Abstract
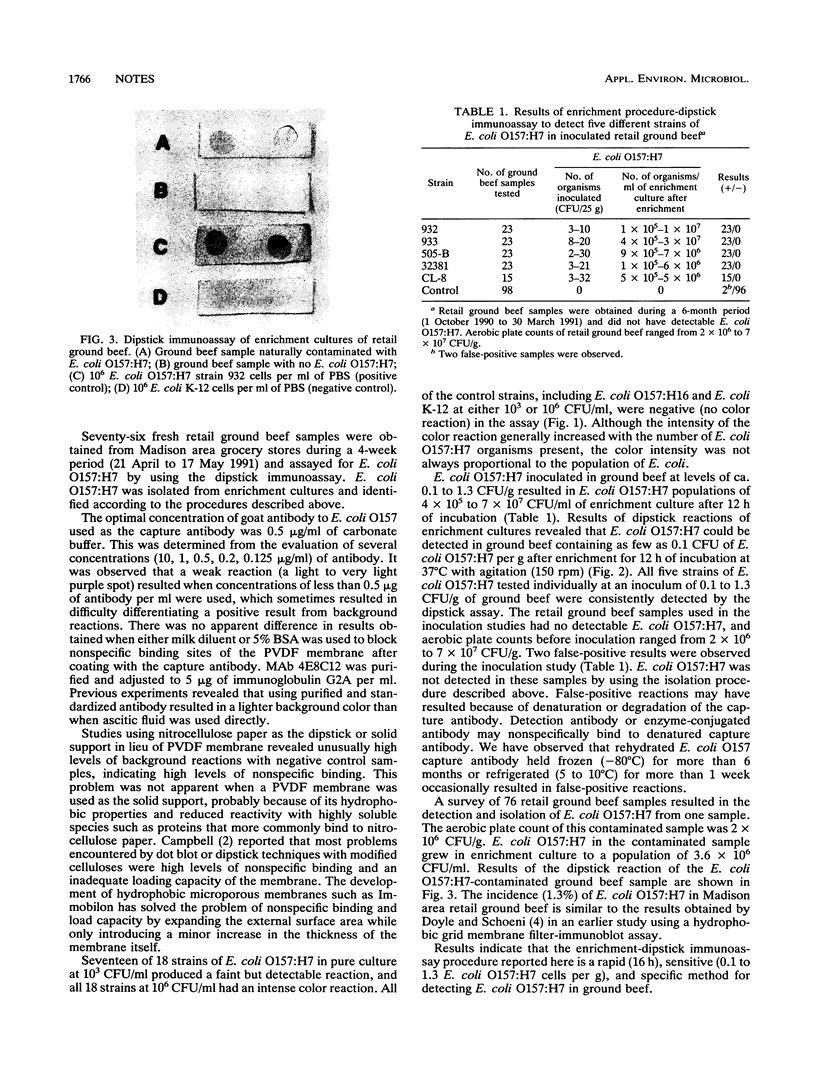
A sensitive and easy-to-perform dipstick immunoassay to detect Escherichia coli O157:H7 in retail ground beef was developed by using a sandwich-type assay (with a polyclonal antibody to E. coli O157 as the capture antibody and a monoclonal antibody to E. coli O157:H7 as the detection antibody) on a hydrophobic polyvinylidine difluoride-based membrane. E. coli O157:H7 in ground beef could be detected within 16 h, including incubation for 12 h in enrichment broth and the immunoassay, which takes 4 h. Pure culture cell suspensions of 10(5) or 10(6) E. coli O157:H7 organisms per ml produced intense color reactions in the immunoassay, whereas faint but detectable reactions occurred with 10(3) CFU/ml. The sensitivity of the combined enrichment-immunoassay procedure as determined by using ground beef inoculated with E. coli O157:H7 was 0.1 to 1.3 cells per g, with a false-positive rate of 2.0%. A survey of retail ground beef using this procedure revealed that 1 of 76 samples was contaminated by E. coli O157:H7.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borczyk A. A., Karmali M. A., Lior H., Duncan L. M. Bovine reservoir for verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli O157:H7. Lancet. 1987 Jan 10;1(8524):98–98. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91928-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell K. L. Solid state assays: reagents and film technology for dipstick assays. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1988;285:237–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter A. O., Borczyk A. A., Carlson J. A., Harvey B., Hockin J. C., Karmali M. A., Krishnan C., Korn D. A., Lior H. A severe outbreak of Escherichia coli O157:H7--associated hemorrhagic colitis in a nursing home. N Engl J Med. 1987 Dec 10;317(24):1496–1500. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198712103172403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle M. P., Schoeni J. L. Isolation of Escherichia coli O157:H7 from retail fresh meats and poultry. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Oct;53(10):2394–2396. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.10.2394-2396.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harel J., Lapointe H., Fallara A., Lortie L. A., Bigras-Poulin M., Larivière S., Fairbrother J. M. Detection of genes for fimbrial antigens and enterotoxins associated with Escherichia coli serogroups isolated from pigs with diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Apr;29(4):745–752. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.4.745-752.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Steele B. T., Petric M., Lim C. Sporadic cases of haemolytic-uraemic syndrome associated with faecal cytotoxin and cytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli in stools. Lancet. 1983 Mar 19;1(8325):619–620. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91795-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Xu J. G., Kaper J. B., Lior H., Prado V., Tall B., Nataro J., Karch H., Wachsmuth K. A DNA probe to identify enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli of O157:H7 and other serotypes that cause hemorrhagic colitis and hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):175–182. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lortie L. A., Dubreuil J. D., Harel J. Characterization of Escherichia coli strains producing heat-stable enterotoxin b (STb) isolated from humans with diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Mar;29(3):656–659. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.3.656-659.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March S. B., Ratnam S. Latex agglutination test for detection of Escherichia coli serotype O157. