Abstract
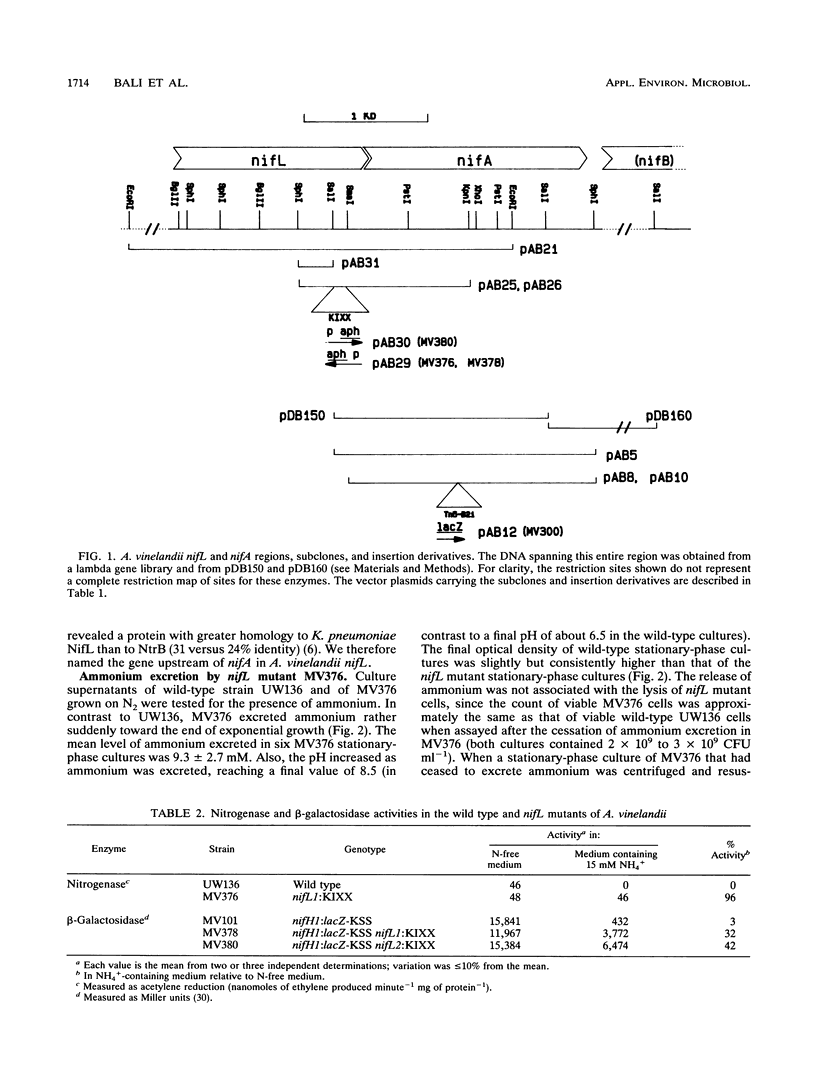
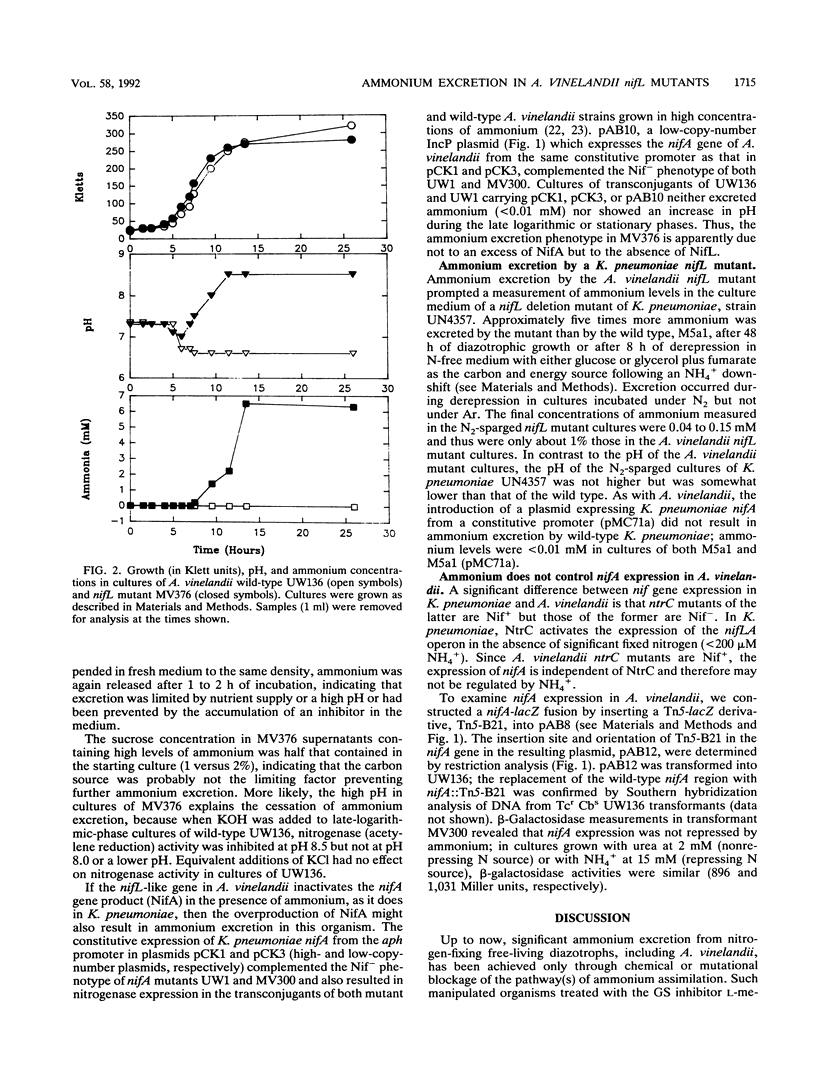
A mutation in the gene upstream of nifA in Azotobacter vinelandii was introduced into the chromosome to replace the corresponding wild-type region. The resulting mutant, MV376, produced nitrogenase constitutively in the presence of 15 mM ammonium. When introduced into a nifH-lacZ fusion strain, the mutation permitted beta-galactosidase production in the presence of ammonium. The gene upstream of nifA is therefore designated nifL because of its similarity to the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifL gene in proximity to nifA, in mutant phenotype, and in amino acid sequence of the gene product. The A. vinelandii nifL mutant MV376 excreted significant quantities of ammonium (approximately 10 mM) during diazotrophic growth. In contrast, ammonium excretion during diazotrophy was much lower in a K. pneumoniae nifL deletion mutant (maximum, 0.15 mM) but significantly higher than in NifL+ K. pneumoniae. The expression of the A. vinelandii nifA gene, unlike that of K. pneumoniae, was not repressed by ammonium.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen K., Shanmugam K. T. Energetics of biological nitrogen fixation: determination of the ratio of formation of H2 to NH4+ catalysed by nitrogenase of Klebsiella pneumoniae in vivo. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Nov;103(1):107–122. doi: 10.1099/00221287-103-1-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett L. T., Cannon F., Dean D. R. Nucleotide sequence and mutagenesis of the nifA gene from Azotobacter vinelandii. Mol Microbiol. 1988 May;2(3):315–321. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00034.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. E., Brill W. J. Genetic analysis of Azotobacter vinelandii mutant strains unable to fix nitrogen. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):954–956. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.954-956.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan-Wollaston V., Cannon M. C., Beynon J. L., Cannon F. C. Role of the nifA gene product in the regulation of nif expression in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):776–778. doi: 10.1038/294776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castorph H., Kleiner D. Some properties of a Klebsiella pneumoniae ammonium transport negative mutant (Amt-). Arch Microbiol. 1984 Oct;139(2-3):245–247. doi: 10.1007/BF00402008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen-Weniger C., Van Veen J. A. NH(4)-Excreting Azospirillum brasilense Mutants Enhance the Nitrogen Supply of a Wheat Host. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Oct;57(10):3006–3012. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.10.3006-3012.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. J., Brill W. J. Control of Klebsiella pneumoniae nif mRNA synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):1186–1190. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.1186-1190.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. J., Roberts G. P., Brill W. J. Posttranscriptional control of Klebsiella pneumoniae nif mRNA stability by the nifL product. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):173–178. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.173-178.