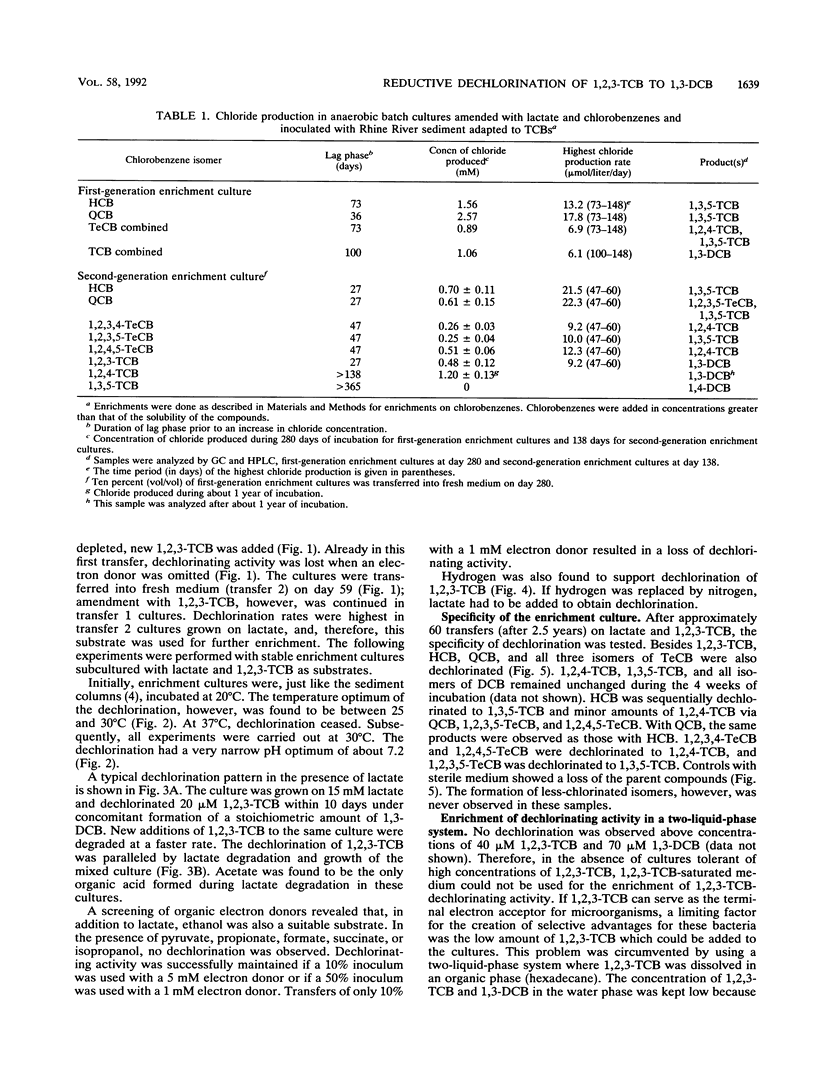
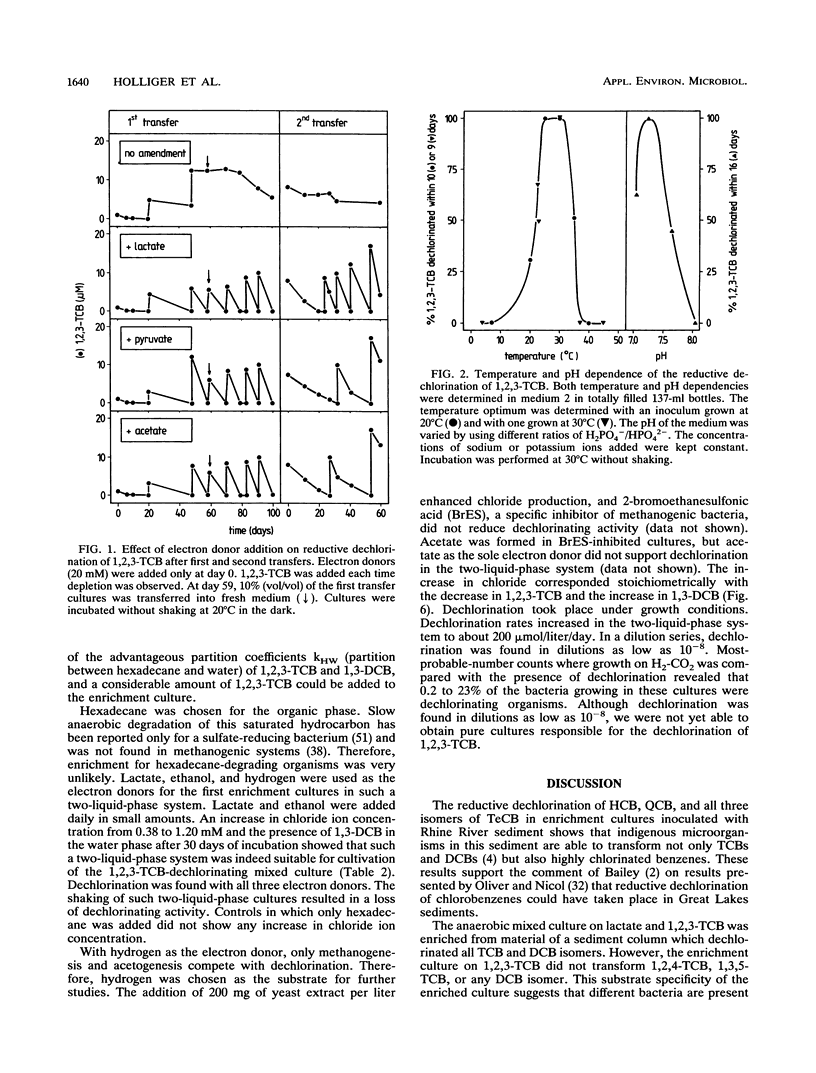
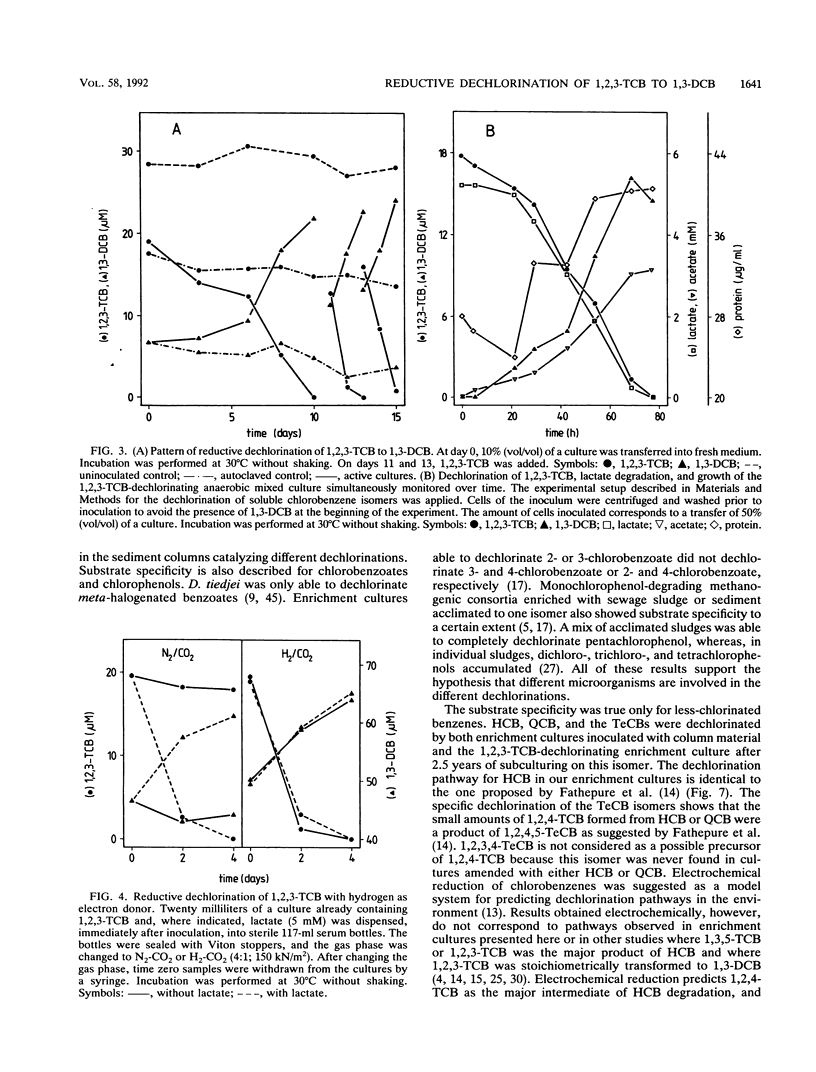
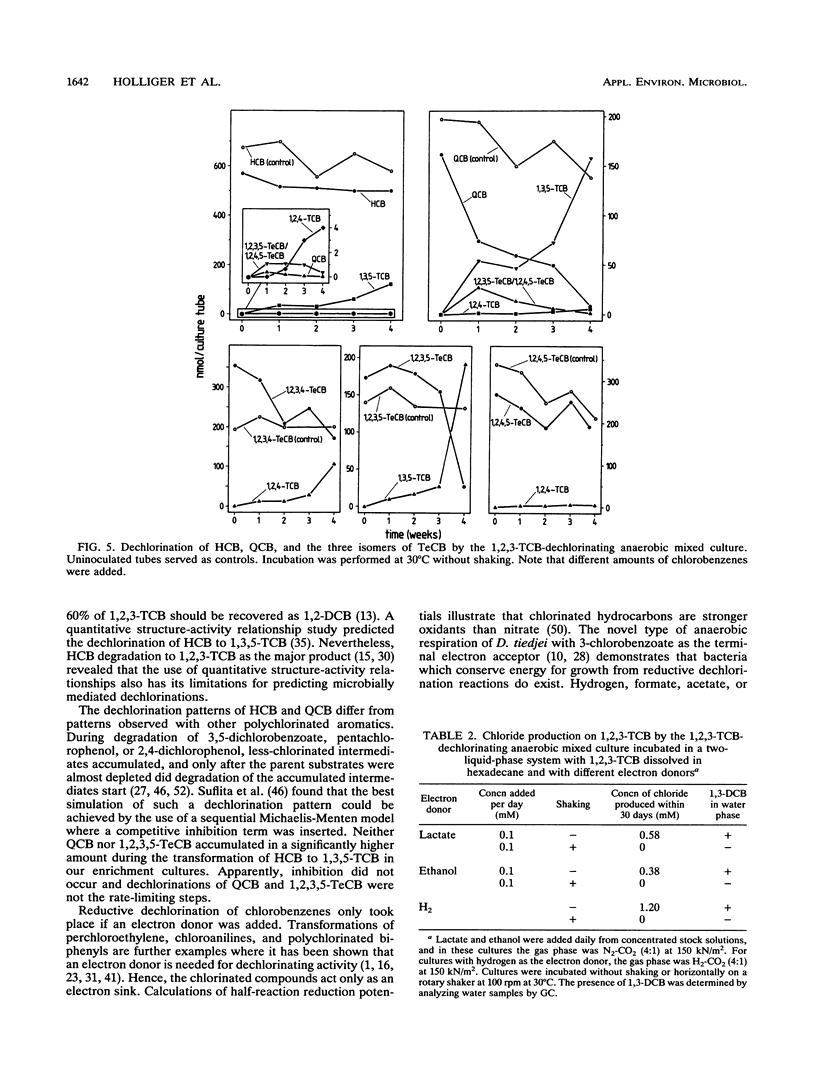
Abstract
Hexachlorobenzene (HCB), pentachlorobenzene (QCB), all three isomers of tetrachlorobenzene (TeCB), 1,2,3-trichlorobenzene (1,2,3-TCB), and 1,2,4-TCB were reductively dechlorinated by enrichment cultures in the presence of lactate, glucose, ethanol, or isopropanol as the electron donor. The enrichment cultures originated from percolation columns filled with Rhine River sediment in which dechlorination of TCBs and dichlorobenzenes (DCBs) occurred. A stable consortium obtained by transfer on lactate as the energy and carbon source in the presence of 1,2,3-TCB dechlorinated this isomer stoichiometrically to 1,3-DCB. Dechlorinating activity could only be maintained when an electron donor was added. Lactate, ethanol, and hydrogen appeared to be the best substrates. Optimal temperature and pH for dechlorination were 30 degrees C and 7.2, respectively. The specificity of the enrichment on lactate and 1,2,3-TCB was tested after approximately 60 transfers (after 2.5 years). HCB and QCB were stoichiometrically dechlorinated to 1,3,5-TCB and minor amounts of 1,2,4-TCB. 1,3,5-TCB was the sole product formed from 1,2,3,5-TeCB, while 1,2,3,4-TeCB and 1,2,4,5-TeCB were converted to 1,2,4-TCB. 1,2,4-TCB, 1,3,5-TCB, and the three isomers of DCB were not dechlorinated during 4 weeks of incubation. For further enrichment of the 1,2,3-TCB-dechlorinating bacteria, a two-liquid-phase (hexadecane-water) system was used with hydrogen as the electron donor and 1,2,3-TCB or CO2 as the electron acceptor. Methanogens and acetogens were the major substrate-competing (H2-CO2) microorganisms in the two-liquid-phase system. Inhibition of methanogenesis by 2-bromoethanesulfonic acid did not influence dechlorination, and acetogens which were isolated from the enrichment culture did not have dechlorinating activity.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagley D. M., Gossett J. M. Tetrachloroethene transformation to trichloroethene and cis-1,2-dichloroethene by sulfate-reducing enrichment cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Aug;56(8):2511–2516. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.8.2511-2516.