., Wong E. Y., Tacon W. C. Secretion and export of IGF-1 in Escherichia coli strain JM101. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Dec;215(1):19–25. doi: 10.1007/BF00331297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olins P. O., Devine C. S., Rangwala S. H., Kavka K. S. The T7 phage gene 10 leader RNA, a ribosome-binding site that dramatically enhances the expression of foreign genes in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1988 Dec 15;73(1):227–235. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90329-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsell D. A., Silber K. R., Sauer R. T. Carboxy-terminal determinants of intracellular protein degradation. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):277–286. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler L. A., Shimomura K., Kessler M. A., Zieler C. G., Bremel R. D. Bovine placental lactogen: molecular cloning and protein structure. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 1;27(22):8443–8448. doi: 10.1021/bi00422a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegele D. A., Hu J. C., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. Altered promoter recognition by mutant forms of the sigma 70 subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 20;206(4):591–603. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90568-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D. B., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. Escherichia coli heat shock gene mutants are defective in proteolysis. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1851–1858. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D. B., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. The heat shock response of E. coli is regulated by changes in the concentration of sigma 32. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):348–351. doi: 10.1038/329348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobe T., Ito K., Yura T. Isolation and physical mapping of temperature-sensitive mutants defective in heat-shock induction of proteins in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(1-2):10–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00332716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobe T., Kusukawa N., Yura T. Suppression of rpoH (htpR) mutations of Escherichia coli: heat shock response in suhA revertants. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4128–4134. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4128-4134.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanBogelen R. A., Neidhardt F. C. Ribosomes as sensors of heat and cold shock in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5589–5593. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong E. Y., Seetharam R., Kotts C. E., Heeren R. A., Klein B. K., Braford S. R., Mathis K. J., Bishop B. F., Siegel N. R., Smith C. E. Expression of secreted insulin-like growth factor-1 in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1988 Sep 7;68(2):193–203. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano R., Nagai H., Shiba K., Yura T. A mutation that enhances synthesis of sigma 32 and suppresses temperature-sensitive growth of the rpoH15 mutant of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):2124–2130. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.2124-2130.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yura T., Tobe T., Ito K., Osawa T. Heat shock regulatory gene (htpR) of Escherichia coli is required for growth at high temperature but is dispensable at low temperature. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6803–6807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Y. N., Kusukawa N., Erickson J. W., Gross C. A., Yura T. Isolation and characterization of Escherichia coli mutants that lack the heat shock sigma factor sigma 32. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3640–3649. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3640-3649.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]