Abstract
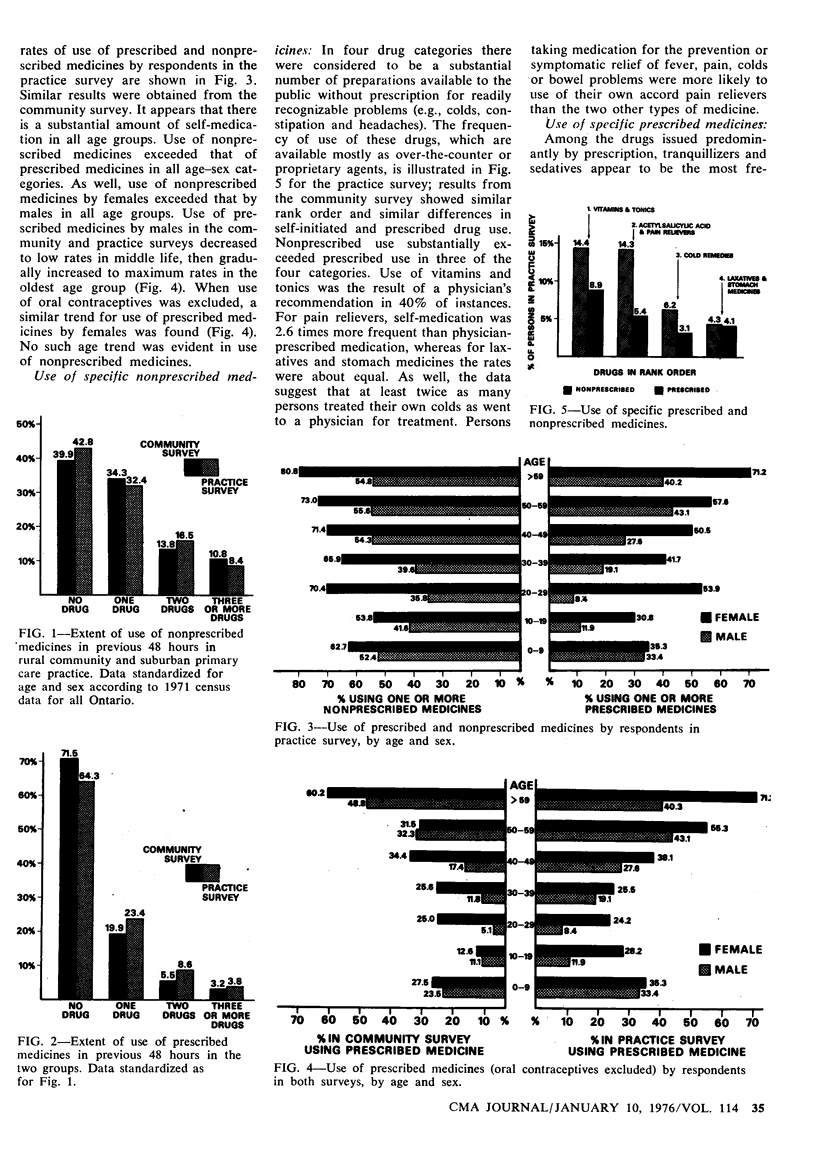
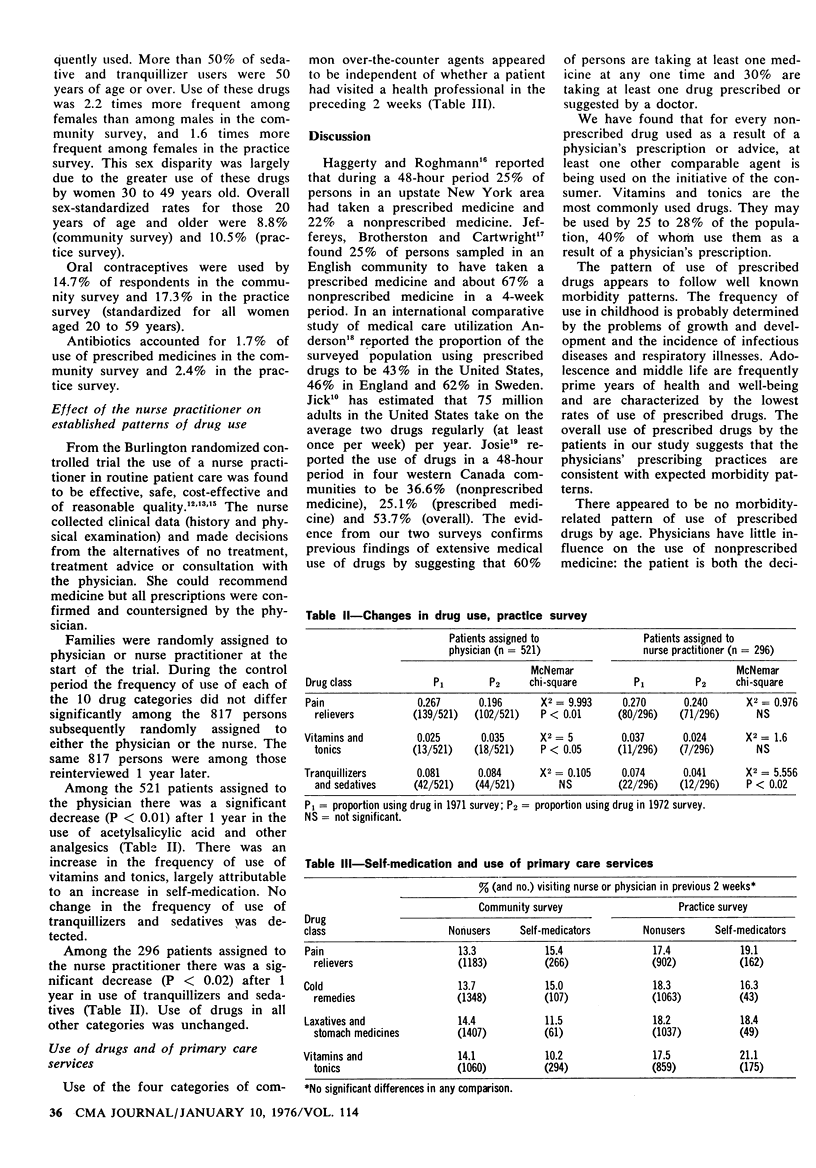
The pattern and extent of medical use of drugs was examined by survey in a rural Ontario community (Smithville) and a suburban (Burlington) family practice. Changes in established patterns of drug use that occur after the introduction of a nurse practitioner were also examined in the suburban practice. In both surveys 60% of respondents were using at least one medication and 30% were taking at least one medication prescribed or suggested by a doctor. There were consistently high rates of use of nonprescribed drugs at all ages, especially among females. Vitamins and tonics were the most commonly used drugs, and were taken by 25 to 28% of the respondents, 40% of whom used them on the advice of a physician. From 8.8 to 10.5% of respondents used sedatives or tranquillizers, and reduction in the prescribed use of these drugs was found among patients managed by the nurse practitioners. Self-medication is apparently unrelated to the frequency of medical consultation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balter M. B., Levine J., Manheimer D. I. Cross-national study of the extent of anti-anxiety-sedative drug use. N Engl J Med. 1974 Apr 4;290(14):769–774. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197404042901404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caranasos G. J., Stewart R. B., Cluff L. E. Drug-induced illness leading to hospitalization. JAMA. 1974 May 6;228(6):713–717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chenoy N. C., Spitzer W. O., Anderson G. D. Nurse practitioners in primary care. II. Prior attitudes of a rural population. Can Med Assoc J. 1973 Apr 21;108(8):998–1003. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haggerty R. J., Roghmann K. J. Noncompliance and self medication. Two neglected aspects of pediatric pharmacology. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1972 Feb;19(1):101–115. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)32669-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz N., Wade O. L. Intensive hospital monitoring of adverse reactions to drugs. Br Med J. 1969 Mar 1;1(5643):531–536. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5643.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JEFFERYS M., BROTHERSTON J. H., CARTWRIGHT A. Consumption of medicines on a working-class housing estate. Br J Prev Soc Med. 1960 Apr;14:64–76. doi: 10.1136/jech.14.2.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. R. Drug surveillance utilizing epidemiologic methods. A report from the Boston Collaborative Drug Surveillance Program. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1973 Jul;30(7):584–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogilvie R. I., Ruedy J. Adverse drug reactions during hospitalization. Can Med Assoc J. 1967 Dec 9;97(24):1450–1457. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rucker T. D. Drug use. Data, sources, and limitations. JAMA. 1974 Nov 11;230(6):888–890. doi: 10.1001/jama.230.6.888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHIMMEL E. M. THE HAZARDS OF HOSPITALIZATION. Ann Intern Med. 1964 Jan;60:100–110. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-60-1-100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sackett D. L., Spitzer W. O., Gent M., Roberts R. S. The Burlington randomized trial of the nurse practitioner: health outcomes of patients. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Feb;80(2):137–142. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-2-137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley J. C., Spitzer W. O., Rudnick K. V., Bell J. D., Bethune R. D., Sackett D. L., Wright K. Quality-of-care appraisal in primary care: a quantitative method. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Jul;83(1):46–52. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-83-1-46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slone D., Gaetano L. F., Lipworth L., Shapiro S., Lewis G. P., Jick H. Computer analysis of epidemiologic data on effect of drugs on hospital patients. Public Health Rep. 1969 Jan;84(1):39–52. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W., Seidl L. G., Cluff L. E. Studies on the epidemiology of adverse drug reactions. V. Clinical factors influencing susceptibility. Ann Intern Med. 1966 Oct;65(4):629–640. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-65-4-629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzer W. O., Sackett D. L., Sibley J. C., Roberts R. S., Gent M., Kergin D. J., Hackett B. C., Olynich A. The Burlington randomized trial of the nurse practitioner. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jan 31;290(5):251–256. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197401312900506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolley P. D., Becker M. H., McEvilla J. D., Lasagna L., Gainor M., Sloane L. M. Drug prescribing and use in an American community. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Apr;76(4):537–540. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-76-4-537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