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras A., Drummond M., Bali A., Blanco G., Garcia E., Bush G., Kennedy C., Merrick M. The product of the nitrogen fixation regulatory gene nfrX of Azotobacter vinelandii is functionally and structurally homologous to the uridylyltransferase encoded by glnD in enteric bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(24):7741–7749. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.24.7741-7749.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond M. H., Contreras A., Mitchenall L. A. The function of isolated domains and chimaeric proteins constructed from the transcriptional activators NifA and NtrC of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jan;4(1):29–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02012.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figurski D. H., Helinski D. R. Replication of an origin-containing derivative of plasmid RK2 dependent on a plasmid function provided in trans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filser M., Merrick M., Cannon F. Cloning and characterisation of nifLA regulatory mutations from Klebsiella pneumoniae. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;191(3):485–491. doi: 10.1007/BF00425767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. R., Brigle K. E., Bennett L. T., Setterquist R. A., Wilson M. S., Cash V. L., Beynon J., Newton W. E., Dean D. R. Physical and genetic map of the major nif gene cluster from Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):1017–1027. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.1017-1027.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joerger R. D., Bishop P. E. Nucleotide sequence and genetic analysis of the nifB-nifQ region from Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1475–1487. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1475-1487.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn D., Hawkins M., Eady R. R. Metabolic control of Klebsiella pneumoniae mRNA degradation by the availability of fixed nitrogen. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Dec;128(12):3011–3018. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-12-3011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy C., Robson R. L. Activation of nif gene expression in Azotobacter by the nifA gene product of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):626–628. doi: 10.1038/301626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy C., Toukdarian A. Genetics of azotobacters: applications to nitrogen fixation and related aspects of metabolism. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:227–258. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.001303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacNeil T., MacNeil D., Roberts G. P., Supiano M. A., Brill W. J. Fine-structure mapping and complementation analysis of nif (nitrogen fixation) genes in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):253–266. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.253-266.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morett E., Kreutzer R., Cannon W., Buck M. The influence of the Klebsiella pneumoniae regulatory gene nifL upon the transcriptional activator protein NifA. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Aug;4(8):1253–1258. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00704.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page W. J., von Tigerstrom M. Induction of transformation competence in Azotobacter vinelandii iron-limited cultures. