Abstract
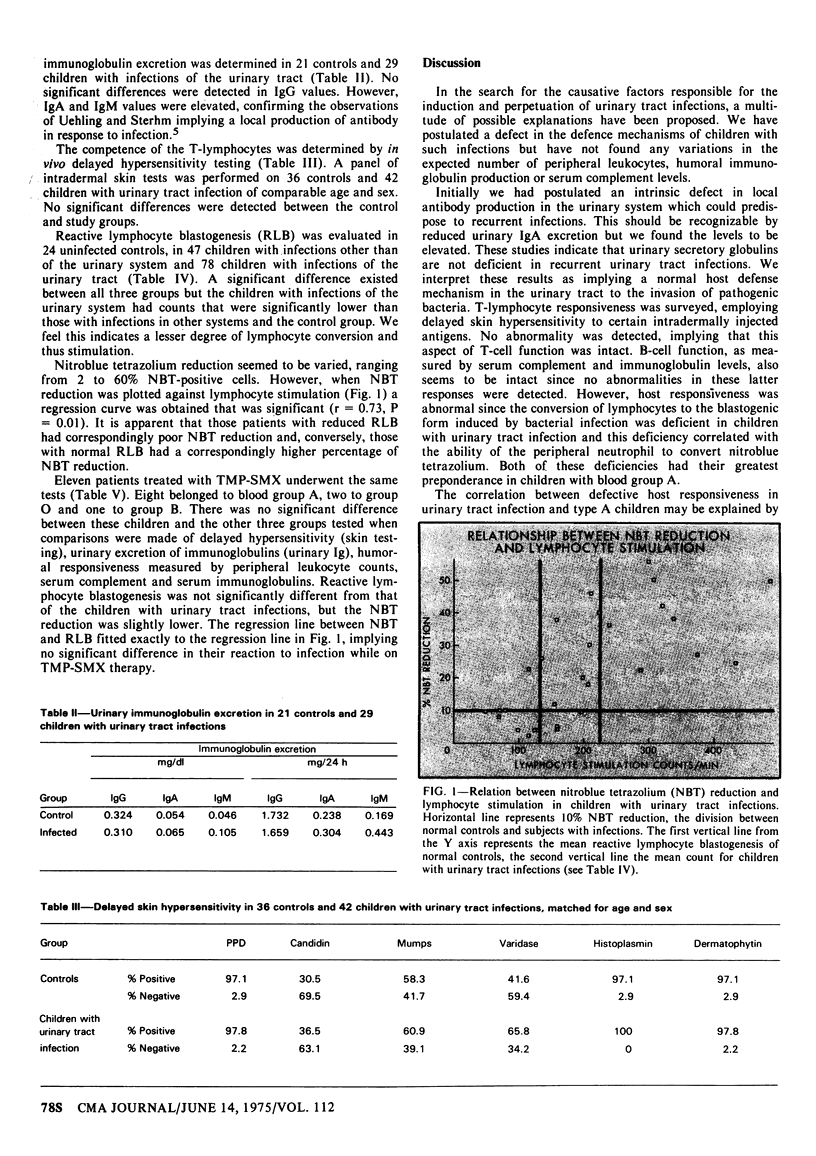
In order to determine whether a deficiency in immunologic response predisposes certain children to recurrent infections of the urinary tract, four groups of children were investigated: a control group; children with extraurinary infections; children with urinary tract infections; and a group of children treated with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX). In none of the groups were there changes in humoral immunoglobulins, peripheral neutrophil counts, serum complement concentrations or urinary excretion of IgG, IgA, or IgM that might might predispose to infection. However, children with urinary tract infections were more likely to belong to blood group A (66.6%; expected frequency, 45%) and had a blunted thymidine uptake of their stimulated lymphocytes (RLB) when compared with children with extraurinary infection. As well, their nitroblue tetrazolium reduction (NBT) was significantly lowered and this paralleled their RLB response. We postulated a shared antigenic feature of either their renal-urinary tissue or bacterial antigen with blood group A antigen; this prevents the mounting of an effective immunologic defence. If TMP-SMX further depresses the lymphocyte response, it may be considered contraindicated in urinary tract infection. In 11 children treated with this drug we found no significant difference between their RLB and NBT responses and those of children with infections of the urinary system treated with other drugs. We conclude that TMP-SMX does not alter the immune responses in children.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crowther D., Fairley G. H., Sewell R. L. Lymphoid cellular responses in the blood after immunization in man. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):849–869. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drach G. W., Reed W. P., Williams R. C., Jr Antigens common to human and bacterial cells: urinary tract pathogens. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Nov;78(5):725–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fudenberg H., Good R. A., Goodman H. C., Hitzig W., Kunkel H. G., Roitt I. M., Rosen F. S., Rowe D. S., Seligmann M., Soothill J. R. Primary immunodeficiencies. Report of a World Health Organization Committee. Pediatrics. 1971 May;47(5):927–946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaylarde P. M., Sarkany I. Suppression of thymidine uptake of human lymphocytes by co-trimoxazole. Br Med J. 1972 Jul 15;3(5819):144–146. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5819.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNIN C. M., DEUTSCHER R., PAQUIN A., Jr URINARY TRACT INFECTION IN SCHOOL CHILDREN: AN EPIDEMIOLOGIC, CLINICAL AND LABORATORY STUDY. Medicine (Baltimore) 1964 Mar;43:91–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman D. B., Katz R., McIntosh R. M. Secretory IgA in urinary tract infections. Br Med J. 1970 Nov 21;4(5733):463–465. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5733.463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunin C. M. The natural history of recurrent bacteriuria in schoolgirls. N Engl J Med. 1970 Jun 25;282(26):1443–1448. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197006252822601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakos M., Ikari N. S. The role of antibody in experimental pyelonephritis. J Pathol. 1969 Mar;97(3):513–525. doi: 10.1002/path.1710970310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matula G., Paterson P. Y. Spontaneous in vitro reduction of nitroblue tetrazolium by neutrophils of adult patients with bacterial infection. N Engl J Med. 1971 Aug 5;285(6):311–317. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197108052850603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. E., North J. D. Editorial: Host response in urinary tract infections. Kidney Int. 1974 Mar;5(3):179–186. doi: 10.1038/ki.1974.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody M. P., Young V. M., Faber J. E. Relationship of blood group antigens of the Enterobacteriaceae to infections in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1969;9:424–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley H. D., Jr Pyelonephritis. Adv Pediatr. 1968;15:191–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uehling D. T., Steihm E. R. Elevated urinary secretory IgA in children with urinary tract infection. Pediatrics. 1971 Jan;47(1):40–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]