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jul;27(7):1675–1677. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.7.1675-1677.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March S. B., Ratnam S. Sorbitol-MacConkey medium for detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 associated with hemorrhagic colitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 May;23(5):869–872. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.5.869-872.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibuchi M., Murakami A., Arita M., Jikuya H., Takano J., Honda T., Miwatani T. Detection with synthetic oligonucleotide probes of nucleotide sequence variations in the genes encoding enterotoxins of Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Oct;27(10):2272–2276. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.10.2272-2276.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padhye N. V., Doyle M. P. Production and characterization of a monoclonal antibody specific for enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli of serotypes O157:H7 and O26:H11. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jan;29(1):99–103. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.1.99-103.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley L. W., Remis R. S., Helgerson S. D., McGee H. B., Wells J. G., Davis B. R., Hebert R. J., Olcott E. S., Johnson L. M., Hargrett N. T. Hemorrhagic colitis associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 24;308(12):681–685. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303243081203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samadpour M., Liston J., Ongerth J. E., Tarr P. I. Evaluation of DNA probes for detection of Shiga-like-toxin-producing Escherichia coli in food and calf fecal samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 May;56(5):1212–1215. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.5.1212-1215.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwood D., Snodgrass D. R., O'Brien A. D. Shiga-like toxin production from Escherichia coli associated with calf diarrhoea. Vet Rec. 1985 Feb 23;116(8):217–218. doi: 10.1136/vr.116.8.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. S., Hodge D. S., Borczyk A. A. Rapid biochemical test to identify verocytotoxin-positive strains of Escherichia coli serotype O157. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Oct;28(10):2165–2168. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.10.2165-2168.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd E. C., Szabo R. A., Peterkin P., Sharpe A. N., Parrington L., Bundle D., Gidney M. A., Perry M. B. Rapid hydrophobic grid membrane filter-enzyme-labeled antibody procedure for identification and enumeration of Escherichia coli O157 in foods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Oct;54(10):2536–2540. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.10.2536-2540.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. G., Shipman L. D., Greene K. D., Sowers E. G., Green J. H., Cameron D. N., Downes F. P., Martin M. L., Griffin P. M., Ostroff S. M. Isolation of Escherichia coli serotype O157:H7 and other Shiga-like-toxin-producing E. coli from dairy cattle. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 May;29(5):985–989. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.5.985-989.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood P. K., Morris J. G., Jr, Small P. L., Sethabutr O., Toledo M. R., Trabulsi L., Kaper J. B. Comparison of DNA probes and the Sereny test for identification of invasive Shigella and Escherichia coli strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Sep;24(3):498–500. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.3.498-500.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]