Abstract
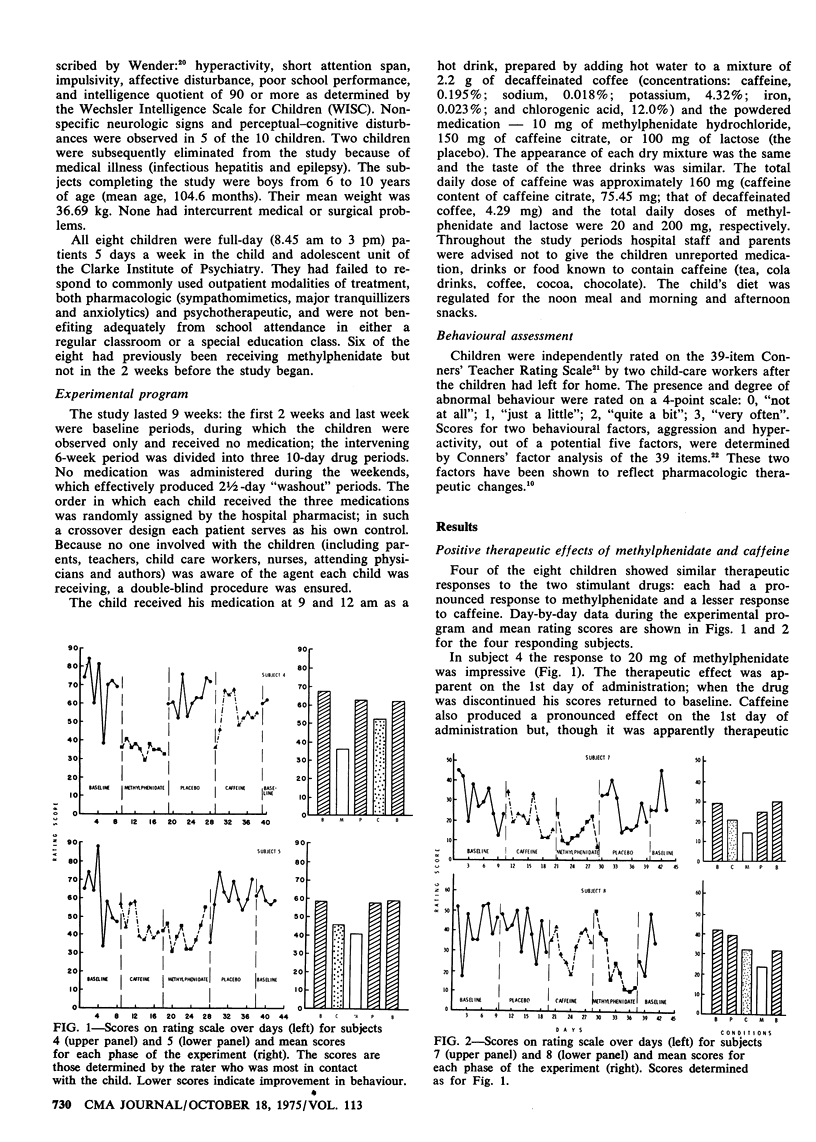
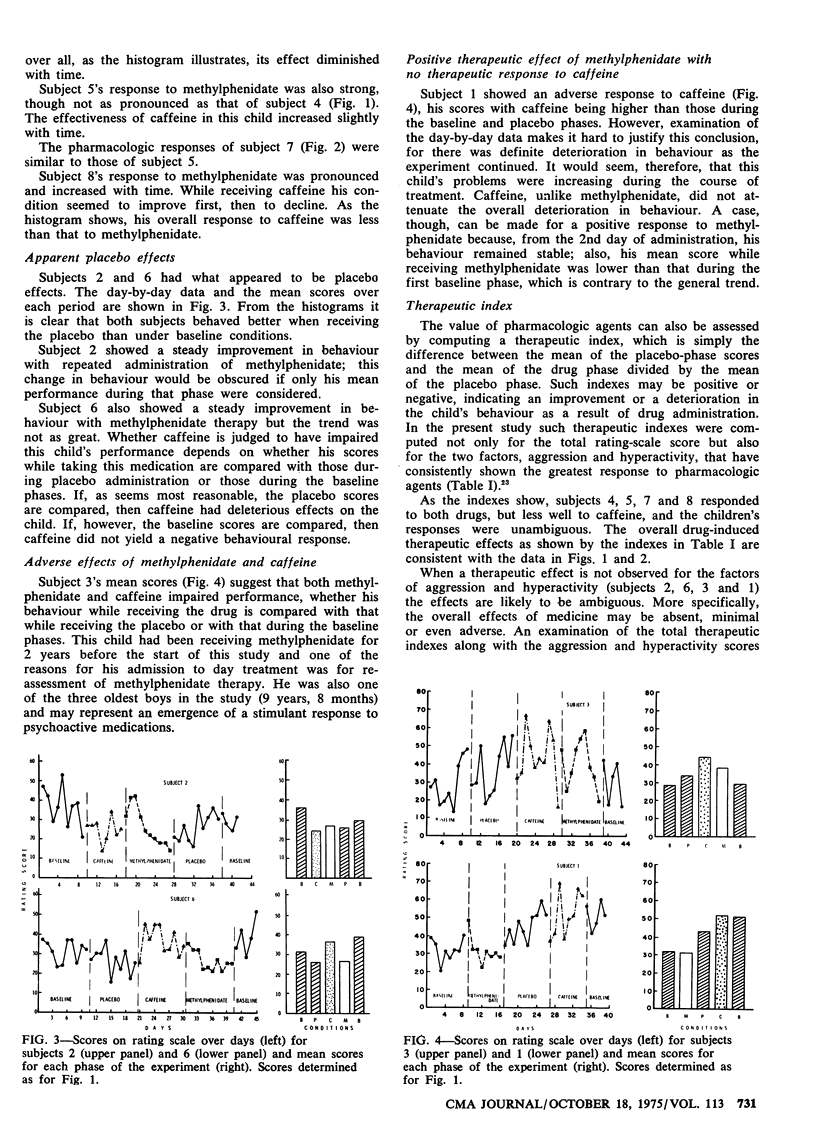
Eight children with minimal brain dysfunction were studied for their individual responses to two stimulant medications--methylphenidate hydrochloride and caffeine citrate. Four types of behavioural responses were observed in the double-blind crossover experiment: four children responded favourably to both psychostimulants, one responded to methylphenidate alone and two responded to the placebo. The behaviour of one child deteriorated while he was taking methylphenidate and caffeine. In general, methylphenidate was superior to caffeine in diminishing hyperactive and aggressive behaviour. It is apparent that such stimulant medication exerts its therapeutic effects in these two areas primarily and would therefore be useful as one aspect of a complete treatment program for children with this syndrome.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carman J. S., Tucker L. S. Letter: Benztropine in childhood hyperkinesis. Lancet. 1973 Dec 8;2(7841):1337–1338. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92923-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conners C. K. A teacher rating scale for use in drug studies with children. Am J Psychiatry. 1969 Dec;126(6):884–888. doi: 10.1176/ajp.126.6.884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conners C. K., Eisenberg L., Barcai A. Effect of dextroamphetamine on children. Studies on subjects with learning disabilities and school behavior problems. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1967 Oct;17(4):478–485. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1967.01730280094011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel B. D., Webster C. D., Sloman L. Methylphenidate and caffeine in the treatment of children with minimal brain dysfunction. Am J Psychiatry. 1975 Jul;132(7):723–728. doi: 10.1176/ajp.132.7.723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg L. M., Deem M. A., McMahon S. Effects of dextroamphetamine, chlorpromazine, and hydroxyzine on behavior and performance in hyperactive children. Am J Psychiatry. 1972 Nov;129(5):532–539. doi: 10.1176/ajp.129.5.532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenhill L. L., Rieder R. O., Wender P. H., Buchsbaum M., Zhan T. P. Lithium carbonate in the treatment of hyperactive children. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1973 May;28(5):636–640. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1973.01750350020004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huessy H. R., Wright A. L. The use of imipramine in children's behavior disorders. Acta Paedopsychiatr. 1970 Dec;37(7):194–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakowski A. J. Amitriptyline in treatment of hyperkinetic children. A double-blind study. Psychosomatics. 1965 Sep-Oct;6(5):355–360. doi: 10.1016/s0033-3182(65)72256-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupietz S., Botti E. Letter: Behavior measurement in pediatric psychopharmacology. Am J Psychiatry. 1974 Jan;131(1):106–106. doi: 10.1176/ajp.131.1.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millichap J. G. Drugs in management of hyperkinetic and perceptually handicapped children. JAMA. 1968 Nov 11;206(7):1527–1530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millichap J. G. Drugs in management of minimal brain dysfunction. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973 Feb 28;205:321–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb43189.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minde K., Weiss G., Mendelson N. A 5-year follow-up study of 91 hyperactive school children. J Am Acad Child Psychiatry. 1972 Jul;11(3):595–610. doi: 10.1016/s0002-7138(09)61211-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison J. R., Stewart M. A. Evidence for polygenetic inheritance in the hyperactive child syndrome. Am J Psychiatry. 1973 Jul;130(7):791–792. doi: 10.1176/ajp.130.7.791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport J. L., Quinn P. O., Lamprecht F. Minor physical anomalies and plasma dopamine-beta-hydroxylase activity in hyperactive boys. Am J Psychiatry. 1974 Apr;131(4):386–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satterfield J. H., Cantwell D. P., Satterfield B. T. Pathophysiology of the hyperactive child syndrome. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1974 Dec;31(6):839–844. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1974.01760180079010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague R. L., Barnes K. R., Werry J. S. Methylphenidate and thioridazine: learning, reaction time, activity, and classroom behavior in disturbed children. Am J Orthopsychiatry. 