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd S. A., Shelton D. R. Anaerobic biodegradation of chlorophenols in fresh and acclimated sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Feb;47(2):272–277. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.2.272-277.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeWeerd K. A., Concannon F., Suflita J. M. Relationship between hydrogen consumption, dehalogenation, and the reduction of sulfur oxyanions by Desulfomonile tiedjei. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jul;57(7):1929–1934. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.7.1929-1934.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deweerd K. A., Suflita J. M. Anaerobic Aryl Reductive Dehalogenation of Halobenzoates by Cell Extracts of "Desulfomonile tiedjei". Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Oct;56(10):2999–3005. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.10.2999-3005.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolfing J. Reductive dechlorination of 3-chlorobenzoate is coupled to ATP production and growth in an anaerobic bacterium, strain DCB-1. Arch Microbiol. 1990;153(3):264–266. doi: 10.1007/BF00249079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efroymson R. A., Alexander M. Biodegradation by an arthrobacter species of hydrocarbons partitioned into an organic solvent. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 May;57(5):1441–1447. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.5.1441-1447.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fathepure B. Z., Tiedje J. M., Boyd S. A. Reductive dechlorination of hexachlorobenzene to tri- and dichlorobenzenes in anaerobic sewage sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):327–330. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.327-330.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman D. L., Gossett J. M. Biological reductive dechlorination of tetrachloroethylene and trichloroethylene to ethylene under methanogenic conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Sep;55(9):2144–2151. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.9.2144-2151.