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Dec;24(12):1590–1594. doi: 10.1139/m78-254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos J. L., Guerrero M. G., Losada M. Sustained Photoproduction of Ammonia from Dinitrogen and Water by the Nitrogen-Fixing Cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. Strain ATCC 33047. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jul;48(1):114–118. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.1.114-118.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santero E., Toukdarian A., Humphrey R., Kennedy C. Identification and characterization of two nitrogen fixation regulatory regions, nifA and nfrX, in Azotobacter vinelandii and Azotobacter chroococcum. Mol Microbiol. 1988 May;2(3):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00033.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah V. K., Davis I. C., Gordon J. K., Orme-Johnson W. H., Brill W. J. Nitrogenase. 3. Nitrogenaseless mutants of Azotobacter vinelandii: activities, cross-reactions and EPR spectra. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 18;292(1):246–255. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90269-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanmugam K. T., Valentine R. C. Microbial production of ammonium ion from nitrogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):136–139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R., Quandt J., Klipp W. New derivatives of transposon Tn5 suitable for mobilization of replicons, generation of operon fusions and induction of genes in gram-negative bacteria. Gene. 1989 Aug 1;80(1):161–169. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiller H., Latorre C., Hassan M. E., Shanmugam K. T. Isolation and characterization of nitrogenase-derepressed mutant strains of cyanobacterium Anabaena variabilis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):412–419. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.412-419.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staskawicz B., Dahlbeck D., Keen N., Napoli C. Molecular characterization of cloned avirulence genes from race 0 and race 1 of Pseudomonas syringae pv. glycinea. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5789–5794. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5789-5794.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas S. P., Zaritsky A., Boussiba S. Ammonium Excretion by an l-Methionine-dl-Sulfoximine-Resistant Mutant of the Rice Field Cyanobacterium Anabaena siamensis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Nov;56(11):3499–3504. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.11.3499-3504.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toukdarian A., Kennedy C. Regulation of nitrogen metabolism in Azotobacter vinelandii: isolation of ntr and glnA genes and construction of ntr mutants. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):399–407. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04225.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toukdarian A., Saunders G., Selman-Sosa G., Santero E., Woodley P., Kennedy C. Molecular analysis of the Azotobacter vinelandii glnA gene encoding glutamine synthetase. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6529–6539. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6529-6539.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall J. D., Gest H. Derepression of nitrogenase activity in glutamine auxotrophs of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1459–1463. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1459-1463.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