1970 Jul;40(4):615–628. doi: 10.1111/j.1939-0025.1970.tb00719.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sroufe L. A., Stewart M. A. Treating problem children with stimulant drugs. N Engl J Med. 1973 Aug 23;289(8):407–413. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197308232890806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg G. G., Troshinsky C., Steinberg H. R. Dextroamphetamine-responsive behavior disorder in school children. Am J Psychiatry. 1971 Aug;128(2):174–179. doi: 10.1176/ajp.128.2.174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss G., Kruger E., Danielson U., Elman M. Effect of long-term treatment of hyperactive children with methylphenidate. Can Med Assoc J. 1975 Jan 25;112(2):159–165. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wender P. H. Minimal brain dysfunction in children. Diagnosis and management. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1973 Feb;20(1):187–202. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)32819-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner E., Bierman J. M., French F. E., Simonian K., Connor A., Smith R. S., Campbell M. Reproductive and environmental casualties: a report on the 10-year follow-up of the children of the Kauai Pregnancy Study. Pediatrics. 1968 Jul;42(1):112–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werry J. S., Weiss G., Douglas V., Martin J. Studies on the hyperactive child. 3. The effect of chlorpromazine upon behavior and learning ability. J Am Acad Child Psychiatry. 1966 Apr;5(2):292–312. doi: 10.1016/s0002-7138(09)62060-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winsberg B. G., Bialer I., Kupietz S., Tobias J. Effects of imipramine and dextroamphetamine on behavior of neuropsychiatrically impaired children. Am J Psychiatry. 1972 May;128(11):1425–1431. doi: 10.1176/ajp.128.11.1425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZRULL J. P., WESTMAN J. C., ARTHUR B., BELL W. A. A COMPARISON OF CHLORDIAZEPOXIDE, D-AMPHETAMINE, AND PLACEBO IN THE TREATMENT OF THE HYPERKINETIC SYNDROME IN CHILDREN. Am J Psychiatry. 1963 Dec;120:590–591. doi: 10.1176/ajp.120.6.590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