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genthner B. R., Price W. A., Pritchard P. H. Characterization of anaerobic dechlorinating consortia derived from aquatic sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1472–1476. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1472-1476.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn E. P., Townsend G. T., Suflita J. M. Effect of sulfate and organic carbon supplements on reductive dehalogenation of chloroanilines in anaerobic aquifer slurries. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Sep;56(9):2630–2637. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.9.2630-2637.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinucci A. C., Bartha R. Biodegradation of 1,2,3- and 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene in soil and in liquid enrichment culture. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Nov;38(5):811–817. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.5.811-817.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikesell M. D., Boyd S. A. Complete reductive dechlorination and mineralization of pentachlorophenol by anaerobic microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):861–865. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.861-865.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohn W. W., Tiedje J. M. Strain DCB-1 conserves energy for growth from reductive dechlorination coupled to formate oxidation. Arch Microbiol. 1990;153(3):267–271. doi: 10.1007/BF00249080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nies L., Vogel T. M. Effects of organic substrates on dechlorination of aroclor 1242 in anaerobic sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Sep;56(9):2612–2617. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.9.2612-2617.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander P., Wittich R. M., Fortnagel P., Wilkes H., Francke W. Degradation of 1,2,4-trichloro- and 1,2,4,5-tetrachlorobenzene by pseudomonas strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 May;57(5):1430–1440. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.5.1430-1440.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schraa G., Boone M. L., Jetten M. S., van Neerven A. R., Colberg P. J., Zehnder A. J. Degradation of 1,4-dichlorobenzene by Alcaligenes sp. strain A175. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Dec;52(6):1374–1381. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.6.1374-1381.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton D. R., Tiedje J. M. Isolation and partial characterization of bacteria in an anaerobic consortium that mineralizes 3-chlorobenzoic Acid. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Oct;48(4):840–848. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.4.840-848.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spain J. C., Nishino S. F. Degradation of 1,4-dichlorobenzene by a Pseudomonas sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):1010–1019. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.1010-1019.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens T. O., Linkfield T. G., Tiedje J. M. Physiological characterization of strain DCB-1, a unique dehalogenating sulfidogenic bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Dec;54(12):2938–2943. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.12.2938-2943.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suflita J. M., Horowitz A., Shelton D. R., Tiedje J. M. Dehalogenation: a novel pathway for the anaerobic biodegradation of haloaromatic compounds. Science. 1982 Dec 10;218(4577):1115–1117. doi: 10.1126/science.218.4577.1115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suflita J. M., Robinson J. A., Tiedje J. M. Kinetics of microbial dehalogenation of haloaromatic substrates in methanogenic environments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 May;45(5):1466–1473. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.5.1466-1473.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X., Wiegel J. Sequential anaerobic degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol in freshwater sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Apr;56(4):1119–1127. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.4.1119-1127.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bont J. A., Vorage M. J., Hartmans S., van den Tweel W. J. Microbial degradation of 1,3-dichlorobenzene. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):677–680. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.677-680.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


